|
Thomas Scott Baldwin
Thomas Scott Baldwin (June 30, 1854 – May 17, 1923) was a pioneer balloonist and U.S. Army major during World War I. He was the first American to descend from a balloon by parachute. Early career Thomas Scott Baldwin was born on June 30, 1854, to Jane and Samuel Yates Baldwin. He worked as a brakeman on the Illinois railroad, then joined a circus working as an acrobat. In 1875, he started an act combining trapeze and a hot air balloon. On January 30, 1887, he made one of the earliest recorded parachute jumps from a balloon. Baldwin repeated the feat on multiple occasions as a paid entertainer, netting $1500 from one dangerous jump over the water from 600 feet at Rockaway Beach in August 1887 marred by parachute difficulties. Powered balloons In 1900, Baldwin created a small pedal-motorized powered airship. It never served as anything more than a curiosity. In 1902-1903 he supervised the construction of ''California Eagle'', based on the ideas of August Greth and financed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marion County, Missouri
Marion County is a county located in the northeastern portion of Missouri. As of the 2010 census, the population was 28,781. Its county seat is Palmyra. Unique from most third-class counties in the state, Marion has two county courthouses, the second located in Hannibal. The county was organized on December 23, 1826 and named for General Francis Marion, the "Swamp Fox," who was from South Carolina and served in the American Revolutionary War. The area was known as the "Two Rivers Country" before organization. Marion County is part of the Hannibal, Missouri Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is included in the Quincy-Hannibal, IL-MO Combined Statistical Area. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land, and (1.7%) is water. Adjacent counties * Lewis County (north) * Adams County, Illinois (northeast) *Pike County, Illinois (southeast) * Ralls County (south) *Monroe County (southwest) * Shelby County (west) Major Roa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn H
Glenn may refer to: Name or surname * Glenn (name) * John Glenn, U.S. astronaut Cultivars * Glenn (mango) * a 6-row barley variety Places In the United States: * Glenn, California * Glenn County, California * Glenn, Georgia, a settlement in Heard County * Glenn, Illinois * Glenn, Michigan * Glenn, Missouri * University, Orange County, North Carolina, formerly called Glenn * Glenn Highway in Alaska Organizations *Glenn Research Center, a NASA center in Cleveland, Ohio See also * New Glenn New Glenn is a heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle in development by Blue Origin. Named after NASA astronaut John Glenn, design work on the vehicle began in 2012. Illustrations of the vehicle, and the high-level specifications, were initial ..., a heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle * * * Glen, a valley * Glen (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn Hammond Curtiss
Glenn Hammond Curtiss (May 21, 1878 – July 23, 1930) was an American aviation and motorcycling pioneer, and a founder of the U.S. aircraft industry. He began his career as a bicycle racer and builder before moving on to motorcycles. As early as 1904, he began to manufacture engines for airships. In 1908, Curtiss joined the Aerial Experiment Association, a pioneering research group, founded by Alexander Graham Bell at Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, to build flying machines. Curtiss won a race at the world's first international air meet in France and made the first long-distance flight in the U.S. His contributions in designing and building aircraft led to the formation of the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company, which later merged into the Curtiss-Wright Corporation. His company built aircraft for the U.S. Army and Navy, and, during the years leading up to World War I, his experiments with seaplanes led to advances in naval aviation. Curtiss civil and military aircraft were some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capt
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, etc. In militaries, the captain is typically at the level of an officer commanding a company or battalion of infantry, a ship, or a battery of artillery, or another distinct unit. The term also may be used as an informal or honorary title for persons in similar commanding roles. Etymology The term "captain" derives from (, , or 'the topmost'), which was used as title for a senior Byzantine military rank and office. The word was Latinized as capetanus/catepan, and its meaning seems to have merged with that of the late Latin "capitaneus" (which derives from the classical Latin word "caput", meaning head). This hybridized term gave rise to the English language term captain and its equivalents in other languages (, , , , , , , , , kapitány, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aero Club Of America
The Aero Club of America was a social club formed in 1905 by Charles Jasper Glidden and Augustus Post, among others, to promote aviation in America. It was the parent organization of numerous state chapters, the first being the Aero Club of New England. It thrived until 1923, when it transformed into the National Aeronautic Association, which still exists today. It issued the first Pilot licensing and certification, pilot's licenses in the United States, and successful completion of its licensing process was required by the United States Army for its pilots until 1914. It sponsored numerous air shows and contests. Cortlandt Field Bishop was president in 1910. Starting in 1911, new president Robert J. Collier began presenting the Collier Trophy. History Although conventional wisdom states that the Aero Club began in 1905, there are photos of high society and adventurers printed in 1902 with the stamp, "Aero Club". In the summer of 1905 several members of the Automobile Club of Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Corps Dirigible No
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signal. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signaling occurs in all organisms even at cellular levels, with cell signaling. Signaling theory, in evolutionary biology, proposes that a substantial driver for evolution is the ability of animals to communicate with each other by developing ways of signaling. In human engineering, signals are typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Signal Corps
The United States Army Signal Corps (USASC) is a branch of the United States Army that creates and manages communications and information systems for the command and control of combined arms forces. It was established in 1860, the brainchild of Major Albert J. Myer, and had an important role in the American Civil War. Over its history, it had the initial responsibility for portfolios and new technologies that were eventually transferred to other U.S. government entities. Such responsibilities included military intelligence, weather forecasting, and aviation. Mission statement Support for the command and control of combined arms forces. Signal support includes network operations (information assurance, information dissemination management, and network management) and management of the electromagnetic spectrum. Signal support encompasses all aspects of designing, installing, data communications networks that employ single and multi-channel satellite, tropospheric scatter, terrestrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are shaped by the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Chesapeake Bay, which provide habitat for much of its flora and fauna. The capital of the Commonwealth is Richmond; Virginia Beach is the most-populous city, and Fairfax County is the most-populous political subdivision. The Commonwealth's population was over 8.65million, with 36% of them living in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The area's history begins with several indigenous groups, including the Powhatan. In 1607, the London Company established the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English colony in the New World. Virginia's state nickname, the Old Dominion, is a reference to this status. Slave labor and land acquired from displaced native tribes fueled the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
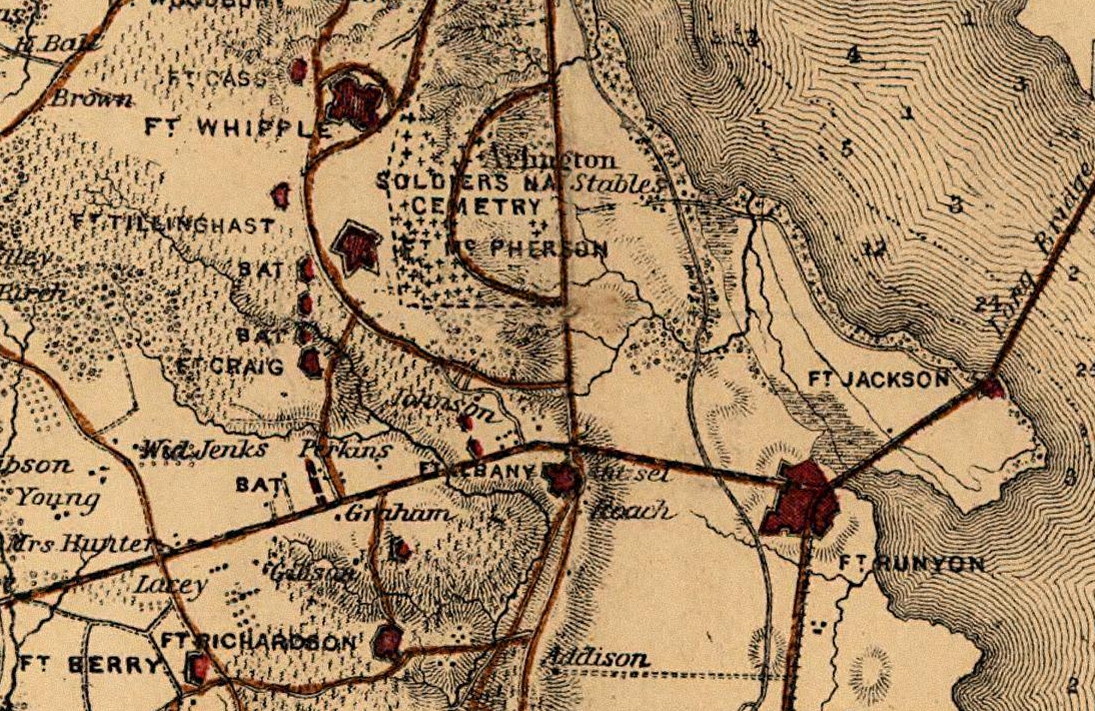
Fort Myer
Fort Myer is the previous name used for a U.S. Army post next to Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, and across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. Founded during the American Civil War as Fort Cass and Fort Whipple, the post merged in 2005 with the neighboring Marine Corps installation, Henderson Hall, and is today named Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall. History In 1861, the land that Fort Myer would eventually occupy was part of the Arlington estate, which Mary Anna Custis Lee, the wife of Robert E. Lee, owned and at which Lee resided when not stationed elsewhere (see Arlington House, The Robert E. Lee Memorial). When the Civil War began, the Commonwealth of Virginia seceded from the United States, Lee resigned his commission, and he and his wife left the estate. The United States Government then confiscated the estate and began to use it as a burial ground for Union Army dead (see Arlington National Cemetery), to house freed slaves (Freedmen's Vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas to the south and Oklahoma, Kansas and Nebraska to the west. In the south are the Ozarks, a forested highland, providing timber, minerals, and recreation. The Missouri River, after which the state is named, flows through the center into the Mississippi River, which makes up the eastern border. With more than six million residents, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 19th-most populous state of the country. The largest urban areas are St. Louis, Kansas City, Missouri, Kansas City, Springfield, Missouri, Springfield and Columbia, Missouri, Columbia; the Capital city, capital is Jefferson City, Missouri, Jefferson City. Humans have inhabited w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana Purchase Exposition
The Louisiana Purchase Exposition, informally known as the St. Louis World's Fair, was an World's fair, international exposition held in St. Louis, Missouri, United States, from April 30 to December 1, 1904. Local, state, and federal funds totaling $15 million were used to finance the event. More than 60 countries and 43 of the then-45 American states maintained exhibition spaces at the fair, which was attended by nearly 19.7 million people. Historians generally emphasize the prominence of the themes of Race (human categorization), race and imperialism, and the fair's long-lasting impact on intellectuals in the fields of history, art history, architecture and anthropology. From the point of view of the memory of the average person who attended the fair, it primarily promoted entertainment, consumer goods and popular culture. The monumental Greco-Roman architecture of this and other fairs of the era did much to influence permanent new buildings and master plans of major cities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |