|
Götavirke
Götavirke (''Geatish Dyke'') are the remains of two parallel defensive walls going from north to south between the villages of Västra Husby () and Söderköping Municipality, Hylinge () in Söderköping Municipality, Östergötland, Sweden. The walls cover the distance between the lakes Asplången () and Lillsjön (). North of Asplången there are remains of several ancient hill forts that may have been part of the defensive line. South of Lake Lillsjön, the terrain is so hard to pass that it hardly needed any defenses. The walls seem to be constructed to protect the Geatish heartland around today's Linköping from attacks from the Baltic Sea. Archaeological excavations have shown that the walls were constructed ca 800. Defense constructions were also built along the 20-kilometer narrow inlet Slätbaken that stretches from the Baltic Sea to Götavirke, and even pass it during the Viking Age when the water level was 1.5 meters higher. The measures that Geats had taken to protect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Götavirke
Götavirke (''Geatish Dyke'') are the remains of two parallel defensive walls going from north to south between the villages of Västra Husby () and Söderköping Municipality, Hylinge () in Söderköping Municipality, Östergötland, Sweden. The walls cover the distance between the lakes Asplången () and Lillsjön (). North of Asplången there are remains of several ancient hill forts that may have been part of the defensive line. South of Lake Lillsjön, the terrain is so hard to pass that it hardly needed any defenses. The walls seem to be constructed to protect the Geatish heartland around today's Linköping from attacks from the Baltic Sea. Archaeological excavations have shown that the walls were constructed ca 800. Defense constructions were also built along the 20-kilometer narrow inlet Slätbaken that stretches from the Baltic Sea to Götavirke, and even pass it during the Viking Age when the water level was 1.5 meters higher. The measures that Geats had taken to protect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
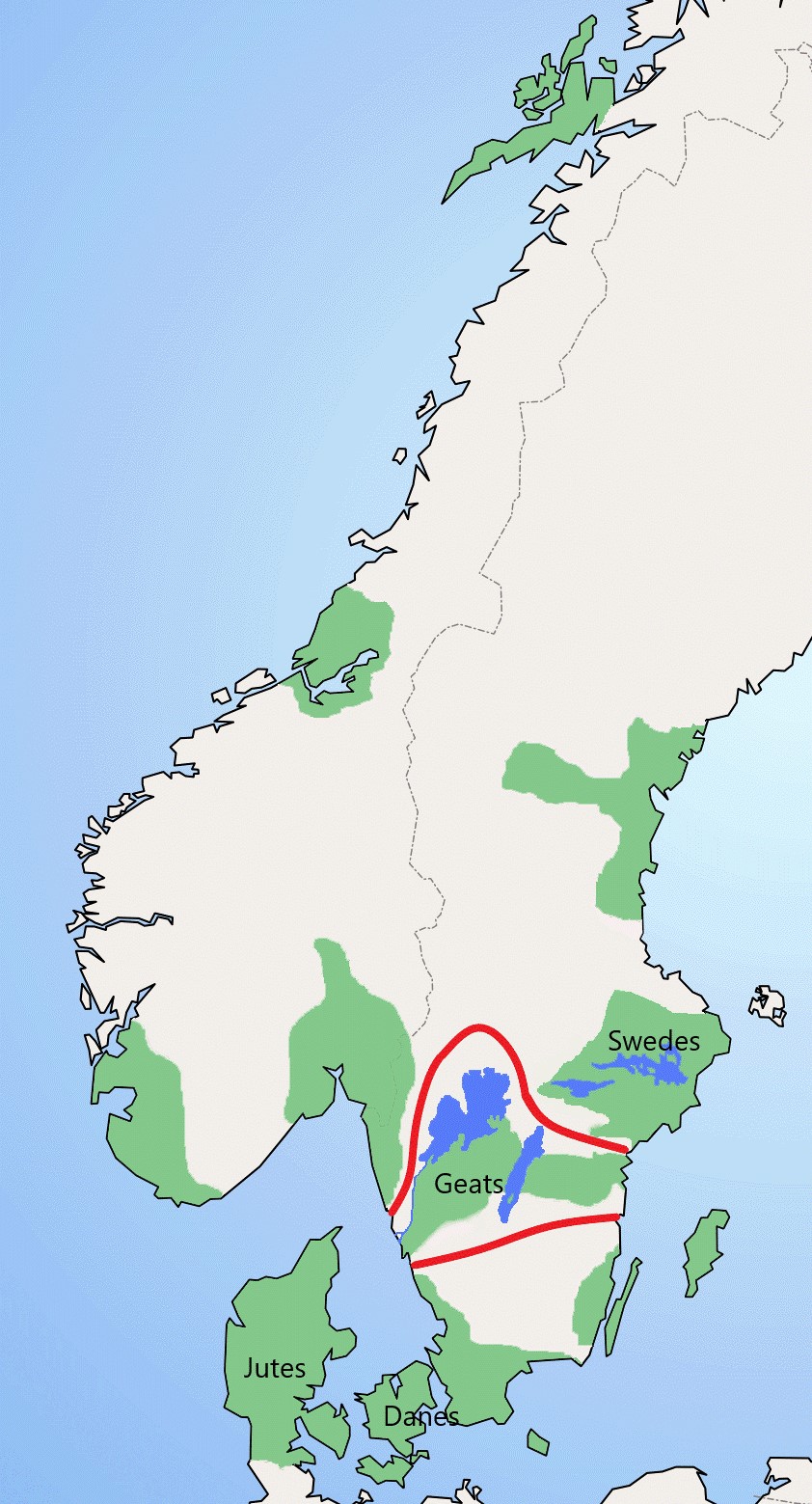
Geat
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of and , the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and ''Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geats
The Geats ( ; ang, gēatas ; non, gautar ; sv, götar ), sometimes called ''Goths'', were a large North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with Swedes (the tribe) and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Swedish provinces of and , the Western and Eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, '' Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and ''Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their seed". (For more information see Goths § Etymology.) The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danevirke
The Danevirke or Danework (modern Danish spelling: ''Dannevirke''; in Old Norse; ''Danavirki'', in German; ''Danewerk'', literally meaning '' earthwork of the Danes'') is a system of Danish fortifications in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. This historically important linear defensive earthwork across the neck of the Cimbrian peninsula was initiated by the Danes in the Nordic Iron Age about AD 650. It was later expanded multiple times during Denmark's Viking Age and High Middle Ages. The Danevirke was last used for military purposes in 1864 during the Second War of Schleswig. The Danevirke consists of several walls, trenches and the Schlei Barrier. The walls stretch for 30 km, from the former Viking trade centre of Hedeby near Schleswig on the Baltic Sea coast in the east to the extensive marshlands in the west of the peninsula. One of the walls (named ''Østervolden''), between the Schlei and Eckernförde inlets, defended the Schwansen peninsula. According to written sources, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, Finland to the east, and is connected to Denmark in the southwest by a bridgetunnel across the Öresund. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country, the third-largest country in the European Union, and the fifth-largest country in Europe. The capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a total population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of , with around 87% of Swedes residing in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden has a nature dominated by forests and a large amount of lakes, including some of the largest in Europe. Many long rivers run from the Scandes range through the landscape, primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offa's Dyke
Offa's Dyke ( cy, Clawdd Offa) is a large linear earthwork that roughly follows the border between England and Wales. The structure is named after Offa, the Anglo-Saxon king of Mercia from AD 757 until 796, who is traditionally believed to have ordered its construction. Although its precise original purpose is debated, it delineated the border between Anglian Mercia and the Welsh kingdom of Powys. The earthwork, which was up to wide (including its flanking ditch) and high, traversed low ground, hills and rivers. Today it is protected as a scheduled monument. Some of its route is followed by the Offa's Dyke Path, a long-distance footpath that runs between Liverpool Bay in the north and the Severn Estuary in the south. Although the Dyke has conventionally been dated to the Early Middle Ages of Anglo-Saxon England, research in recent decades – using techniques such as radioactive carbon dating – has challenged the conventional historiography and theories about the earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Söderköping Municipality
Söderköping Municipality (''Söderköpings kommun'') is a municipality in Östergötland County in southeast Sweden. Its seat is located in the city of Söderköping. The present municipality was created in 1971-1973 when the former ''City of Söderköping'' in two steps was amalgamated with three surrounding rural municipalities. Elections Riksdag These are the results of the Riksdag elections of Söderköping Municipality since the 1972 municipality reform. The results of the Sweden Democrats were not published by SCB between 1988 and 1998 at a municipal level to the party's small nationwide size at the time. "Turnout" denotes the percentage of the electorate casting a ballot, whereas "Votes" only denotes valid votes. Blocs This lists the relative strength of the socialist and centre-right blocs since 1973, but parties not elected to the Riksdag are inserted as "other", including the Sweden Democrats results from 1988 to 2006, but also the Christian Democrats pre-1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortifications In Sweden
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Archaeological Sites
Germanic may refer to: * Germanic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group identified by their use of the Germanic languages ** List of ancient Germanic peoples and tribes * Germanic languages :* Proto-Germanic language, a reconstructed proto-language of all the Germanic languages * Germanic name * Germanic mythology, myths associated with Germanic paganism * Germanic religion (other) * SS Germanic (1874), SS ''Germanic'' (1874), a White Star Line steamship See also * Germania (other) * Germanus (other) * German (other) * Germanicia Caesarea * * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Sweden
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesia Walls
The Silesian Walls ( pl, Wały Śląskie, german: Dreigräben) are a line of three (or sometimes fewer) parallel earthen ramparts and ditches that run through Lower Silesia in Poland, by the towns Szprotawa and Kożuchów. The walls are about 2.5 metres tall and, at their widest, 47 metres. They run for about 30 kilometres. It is hypothesized by Maciej Boryna of the Muzeum Ziemi Szprotawskiej that the Silesia Walls were the southwest border of the Duchy of Głogów The Duchy of Głogów ( pl, Księstwo głogowskie, cs, Hlohovské knížectví) or Duchy of Glogau (german: Herzogtum Glogau) was one of the Duchies of Silesia ruled by the Silesian Piasts. Its capital was Głogów in Lower Silesia. Histor ... and built in 1413–1467. It is possible that rather than being military in nature the walls were designed as a type of '' landwehr'' to reduce smuggling. References * M. Boryna: ''Raport z programu badawczego Wały Śląskie 2000–2006''. * W. Schöpke: ''Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birca
Birka (''Birca'' in medieval sources), on the island of Björkö (lit. "Birch Island") in present-day Sweden, was an important Viking Age trading center which handled goods from Scandinavia as well as many parts of the European continent and the Orient. Björkö is located in Lake Mälaren, 30 kilometers west of contemporary Stockholm, in the municipality of Ekerö. Birka was founded around AD 750 and it flourished for more than 200 years. It was abandoned c. AD 975, around the same time Sigtuna was founded as a Christian town some 35 km to the northeast. It has been estimated that the population in Viking Age Birka was between 500 and 1000 people. The archaeological sites of Birka and Hovgården, on the neighbouring island of Adelsö, make up an archaeological complex which illustrates the elaborate trading networks of Viking Scandinavia and their influence on the subsequent history of Europe. Generally regarded as Sweden's oldest town, Birka (along with Hovgården) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
