|
Thomas Penyngton Kirkman
Thomas Penyngton Kirkman FRS (31 March 1806 – 3 February 1895) was a British mathematician and ordained minister of the Church of England. Despite being primarily a churchman, he maintained an active interest in research-level mathematics, and was listed by Alexander Macfarlane as one of ten leading 19th-century British mathematicians... In the 1840s, he obtained an existence theorem for Steiner triple systems that founded the field of combinatorial design theory, while the related Kirkman's schoolgirl problem is named after him. Early life and education Kirkman was born 31 March 1806 in Bolton, in the north west of England, the son of a local cotton dealer. In his schooling at the Bolton Grammar School, he studied classics, but no mathematics was taught in the school. He was recognised as the best scholar at the school, and the local vicar guaranteed him a scholarship at Cambridge, but his father would not allow him to go. Instead, he left school at age 14 to work in his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolton
Bolton (, locally ) is a large town in Greater Manchester in North West England, formerly a part of Lancashire. A former mill town, Bolton has been a production centre for textiles since Flemish people, Flemish weavers settled in the area in the 14th century, introducing a wool and cotton-weaving tradition. The urbanisation and development of the town largely coincided with the introduction of textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution. Bolton was a 19th-century boomtown and, at its zenith in 1929, its 216 cotton mills and 26 bleaching and dyeing works made it one of the largest and most productive centres of Spinning (textiles), cotton spinning in the world. The British cotton industry declined sharply after the First World War and, by the 1980s, cotton manufacture had virtually ceased in Bolton. Close to the West Pennine Moors, Bolton is north-west of Manchester and lies between Manchester, Darwen, Blackburn, Chorley, Bury, Greater Manchester, Bury and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christ Church, Croft
Christ Church is in Lady Lane, Croft, Cheshire, England. It is an active Anglican parish church in the deanery of Winwick, the archdeaconry of Warrington, and the diocese of Liverpool. Its benefice is united with that of Newchurch. The church is designated by English Heritage as a Grade II listed building. It was a Commissioners' church, having received a grant towards its construction from the Church Building Commission. History The church was built between 1832 and 1833 to a design by Edward Blore. A grant of £1,457 (equivalent to £ in ) was given towards its construction by the Church Building Commission. Its total cost was £2,667. The church was consecrated on 29 November 1833 by the Bishop of Chester. From 1839 until 1892, the rector of Croft with Southworth was Thomas Penyngton Kirkman, who in addition to his ministerial work was also a mathematician, for whom Kirkman triple systems are named.. Architecture Christ Church is constructed in red sandstone wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
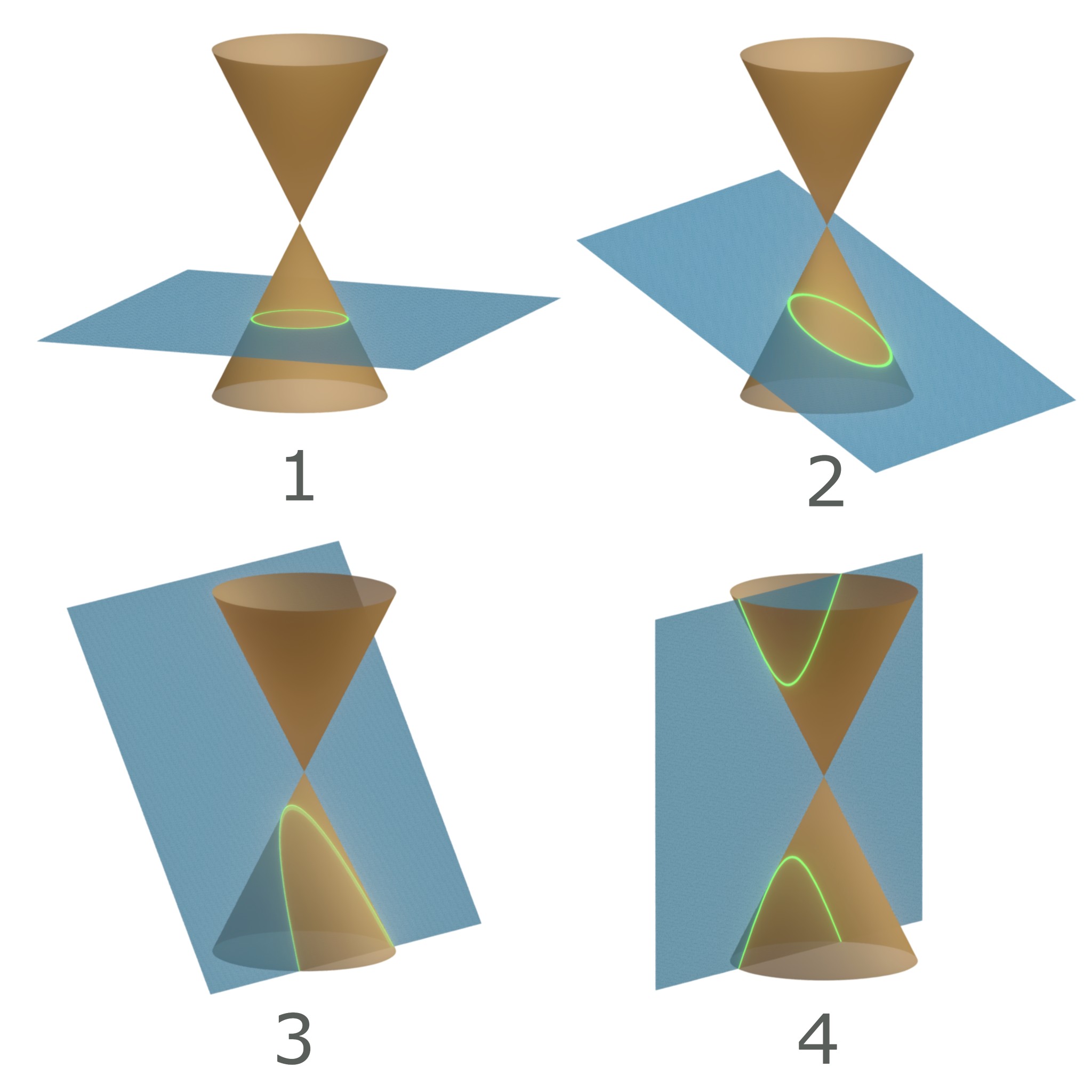
Conic Section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°. Regular hexagon A ''regular polygon, regular hexagon'' has Schläfli symbol and can also be constructed as a Truncation (geometry), truncated equilateral triangle, t, which alternates two types of edges. A regular hexagon is defined as a hexagon that is both equilateral polygon, equilateral and equiangular polygon, equiangular. It is bicentric polygon, bicentric, meaning that it is both cyclic polygon, cyclic (has a circumscribed circle) and tangential polygon, tangential (has an inscribed circle). The common length of the sides equals the radius of the circumscribed circle or circumcircle, which equals \tfrac times the apothem (radius of the inscribed figure, inscribed circle). All internal angles are 120 degree (angle), degrees. A regular hexago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal's Theorem
In projective geometry, Pascal's theorem (also known as the ''hexagrammum mysticum theorem'') states that if six arbitrary points are chosen on a conic (which may be an ellipse, parabola or hyperbola in an appropriate affine plane) and joined by line segments in any order to form a hexagon, then the three pairs of opposite sides of the hexagon ( extended if necessary) meet at three points which lie on a straight line, called the Pascal line of the hexagon. It is named after Blaise Pascal. The theorem is also valid in the Euclidean plane, but the statement needs to be adjusted to deal with the special cases when opposite sides are parallel. This theorem is a generalization of Pappus's (hexagon) theorem, which is the special case of a degenerate conic of two lines with three points on each line. Euclidean variants The most natural setting for Pascal's theorem is in a projective plane since any two lines meet and no exceptions need to be made for parallel lines. However, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding. Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imagery as specific tools to encode information in a way that allows for efficient storage and retrieval. Mnemonics aid original information in becoming associated with something more accessible or meaningful—which, in turn, provides better retention of the information. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often used for lists and in auditory form, such as short poems, acronyms, initialisms, or memorable phrases, but mnemonics can also be used for other types of information and in visual or kinesthetic forms. Their use is based on the observation that the human mind more easily remembers spatial, personal, surprising, physical, sexual, humorous, or otherwise "relatable" information, rather than more abstract or impersonal forms of informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakob Steiner
Jakob Steiner (18 March 1796 – 1 April 1863) was a Swiss mathematician who worked primarily in geometry. Life Steiner was born in the village of Utzenstorf, Canton of Bern. At 18, he became a pupil of Heinrich Pestalozzi and afterwards studied at Heidelberg. Then, he went to Berlin, earning a livelihood there, as in Heidelberg, by tutoring. Here he became acquainted with A. L. Crelle, who, encouraged by his ability and by that of Niels Henrik Abel, then also staying at Berlin, founded his famous ''Journal'' (1826). After Steiner's publication (1832) of his ''Systematische Entwickelungen'' he received, through Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi, who was then professor at Königsberg University, and earned an honorary degree there; and through the influence of Jacobi and of the brothers Alexander and Wilhelm von Humboldt a new chair of geometry was founded for him at Berlin (1834). This he occupied until his death in Bern on 1 April 1863. He was described by Thomas Hirst as follows: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wesley S
Wesley may refer to: People and fictional characters * Wesley (name), a given name and a surname Places United States * Wesley, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Wesley, Georgia, an unincorporated community * Wesley Township, Will County, Illinois * Wesley, Iowa, a city in Kossuth County * Wesley Township, Kossuth County, Iowa * Wesley, Maine, a town * Wesley Township, Washington County, Ohio * Wesley, Oklahoma, an unincorporated community * Wesley, Indiana, an unincorporated town * Wesley, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Elsewhere * Wesley, a hamlet in the township of Stone Mills, Ontario, Canada * Wesley, Dominica, a village * Wesley, New Zealand, a suburb of Auckland * Wesley, Eastern Cape, South Africa, a town Schools * Wesley College (other) * Wesley Institute, Sydney, Australia * Wesley Seminary, Marion, Indiana * Wesley Biblical Seminary, Jackson, Mississippi * Wesley Theological Seminary, Washington, DC * Wesley University of Science and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lady's And Gentleman's Diary
''The Lady's and Gentleman's Diary'' was a recreational mathematics magazine formed as a successor of ''The Ladies' Diary'' and ''Gentleman's Diary'' in 1841. It was published annually between 1841 and 1871 by the Company of Stationers; its editor from 1844 to 1865 was Wesley S. B. Woolhouse. It consisted mostly of problems posed by its readers, with their solutions given in later volumes, though it also contained word puzzles and poetry. The magazine was based in London. It ceased publication in 1871. This should not be confused with ''Ladies and Gentlemens Diary, or Royal Almanack'' (1775 to 1786) which was printed by Thomas Carnan and edited by Reuben Burrow and was a short lived competitor to ''The Ladies' Diary''. Kirkman's schoolgirl problem Kirkman's schoolgirl problem is a problem in combinatorics proposed by Rev. Thomas Penyngton Kirkman in 1850 as Query VI in '' The Lady's and Gentleman's Diary'' (pg.48). The problem states: Fifteen young ladies in a school walk o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Materialism
Materialism is a form of philosophical monism which holds matter to be the fundamental substance in nature, and all things, including mental states and consciousness, are results of material interactions. According to philosophical materialism, mind and consciousness are by-products or epiphenomena of material processes (such as the biochemistry of the human brain and nervous system), without which they cannot exist. This concept directly contrasts with idealism, where mind and consciousness are first-order realities to which matter is dependent while material interactions are secondary. Materialism is closely related to physicalism—the view that all that exists is ultimately physical. Philosophical physicalism has evolved from materialism with the theories of the physical sciences to incorporate more sophisticated notions of physicality than mere ordinary matter (e.g. spacetime, physical energies and forces, and dark matter). Thus, the term ''physicalism'' is preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |