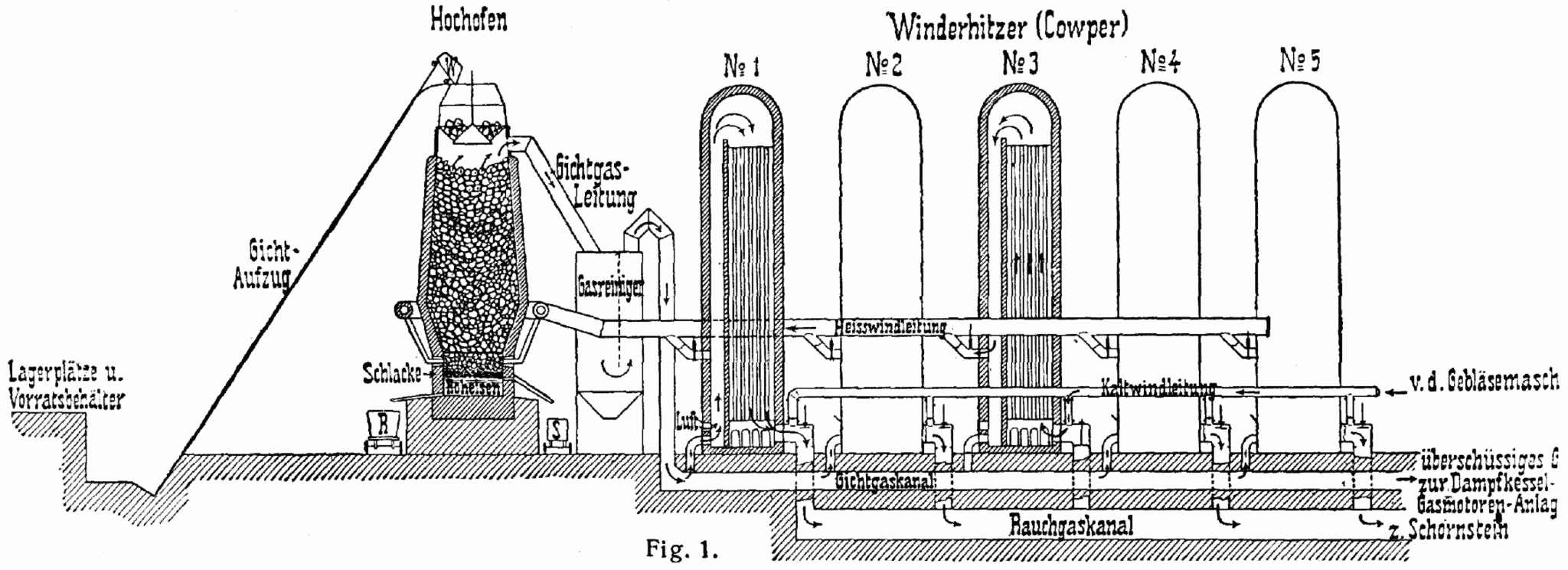
|
Thermomechanical Generator
The Harwell TMG Stirling engine, an abbreviation for "Thermo-Mechanical Generator", was invented in 1967 by E. H. Cooke-Yarborough at the Harwell Labs of the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority. It was intended to be a remote electrical power source with low cost and very long life, albeit by sacrificing some efficiency. The TMG (model TMG120) was at one time the only Stirling engine sold by a manufacturer, namely HoMach Systems Ltd., England. p. 195, 113, 109, 195 Description The engine has near isothermal cylinders because 1) the heater area covers the entire cylinder end, 2) it is a short stroke device, with wide shallow cylinders, yielding a high surface area to volume ratio, 3) the average thickness of the gas space is about 0.1 cm, and 4) the working fluid is Helium, a gas having good thermal properties for Stirling engines. The engine's displacer also has very low losses. These low-loss operating characteristics simplify the engine analysis, compared to more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
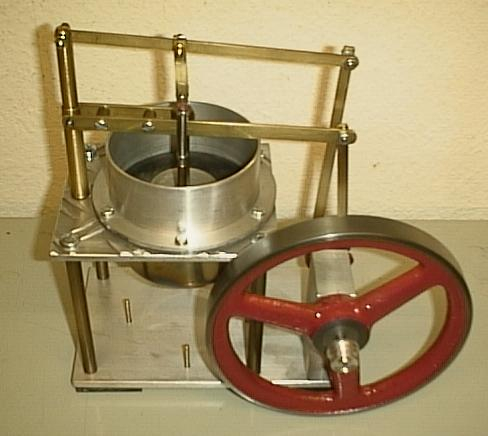
TMG Freebody1
TMG may refer to: Computing * TMG (language) * Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway * The Master Genealogist, software Science and technology * Tensiomyography, for detecting muscle properties * Trimethylglycine, an amino acid derivative * Trimethylgallium, Ga(CH3)3 * Touring motor glider * Thermal Micrometeoroid Garment, the outer layer of a space suit * Thermomechanical generator, the Harwell Stirling engine Music * Ted Mulry Gang, an Australian rock group * The Militia Group, a record label * Tak Matsumoto Group, a Japanese supergroup * Tiny Meat Gang, an American rap comedy duo * The Mountain Goats, an American indie rock band Other media * Tele München Gruppe, Munich, Germany * Telegraaf Media Groep, Netherlands * Times Media Group, South Africa Other uses * Tunney Media Group, fictional owner of NBS on Studio 60 on the Sunset Strip * Tennessee Meiji Gakuin High School * Têxtil Manuel Gonçalves, a Portuguese company * The Monitoring Group, a UK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacer
A Stirling engine is a heat engine that is operated by the cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gas (the ''working fluid'') between different temperatures, resulting in a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical work. More specifically, the Stirling engine is a closed-cycle regenerative heat engine with a permanent gaseous working fluid. ''Closed-cycle'', in this context, means a thermodynamic system in which the working fluid is permanently contained within the system, and ''regenerative'' describes the use of a specific type of internal heat exchanger and thermal store, known as the ''regenerator''. Strictly speaking, the inclusion of the regenerator is what differentiates a Stirling engine from other closed-cycle hot air engines. In the Stirling engine, a gas is heated and expanded by energy supplied from outside the engine's interior space (cylinder). It is then shunted to a different location within the engine, where it is cooled and compressed. A piston (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th century; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosyphon
Thermosiphon (or thermosyphon) is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney. This circulation can either be open-loop, as when the substance in a holding tank is passed in one direction via a heated transfer tube mounted at the bottom of the tank to a distribution point—even one mounted above the originating tank—or it can be a vertical closed-loop circuit with return to the original container. Its purpose is to simplify the transfer of liquid or gas while avoiding the cost and complexity of a conventional pump. Simple thermosiphon Natural convection of the liquid starts when heat transfer to the liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Alternator
A linear alternator is essentially a linear motor used as an electrical generator. An alternator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator. The devices are often physically equivalent. The principal difference is in how they are used and which direction the energy flows. An alternator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy, whereas a motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. Like most electric motors and electric generators, the linear alternator works by the principle of electromagnetic induction. However, most alternators work with rotary motion, whereas ''linear'' alternators work with ''linear'' motion (i.e. motion in a straight line). Theory When a magnet moves in relation to an electromagnetic coil, this changes the magnetic flux passing through the coil, and thus induces the flow of an electric current, which can be used to do work. A linear alternator is most commonly used to convert back-and-forth motion directly into electrical ene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Mesh
Overhead power cabling. The conductor consists of seven strands of steel (centre, high tensile strength), surrounded by four outer layers of aluminium (high conductivity). Sample diameter 40 mm A wire is a flexible strand of metal. Wire is commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Wire gauges come in various standard sizes, as expressed in terms of a gauge number. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads, often in the form of wire rope. In electricity and telecommunications signals, a "wire" can refer to an electrical cable, which can contain a "solid core" of a single wire or separate strands in stranded or braided forms. Usually cylindrical in geometry, wire can also be made in square, hexagonal, flattened rectangular, or other cross-sections, either for decorative purposes, or for technical purposes such as high-efficiency voice coils in loudspeakers. Edge-wound coil springs, such as the Slinky toy, are made of special flattened wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regenerative Heat Exchanger
A regenerative heat exchanger, or more commonly a regenerator, is a type of heat exchanger where heat from the hot fluid is intermittently stored in a thermal storage medium before it is transferred to the cold fluid. To accomplish this the hot fluid is brought into contact with the heat storage medium, then the fluid is displaced with the cold fluid, which absorbs the heat. In regenerative heat exchangers, the fluid on either side of the heat exchanger can be the same fluid. The fluid may go through an external processing step, and then it is flowed back through the heat exchanger in the opposite direction for further processing. Usually the application will use this process cyclically or repetitively. Regenerative heating was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution when it was used in the hot blast process on blast furnaces. It was later used in glass melting furnaces and steel making, to increase the efficiency of open hearth furnaces, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulus (mathematics)
In mathematics, an annulus (plural annuli or annuluses) is the region between two concentric circles. Informally, it is shaped like a ring or a hardware washer. The word "annulus" is borrowed from the Latin word ''anulus'' or ''annulus'' meaning 'little ring'. The adjectival form is annular (as in annular eclipse). The open annulus is topologically equivalent to both the open cylinder and the punctured plane. Area The area of an annulus is the difference in the areas of the larger circle of radius and the smaller one of radius : :A = \pi R^2 - \pi r^2 = \pi\left(R^2 - r^2\right). The area of an annulus is determined by the length of the longest line segment within the annulus, which is the chord tangent to the inner circle, in the accompanying diagram. That can be shown using the Pythagorean theorem since this line is tangent to the smaller circle and perpendicular to its radius at that point, so and are sides of a right-angled triangle with hypotenuse , and the ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentric
In geometry, two or more objects are said to be concentric, coaxal, or coaxial when they share the same center or axis. Circles, regular polygons and regular polyhedra, and spheres may be concentric to one another (sharing the same center point), as may cylinders (sharing the same central axis). Geometric properties In the Euclidean plane, two circles that are concentric necessarily have different radii from each other.. However, circles in three-dimensional space may be concentric, and have the same radius as each other, but nevertheless be different circles. For example, two different meridians of a terrestrial globe are concentric with each other and with the globe of the earth (approximated as a sphere). More generally, every two great circles on a sphere are concentric with each other and with the sphere. By Euler's theorem in geometry on the distance between the circumcenter and incenter of a triangle, two concentric circles (with that distance being zero) are the cir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring (device)
A spring is an elastic object that stores mechanical energy. In everyday use the term often refers to coil springs, but there are many different spring designs. Modern springs are typically manufactured from spring steel, although some non-metallic objects like the bow are also springs. When a conventional spring, without stiffness variability features, is compressed or stretched from its resting position, it exerts an opposing force approximately proportional to its change in length (this approximation breaks down for larger deflections). The ''rate'' or ''spring constant'' of a spring is the change in the force it exerts, divided by the change in deflection of the spring. That is, it is the gradient of the force versus deflection curve. An extension or compression spring's rate is expressed in units of force divided by distance, for example or N/m or lbf/in. A torsion spring is a spring that works by twisting; when it is twisted about its axis by an angle, it produces a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corrosion resistance, resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a Passivation (chemistry), passive film that can protect the material and self-healing material, self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into Sheet metal, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both alumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder Seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in length, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally wet clay. According to some sources, cylinder seals were invented around 3500 BC in the Near East, at the contemporary sites of Uruk in southern Mesopotamia and slightly later at Susa in south-western Iran during the Proto-Elamite period, and they follow the development of stamp seals in the Halaf culture or slightly earlier. They are linked to the invention of the latter's cuneiform writing on clay tablets. Other sources, however, date the earliest cylinder seals to a much earlier time, to the Late Neolithic period (7600-6000 BC), hundreds of years before the invention of writing. Cylinder seals are a form of impression seal, a category which includes the stamp seal and finger ring seal. They survive in fairly large numbers and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)