|
Thomas Henshaw (alchemist)
Thomas Henshaw (1618–1700) was an English lawyer, courtier, diplomat and scientific writer. While not a published alchemist, he was a significant figure in English alchemical work from the 1650s onwards; he is known to have used the pen-name "Halophilus". Early life The son of Benjamin Henshaw and his wife Anne, and brother to Nathaniel Henshaw. he was baptised at St. Mary Magdalen, Milk Street, City of London, on 15 June 1618. After attending school at Barnet and then at Cripplegate, London, under Thomas Farnaby, he was entered as commoner at University College, Oxford, in 1634, and remained there five years without taking a degree. At the suggestion of Obadiah Walker and Abraham Woodhead, he studied mathematics, a student of William Oughtred at Albury, Surrey for nine months from 1636, finding it more stimulating than the teaching of his tutor John Elmherst. He also knew the Rosicrucian scholar William Backhouse, who was another of Oughtred's pupils.Darley, p. 49. Hens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
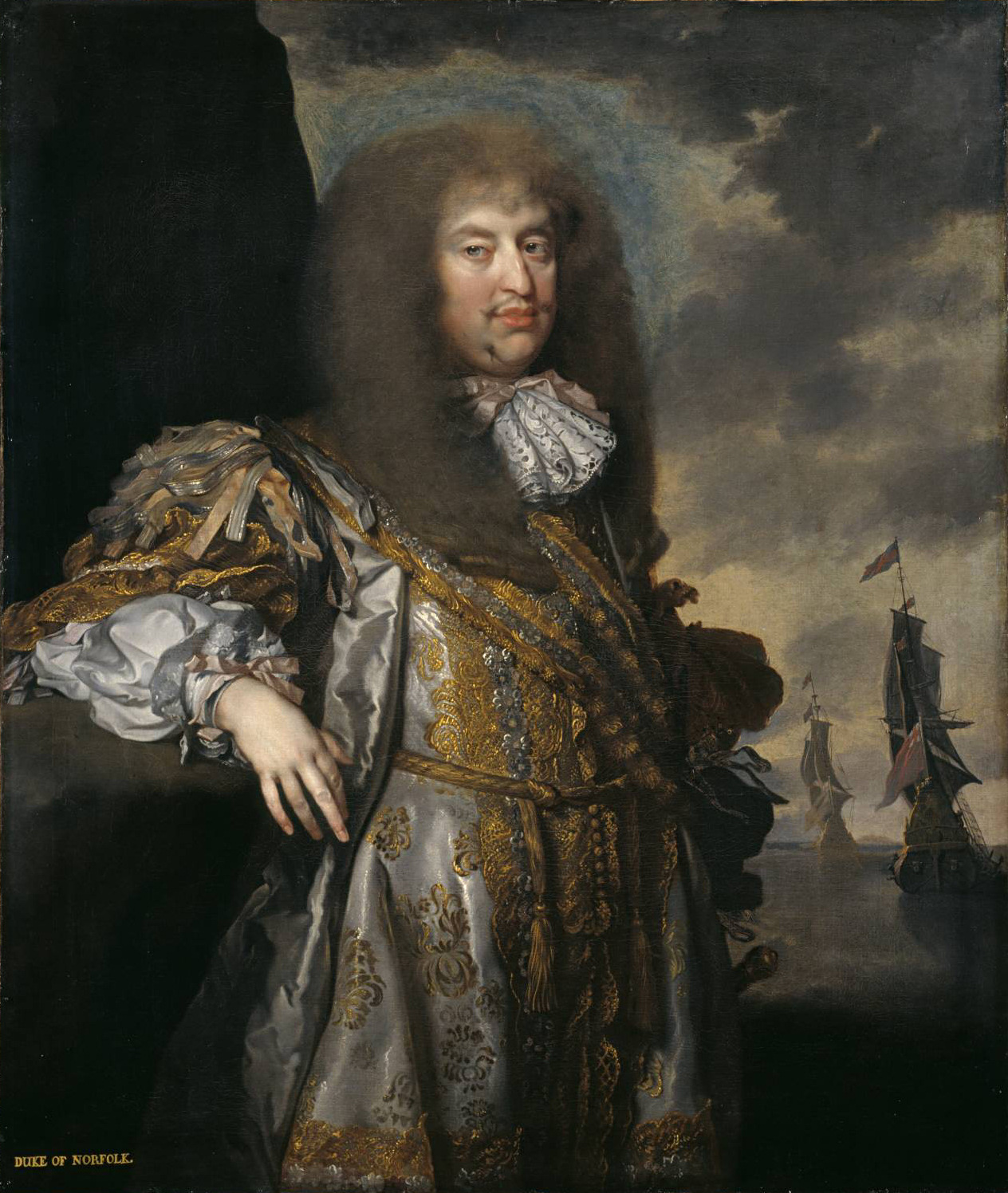
John Closterman (1660-1711) (style Of) - Thomas Henshaw, Aged 77 - 959518 - National Trust
John Closterman (also spelt Cloosterman, Klosterman; 1660 – 24 May 1711 (buried)) was a Westphalian portrait painter of the late 17th and early 18th centuries. His subjects were mostly European noblemen and their families. Career Born in Osnabrück in the Holy Roman Empire (now in Lower Saxony), Closterman was the son of an artist who taught him the rudiments of design. In 1679, Closterman went to Paris and worked under François de Troy. In 1681, he went to Kingdom of England, England. He worked for John Riley (painter), John Riley, painting the draperies in Riley's portraits When Riley died in 1691, Closterman finished several of his portraits. Because of his work on Riley's portraits, Charles Seymour, 6th Duke of Somerset, hired him to create some paintings. However, Somerset became dissatisfied with a portrait of the Italian painter Guercino that Closterman had painted for him, ending the relationship. Charles Montagu, 1st Earl of Halifax, Lord Halifax eventually purcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William II, Prince Of Orange
William II (27 May 1626 – 6 November 1650) was sovereign Prince of Orange and Stadtholder of County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Lordship of Utrecht, Utrecht, Guelders, Lordship of Overijssel, Overijssel and Groningen (province), Groningen in the United Provinces of the Netherlands from 14 March 1647 until his death three years later. His only child, William III of England, William III, reigned as King of England, Ireland, and Scotland. Early life William II, Prince of Orange, was the son of Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange, and Amalia of Solms-Braunfels. Frederick Henry was the youngest son of William the Silent (stadtholder 1559–1584); his older half brother Maurits of Nassau was stadtholder (1585–1625); he was stadtholder from 1625 to 1647. The stadtholders governed in conjunction with the Netherlands States-General, States-General, an assembly of representatives from each of the seven provinces, but usually dominated by the largest and wealthiest pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Baptist Van Helmont
Jan Baptist van Helmont (; ; 12 January 1580 – 30 December 1644) was a chemist, physiologist, and physician from Brussels. He worked during the years just after Paracelsus and the rise of iatrochemistry, and is sometimes considered to be "the founder of pneumatic chemistry". Van Helmont is remembered today largely for his ideas on spontaneous generation, his 5-year willow tree experiment, and his introduction of the word "gas" (from the Greek word ''chaos'') into the vocabulary of science. His name is also found rendered as Jan-Baptiste van Helmont, Johannes Baptista van Helmont, Johann Baptista von Helmont, Joan Baptista van Helmont, and other minor variants switching between ''von'' and ''van''. Early life and education Jan Baptist van Helmont was the youngest of five children of Maria (van) Stassaert and Christiaen van Helmont, a public prosecutor and Brussels council member, who had married in the Sint-Goedele church in 1567.Van den Bulck, E. (1999Johannes Bapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkahest
In Renaissance alchemy, alkahest was the theorized "universal solvent". It was supposed to be capable of dissolving any other substance, including gold, without altering or destroying its fundamental components. Among its philosophical and spiritual preoccupations, Hermeticism was more anciently concerned with the panacea, but (in the context of reformed understandings of human physiology) the emergent Latin alchemy associated with European humanism was itself transmuted into a new medical and pharmaceutical philosophy. The Swiss physician and alchemist Philippus Paracelsus (1493-1541), who gave his name to the early modern school of medical theory known as Paracelcism, first made mention of the alkahest as a chemical which could fortify the liver, and (in instances where the liver failed) could act as a substitute for its functions (see ''De Viribus Membrorum Spiritualium'', Cap. VI, "De Cura Epatis", at p. 10). By reducing or dissolving substances into their fundamental v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Hartlib
Samuel Hartlib or Hartlieb (c. 1600 – 10 March 1662) M. Greengrass, "Hartlib, Samuel (c. 1600–1662)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (Oxford, UK: OUP, 2004 Retrieved 26 April 2016, pay-walled for date of death. was a born, English educational and agricultural reformer of German-Polish origin who settled, married and died in . He was a son of George Hartlib, a |
Thomas Vaughan (philosopher)
Thomas Vaughan (17 April 1621 − 27 February 1666) was a Welsh clergyman, philosopher, and alchemist, who wrote in English. He is now remembered for his work in the field of natural magic. He also published under the pseudonym Eugenius Philalethes. His influences included Johannes Trithemius (1462–1516), Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa (1486–1535), Michael Sendivogius (1566–1636), and Rosicrucianism (early 17th century). Life A Royalist clergyman from Brecon, Wales, Thomas was the twin brother of the poet Henry Vaughan," enry'stwin brother was Thomas Vaughan (1621–1666). . .Vaughan, Henryin Welsh Biography Online, at National Library of Wales both being born at Newton, in the parish of St. Bridget's, in 1621.The twins were the sons of Thomas Vaughan of Trenewydd, Newton . . . "who m. the heiress of Newton in Llansantffraed.VAUGHAN family, of Tretower Courtin Welsh Biography Online, at National Library of Wales. He entered Jesus College, Oxford, in 1638, and remained there fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Child (agriculturalist)
Robert Child (1613–1654) was an English physician, agriculturalist and alchemist. A recent view is that his approach to agriculture belongs to the early ideas on political economy. Early life The son of John Child of Northfleet in Kent he was educated at Corpus Christi College, Cambridge. He then attended the universities of Leiden and Padua, taking a medical degree at Leiden in 1635, and his M.D. at Padua in 1638. In New England Child did not practise medicine as a new graduate. In 1638 he travelled to New England, where his first stay lasted to 1641. There he came to know John Winthrop the younger, and a supporter of his ironworks project. Residing in Watertown, he joined the Nashaway Company, who were interested in iron ore; but left to go back to England. Moore writes that, during the period from 1641, Child worked in England using good contacts, trying to make New England self-sufficient in iron. He also travelled widely in continental Europe, meeting the alchemist P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kensington
Kensington is a district in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in the West End of London, West of Central London. The district's commercial heart is Kensington High Street, running on an east–west axis. The north-east is taken up by Kensington Gardens, containing the Albert Memorial, the Serpentine Gallery and John Hanning Speke, Speke's monument. South Kensington and Gloucester Road, London, Gloucester Road are home to Imperial College London, the Royal College of Music, the Royal Albert Hall, Natural History Museum, London, Natural History Museum, Victoria and Albert Museum, and Science Museum, London, Science Museum. The area is also home to many embassies and consulates. Name The Manorialism, manor of ''Chenesitone'' is listed in the Domesday Book of 1086, which in the Old English language, Anglo-Saxon language means "Chenesi's List of generic forms in place names in Ireland and the United Kingdom, ton" (homestead/settlement). One early spelling is ''Kesyngton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Bramston
Francis Bramston or Brampston (died 1683) was an English judge and Baron of the Exchequer. Life Bramston, the third son of Sir John Bramston the elder, was educated at the school of Thomas Farnabie, in Goldsmiths' Alley, Cripplegate, and at Queens' College, Cambridge, where Edward Martin was then the President, graduating B.A. in 1637 and M.A. in 1640. He was admitted to the Middle Temple as a student in 1634, but as his health was weak he for a time entertained the idea of taking holy orders. Shortly before the final rupture between the king and the parliament he was elected a Fellow of Queens' College, and after being called to the bar (14 June 1642) left the country. He spent the next four years (1642–46) travelling in France and Italy, falling in with John Evelyn and his friend Thomas Henshaw at Rome in the spring of 1645, and again at Padua and Venice in the autumn of 1645. On his return to England Bramston devoted himself to the study and practice of the law. His hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Howard, 6th Duke Of Norfolk
Henry Howard, 6th Duke of Norfolk (12 July 162813 January 1684) was an English nobleman and politician. He was the second son of Henry Howard, 22nd Earl of Arundel, and Lady Elizabeth Stuart. He succeeded his brother Thomas Howard, 5th Duke of Norfolk after Thomas's death in 1677. Life He had previously been created 1st Baron Howard of Castle Rising in 1669 and 1st Earl of Norwich in 1672, on the latter occasion obtaining the restoration of the office of Earl Marshal of England to him and to his family. There had been near unanimity in the House of Lords in persuading King Charles II to revive the Dukedom of Norfolk in 1660; but since the 5th Duke was insane, and confined to an asylum in Padua, it was felt desirable to summon his brother to the Lords in his own right. His career as Duke began inauspiciously when he announced that he had married Jane Bickerton, who had been his mistress for many years: this caused a violent family quarrel, as a result of which he went abroad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 – 27 November 1680) was a German Jesuit scholar and polymath A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ... who published around 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine. Kircher has been compared to fellow Jesuit Roger Joseph Boscovich and to Leonardo da Vinci for his enormous range of interests, and has been honoured with the title "Master of a Hundred Arts".Woods, p. 108. He taught for more than 40 years at the Roman College, where he set up a wunderkammer. A resurgence of interest in Kircher has occurred within the scholarly community in recent decades. Kircher claimed to have deciphered the Egyptian hieroglyphs, hieroglyphic writing of the ancient Egyptian language, but most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the city contains more than twenty other historic churches, several medieval palaces, and bridges across the Arno. Much of the city's architecture was financed from its history as one of the Italian maritime republics. The city is also home to the University of Pisa, which has a history going back to the 12th century, the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa, founded by Napoleon in 1810, and its offshoot, the Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies.Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna di Pisa Information statistics History ...
|
_(style_of)_-_Thomas_Henshaw%2C_Aged_77_-_959518_-_National_Trust.jpg)