Geats on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
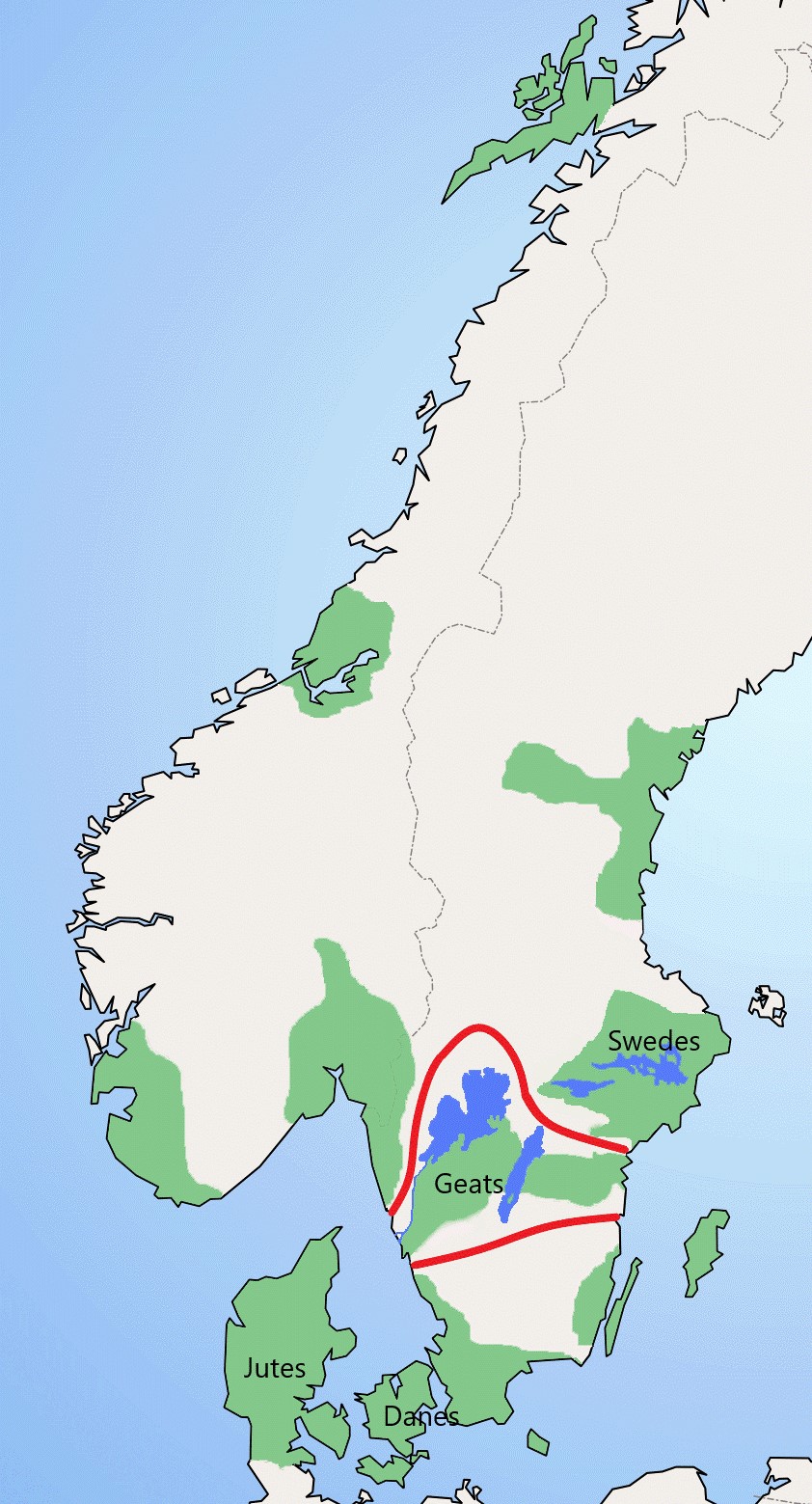 The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called '' Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called '' Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the
 In his '' Gesta Danorum'' (book 13), the Danish 12th-century chronicler Saxo Grammaticus noted that the Geats had no say in the election of the king, only the Swedes. When the West Geatish law or Westrogothic law was put to paper, it reminded the Geats that they had to accept the election of the Swedes: ''Sveær egho konong at taka ok sva vrækæ'' meaning ''"It is the Swedes who have the right of choosing taking"and also deposing the king"'' and then he rode Eriksgatan ''"mæþ gislum ofvan"'' – ''"with hostages from above
In his '' Gesta Danorum'' (book 13), the Danish 12th-century chronicler Saxo Grammaticus noted that the Geats had no say in the election of the king, only the Swedes. When the West Geatish law or Westrogothic law was put to paper, it reminded the Geats that they had to accept the election of the Swedes: ''Sveær egho konong at taka ok sva vrækæ'' meaning ''"It is the Swedes who have the right of choosing taking"and also deposing the king"'' and then he rode Eriksgatan ''"mæþ gislum ofvan"'' – ''"with hostages from above
 ''Geatas'' was originally Proto-Germanic *''Gautoz'' and ''Goths'' and '' Gutar'' (''Gotlanders'') were *''Gutaniz''. *''Gautoz'' and *''Gutaniz'' are two ablaut grades of a Proto-Germanic word *''geutan'' with the meaning "to pour" (modern Swedish ''gjuta'', modern German ''giessen''). The word comes from an Indo-European root meaning ''to pour, offer sacrifice.'' There were consequently two derivations from the same Proto-Germanic ethnonym.
It is a long-standing controversy whether the Goths were Geats. Both Old Icelandic and Old English literary sources clearly separate the Geats (Isl. ''Gautar'', OEng ''Geatas'') from the Goths/ Gutar (Isl. ''Gotar'', OEng. ''Gotenas''); but the Gothic historian Jordanes wrote that the Goths came originally to Dacia from the island of Scandza. Moreover, he described that on this island there were three tribes called the ''Gautigoths'' (cf. ''Geat/Gaut''), the ''Ostrogoths'' (cf. the Swedish province of ''
''Geatas'' was originally Proto-Germanic *''Gautoz'' and ''Goths'' and '' Gutar'' (''Gotlanders'') were *''Gutaniz''. *''Gautoz'' and *''Gutaniz'' are two ablaut grades of a Proto-Germanic word *''geutan'' with the meaning "to pour" (modern Swedish ''gjuta'', modern German ''giessen''). The word comes from an Indo-European root meaning ''to pour, offer sacrifice.'' There were consequently two derivations from the same Proto-Germanic ethnonym.
It is a long-standing controversy whether the Goths were Geats. Both Old Icelandic and Old English literary sources clearly separate the Geats (Isl. ''Gautar'', OEng ''Geatas'') from the Goths/ Gutar (Isl. ''Gotar'', OEng. ''Gotenas''); but the Gothic historian Jordanes wrote that the Goths came originally to Dacia from the island of Scandza. Moreover, he described that on this island there were three tribes called the ''Gautigoths'' (cf. ''Geat/Gaut''), the ''Ostrogoths'' (cf. the Swedish province of ''
 The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called '' Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called '' Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor
In genealogy, the progenitor (rarer: primogenitor; german: Stammvater or ''Ahnherr'') is the – sometimes legendary – founder of a family, line of descent, clan or tribe, noble house, or ethnic group..
Ebenda''Ahnherr:''"Stammvater eines G ...
groups of modern Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces
The provinces of Sweden ( sv, Sveriges landskap) are historical, geographical and cultural regions. Sweden has 25 provinces; they have no administrative function (except for in some cases as sport districts), but remain historical legacies and ...
of and , the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms.
The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''.
Etymology
The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of '' Goths'' and '' Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The names could also allude to watercourses in the land where they were living, but this is not generally accepted to be the case, partly because that would mean that the names' similarity would be coincidental. A more specific theory about the word ''Gautigoths'' is that it means the Goths who live near the river ''Gaut'', today's Göta älv ( non, Gautelfr). It might also have been a conflation of the word ''Gauti'' with a gloss of ''Goths''. In the 17th century the name ''Göta älv'', 'River of the Geats', replaced the earlier names ''Götälven'' and ''Gautelfr''. The etymology of the word ''Gaut'' (as mentioned above) derives from the Proto-Germanic word *''geutan'', and the extended meaning of "to pour" is "flow, stream, waterfall", which could refer to Trollhättan Falls or to the river itself. The short form of ''Gautigoths'' was the Old Norse ', which originally referred to just the inhabitants of Västergötland, or the western parts of today's Götaland, a meaning which is retained in some Icelandic sagas.History
Early history
The earliest known surviving mention of the Geats appears in Ptolemy (2nd century AD), who refers to them as ''Goutai''. In the 6th century, Jordanes writes of the ''Gautigoths'' and ''Ostrogoths'' (the Ostrogoths of Scandza); and Procopius refers to ''Gautoi''. The Norse Sagas know them as ''Gautar''; ''Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The ...
'' and '' Widsith'' as ''Gēatas''. ''Beowulf'' and the Norse sagas name several Geatish kings, but only Hygelac finds confirmation in ''Liber Monstrorum'' where he is referred to as "Rex Getarum" and in a copy of ''Historiae Francorum'' where he is called "Rege Gotorum". These sources concern a raid into Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Ger ...
, ca 516, which is also described in ''Beowulf''. C. 551, some decades after Hygelac's raid, Jordanes described the Geats as a nation which was "bold, and quick to engage in war".
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain included many North Germanic people who were losers in the brutal tribal warfare of Scandinavia. The place-name ''-gate'' marks the site of Geatish settlement, often alongside strategically important Roman roads and nearby Visigothic and/or Jutish settlements. Defeated Jutes like Hengest and his brother Horsa fled to Kent, while Geats defeated by encroaching Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
moved to Yorkshire where they founded Gillingshire by the Tees, originally the settlement of the ''Geatlings''. It has also been suggested that East Anglia was settled by Geats at this time, or by Wulfings who also came from Götaland, bringing the traditions of ''Beowulf'' with them.
Any peace that eventually settled in southern Scandinavia was most likely due to exhaustion, and a Danish archaeologist has summarized that in the mid-6th century, and after, Scandinavia "went down to hell". Scandinavian wares appear to have stopped arriving in England, c. 550, suggesting that contact was broken.
Political centralization in Scandinavia
According to Procopius there were 13 "very numerous nations" on the Scandinavian peninsula in the 6th century, which is supported by recent archaeological analyses. Several scholars consider this to be a reasonable number of independent kingdoms at the time, with each consisting of one or more tribes, as reported by Jordanes. However, by 1350, these 13 kingdoms had been reduced in number to only two, Norway and Sweden. The Geats were one of the largest tribes, Procopius and Jordanes both mention the Geats, but after them, foreign sources about Scandinavia are scarce until the 9th century, when Anglosaxon and Frankish sources does shed some light on the area. In these, the Geats are absent, which has led some scholars to conclude that they were no longer an independent nation and had been subsumed by the Swedes. Norwegian and Icelandic scaldic sources from the 10th century does however indicate that they were still politically independent, sometimes opposing Norwegian kings. Their absence in older sources have instead been suggested to be due to them being an inland people. The nature and the processes of how Geats and Swedes came to form one kingdom have been much debated among Swedish scholars. The scarcity and sometimes debated veracity of sources has left much room open for interpretation. The oldest medieval Swedish sources present the Swedish kingdom as having remaining differences between provinces, in laws as well as in weights and measurements. Some scholars have argued that the Geats were subjugated by the Swedes, and have suggested various dates for such an event, from the sixth to the 9th century. Others have wanted to see a more gradual merging, and that the Geats were slowly subsumed into the more powerful kingdom of Sweden, and in many respects they maintained their own cultural identity during the Middle Ages. Still others have put emphasis on how it was individual rulers, not ethnic groups, that were driving the process towards a unified kingdom, and that the process was very complicated. Papal letters from the 1080s style the recipients as "king of the Swedes" or "king of the West Geats". In another papal letter from the 1160s, the title ''rex Sweorum et Gothorum'' is first attested. The Swedish kings began the custom of styling themselves as also the king of the Geats in the 1270s.Dynastic struggles
In the 11th century, the Swedish House of Munsö became extinct with the death of Emund the Old.Stenkil
Stenkil (Old Norse: ''Steinkell'') was a King of Sweden who ruled c. 1060 until 1066. He succeeded Emund the Old and became the first king from the House of Stenkil. He is praised as a devout Christian, but with an accommodating stance towards th ...
, a Geat, was elected king of the Swedes, and the Geats would be influential in the shaping of Sweden as a Christian kingdom. However, this election also ushered in a long period of civil unrest between Christians and pagans and between Geats and Swedes. The Geats tended to be more Christian, and the Swedes more pagan, which was why the Christian Swedish king Inge the Elder fled to Västergötland when deposed in favour of Blot-Sweyn
Blot-Sweyn (Swedish:''Blot-Sven'') was a Swedish king c. 1080, who replaced his Christian brother-in-law Inge as King of Sweden, when Inge had refused to administer the blóts (pagan sacrifices) at the Temple at Uppsala. There is no mention of Swey ...
, a king more favourable towards Norse paganism, in the 1080s. Inge would retake the throne and rule until his death c. 1100.
 In his '' Gesta Danorum'' (book 13), the Danish 12th-century chronicler Saxo Grammaticus noted that the Geats had no say in the election of the king, only the Swedes. When the West Geatish law or Westrogothic law was put to paper, it reminded the Geats that they had to accept the election of the Swedes: ''Sveær egho konong at taka ok sva vrækæ'' meaning ''"It is the Swedes who have the right of choosing taking"and also deposing the king"'' and then he rode Eriksgatan ''"mæþ gislum ofvan"'' – ''"with hostages from above
In his '' Gesta Danorum'' (book 13), the Danish 12th-century chronicler Saxo Grammaticus noted that the Geats had no say in the election of the king, only the Swedes. When the West Geatish law or Westrogothic law was put to paper, it reminded the Geats that they had to accept the election of the Swedes: ''Sveær egho konong at taka ok sva vrækæ'' meaning ''"It is the Swedes who have the right of choosing taking"and also deposing the king"'' and then he rode Eriksgatan ''"mæþ gislum ofvan"'' – ''"with hostages from above he realm
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
'' through Södermanland, the Geatish provinces and then through Närke and Västmanland to be judged to be the lawful king by the lawspeakers of their respective things. One of these Swedish kings was Ragnvald Knaphövde, who in 1125 was riding with his retinue in order to be accepted as king by the different provinces. According to material appended to the oldest manuscript of the Westrogothic law, he decided not to demand hostages as he despised the Geats, and was slain near Falköping.
In a new general law of Sweden that was issued by Magnus Eriksson in the 1350s, it was stated that twelve men from each province, chosen by their things, should be present at the Stone of Mora when a new king was elected.
The distinction between Swedes and Geats lasted during the Middle Ages, but the Geats became increasingly important for Swedish national claims of greatness due to the Geats' old connection with the Goths. They argued that since the Goths and the Geats were the same nation, and the Geats were part of the kingdom of Sweden, this meant that the Swedes had defeated the Roman empire. The earliest attestation of this claim comes from the Council of Basel, 1434, during which the Swedish delegation argued with the Spanish about who among them were the true Goths. The Spaniards argued that it was better to be descended from the heroic Visigoths than from stay-at-homers. This cultural movement, which was not restricted to Sweden went by the name '' Gothicismus'' or in Swedish ''Göticism'', i.e. ''Geaticism''.
After the 15th century and the Kalmar Union
The Kalmar Union (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and sv, Kalmarunionen; fi, Kalmarin unioni; la, Unio Calmariensis) was a personal union in Scandinavia, agreed at Kalmar in Sweden, that from 1397 to 1523 joined under ...
, the Swedes and the Geats appear to have begun to perceive themselves as one nation, which is reflected in the evolution of ''svensk'' into a common ethnonym.The article ''Svear'' in '' Nationalencyklopedin''. It was originally an adjective referring to those belonging to the Swedish tribe, who are called ''svear'' in Swedish. As early as the 9th century, ''svear'' had been vague, both referring to the Swedish tribe and being a collective term including the Geats, and this is the case in Adam of Bremen's work where the Geats (''Goths'') appear both as a proper nation and as part of the ''Sueones''. The merging/assimilation of the two nations took a long time, however. In the early-20th century, ''Nordisk familjebok
''Nordisk familjebok'' (, "Nordic Family Book") is a Swedish encyclopedia that was published in print from between 1876 and 1993, and that is now fully available in digital form via Project Runeberg at Linköping University. Despite their consi ...
'' noted that ''svensk'' had almost replaced ''svear'' as a name for the Swedish people.
At the same time, the Swedish ancestors were often referred to as Geats, especially when their heroism or connection to the Goths was to be stressed. This practice disappeared during the 19th century, when the vikings gradually took over the role as the heroic ancestors.
Society
The Geats were traditionally divided into several petty kingdoms, or districts, which had their own things (popular assemblies) and laws. The largest one of these districts was Västergötland (West Geatland), and it was in Västergötland that the Thing of all Geats was held every year, in the vicinity of Skara. Despite the name, the thing was only for the inhabitants of Västergötland and Dalsland. The equivalent inÖstergötland
Östergötland (; English exonym: East Gothland) is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish) in the south of Sweden. It borders Småland, Västergötland, Närke, Södermanland and the Baltic Sea. In older English li ...
was Lionga thing.
Unlike the Swedes, who used the division hundare, the Geats used ''hærrad'' (modern Swedish ''härad
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Southern Schleswig, Sweden, Finland, Norway, the Bishopric of Ösel–Wiek ...
''), like the Norwegians and the Danes. Surprisingly, it would be the Geatish name that became the common term in the Swedish kingdom. This is possibly related to the fact that several of the medieval Swedish kings were of Geatish extraction and often resided primarily in Götaland. In Västergötland and Dalsland, there were also a higher-level division where one or more hærrad made up a ''bo'' linked to a kongsgård.
Modern legacy
Today, the merger of the two nations is complete, as there is no longer any tangible identification in Götaland with a Geatish identity, apart from the common tendency of residents of the provinces of Västergötland andÖstergötland
Östergötland (; English exonym: East Gothland) is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish) in the south of Sweden. It borders Småland, Västergötland, Närke, Södermanland and the Baltic Sea. In older English li ...
to refer to themselves as ''västgötar'' (West Geats) and ''östgötar'' (East Geats), similar to how residents of other provinces refer to themselves. The dialects spoken in those provinces and some surrounding areas are also collectively called götamål. Although, the city ''Göteborg'', known in English as Gothenburg
Gothenburg (; abbreviated Gbg; sv, Göteborg ) is the second-largest city in Sweden, fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and capital of the Västra Götaland County. It is situated by the Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has ...
, has formerly been considered to have been named after the river Göta älv, it may instead have been named after the Geats ('fortress of the Geats'), when it was founded in 1621.
Until 1973 the official title of the Swedish king was King of Sweden (earlier: of the Swedes), the Geats/Goths and the Wends (with the formula "Sveriges, Götes och Vendes konung", in Latin "N.N. Dei Gratia, Suecorum, Gothorum et Vandalorum Rex."). The title "King of the Wends" was copied from the Danish title, while the Danish kings called themselves "King of the Gotlanders" (which, like "Geats", was translated into "Goths" in Latin) were also used by Danish royalty. The Wends is a term normally used to describe the Slavic peoples who inhabited large areas of modern east Germany and Pomerania. See further in the Wikipedia articles King of the Goths
:''This is about the medieval title; for the migration-era Goths, see King of the Visigoths, King of the Ostrogoths.''
The title of King of the Goths ( sv, Götes konung, da, Goternes konge, la, gothorum rex) was for many centuries borne by both ...
and King of the Wends.
The titles, however, changed when the new king Carl XVI Gustaf
Carl XVI Gustaf (Carl Gustaf Folke Hubertus; born 30 April 1946) is King of Sweden. He ascended the throne on the death of his grandfather, Gustaf VI Adolf, on 15 September 1973.
He is the youngest child and only son of Prince Gustaf Adolf, Du ...
in 1973 decided that his royal title should simply be King of Sweden. The disappearance of the old title was a decision made entirely by the king.
Goths
Östergötland
Östergötland (; English exonym: East Gothland) is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish) in the south of Sweden. It borders Småland, Västergötland, Närke, Södermanland and the Baltic Sea. In older English li ...
'') and ''Vagoths'' ( Gutar?) ‒ this implies that the Geats were Goths rather than vice versa. The word ''Goth'' is also a term used by the Romans to describe related, culturally linked tribes like the Tervingi and the Greuthungs, so it may be correct to label Geats as Goths.
Scandinavian burial customs, such as the stone circles (domarringar), which are most common in Götaland and Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the ...
, and stelae (bautastenar) appeared in what is now northern Poland in the 1st century AD, suggesting an influx of Scandinavians during the formation of the Gothic Wielbark culture. Moreover, in Östergötland
Östergötland (; English exonym: East Gothland) is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap'' in Swedish) in the south of Sweden. It borders Småland, Västergötland, Närke, Södermanland and the Baltic Sea. In older English li ...
, in Sweden, there is a sudden disappearance of villages during this period. Contemporary accounts beginning in the fourth century further associated these groups with the earlier ''Getae
The Getae ( ) or Gets ( ; grc, Γέται, singular ) were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form ''Get'' an ...
'' of Dacia, but this is now disputed.
Fringe theories
Götaland theory
The Götaland theory (Swedish "Västgötaskolan") is a disparate group of theories, which have attempted to prove that some events and even places that are traditionally placed around Mälaren, especially ones that are associated with the formation of medieval Sweden, instead should be located to Västergötland. The methods ranged from relatively scholarly efforts to dowsing. This "school" was brought to prominence in the 1980s following a TV series byDag Stålsjö
Dag, or variant forms, may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''DAG'' (American TV series), 2000–2001
* ''Dag'' (Norwegian TV series), 2010–2015
* ''DAG'' (newspaper), a former free Dutch newspaper
* DAG (band), an American funk band
* D ...
. While some serious scholars have attempted to place more emphasis on the Geats in the early history of Sweden than was traditional, Västgötaskolan has never reached any acceptance.
Identity of the Gēatas
The generally accepted identification of Old English ''Gēatas'' as the same ethnonym as Swedish ''götar'' and Old Norse ''gautar'' is based on the observation that the ''ö'' monophthong of modern Swedish and the ''au'' diphthong of Old Norse correspond to the ''ēa'' diphthong ofOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
.
Thus, ''Gēatas'' is the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
form of Old Norse ''Gautar'' and modern Swedish ''Götar''. This correspondence seems to tip the balance for most scholars. It is also based on the fact that in ''Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The ...
'', the ''Gēatas'' live east of the '' Dani'' (across the sea) and in close contact with the ''Sweon'', which fits the historical position of the Geats between the Danes and the Swedes. Moreover, the story of Beowulf, who leaves ''Geatland'' and arrives at the Danish court after a naval voyage, where he kills a beast, finds a parallel in Hrólf Kraki's saga. In this saga, Bödvar Bjarki leaves ''Gautland'' and arrives at the Danish court after a naval voyage and kills a beast that has been terrorizing the Danes for two years (see also Origins for Beowulf and Hrólf Kraki).
Jutish hypothesis
There is a hypothesis that the Jutes also were Geats, and which was proposed by Pontus Fahlbeck in 1884. According to this hypothesis the Geats would have not only resided in southern Sweden but also in Jutland, whereBeowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The ...
would have lived.
The Geats and the Jutes are mentioned in ''Beowulf'' as different tribes, and whereas the Geats are called ''gēatas'', the Jutes are called ''ēotena'' (genitive) or ''ēotenum'' (dative). Moreover, the Old English poem '' Widsith'' also mentions both Geats and Jutes, and it calls the latter ''ȳtum''. However, Fahlbeck proposed in 1884 that the Gēatas of ''Beowulf'' referred to Jutes and he proposed that the Jutes originally also were Geats like those of southern Sweden. This theory was based on an Old English translation of Venerable Bede's '' Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' attributed to Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bot ...
where the Jutes (''iutarum'', ''iutis'') once are rendered as ''gēata'' (genitive) and twice as ''gēatum'' (dative) (see e.g. the '' OED'' which identifies the Geats through ''Eotas'', ''Iótas'', ''Iútan'' and ''Geátas''). Fahlbeck did not, however, propose an etymology for how the two ethnonyms could be related.
Fahlbeck's theory was refuted by Schück who in 1907 noted that another Old English source, the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'', called the Jutes ''īutna'', ''īotum'' or ''īutum''. Moreover, Schück pointed out that when Alfred the Great's translation mentions the Jutes for the second time (book IV, ch. 14(16)) it calls them ''ēota'' and in one manuscript ''ȳtena''. Björkman proposed in 1908 that Alfred the Great's translation of Jutes as Geats was based on a confusion between the West Saxon form ''Geotas'' ("Jutes") and ''Gēatas'' ("Geats").
As for the origins of the ethnonym ''Jute'', it may be a secondary formation of the toponym Jutland, where ''jut'' is derived from a Proto-Indo-European root *''eud'' meaning "water".
Gutnish hypothesis
Since the 19th century, there has also been a suggestion that Beowulf's people were Gutes (from the island ofGotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the ...
in Sweden). According to the poem, the ''weather-geats'' or ''sea-geats'', as they are called are supposed to have lived east of the Danes/Dacians and be separated from the Swedes by wide waters. Some researchers have found it a little far-fetched that ''wide waters'' relates to Vänern in Västergötland or Mälaren
Mälaren ( , , or ), historically referred to as Lake Malar in English, is the third-largest freshwater lake in Sweden (after Vänern and Vättern). Its area is 1,140 km2 and its greatest depth is 64 m. Mälaren spans 120 kilometers from e ...
. The ''weather'' in ''weather-geats'', and ''sea-geats'' marks a people living at a windy, stormy coast by the sea. The Geats of Västergötland were historically an inland people, making an epithet such as ''weather-'' or ''sea-'' a little strange. Moreover, when Beowulf dies he is buried in a mound at a place called ''Hrones-naesse'', meaning "the cape of whales". Whales have for obvious reasons never lived in Vänern, where, according to Birger Nerman, Beowulf is buried. However, an expanse of water separates the island of Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the ...
from the Swedes. The island lies east of Denmark/Dacia and whales were once common in the Baltic Sea where Gotland is situated. The name of the Gutes in Swedish, '' Gutar'', is an ablaut-grade of the same name as that of the Geats in Beowulf. These facts made the archaeologist Gad Rausing come to the conclusion that the ''weather-Geats'' may have been Gutes. This was supported by another Swedish archaeologist Bo Gräslund
Bo or BO may refer to
Arts and entertainment
Film, television, and theatre
*Box office, where tickets to an event are sold, and by extension, the amount of business a production receives
*'' BA:BO'', 2008 South Korean film
* ''Bo'' (film), a ...
. According to Rausing, Beowulf may be buried in a place called ''Rone'' on Gotland, a name corresponding to the ''Hrones'' in ''Hrones-naesse''. Not far from there lies a place called ''Arnkull'' corresponding to the ''Earnar-naesse'' in Beowulf, which according to the poem was situated closely to Hrones-naesse.
This theory does not exclude the ancient population of Västergötland and Östergötland from being Geats, but rather holds that the Anglo-Saxon name ''Geat'' could refer to West-geats (Västergötland), East-geats (Östergötland) as well as weather-geats (Gotland), in accordance with Jordanes account of the Scandinanian tribes Gautigoth, Ostrogoth and Vagoth.
See also
* Blenda * Geatish Society *Göta
Göta is a Swedish given name, which is the female equivalent of Göte. It may refer to:
*Göta Ljungberg (1893–1955), Swedish singer
*Göta Pettersson (1926–1993), Swedish gymnast
Other uses
*Göta, Sweden
*Göta älv, a river in Sweden
*G ...
* Götavirke (Geatish Dyke)
* Varangian
* Viking
References
{{Beowulf Early Germanic peoples North Germanic tribes Götaland Goths