|
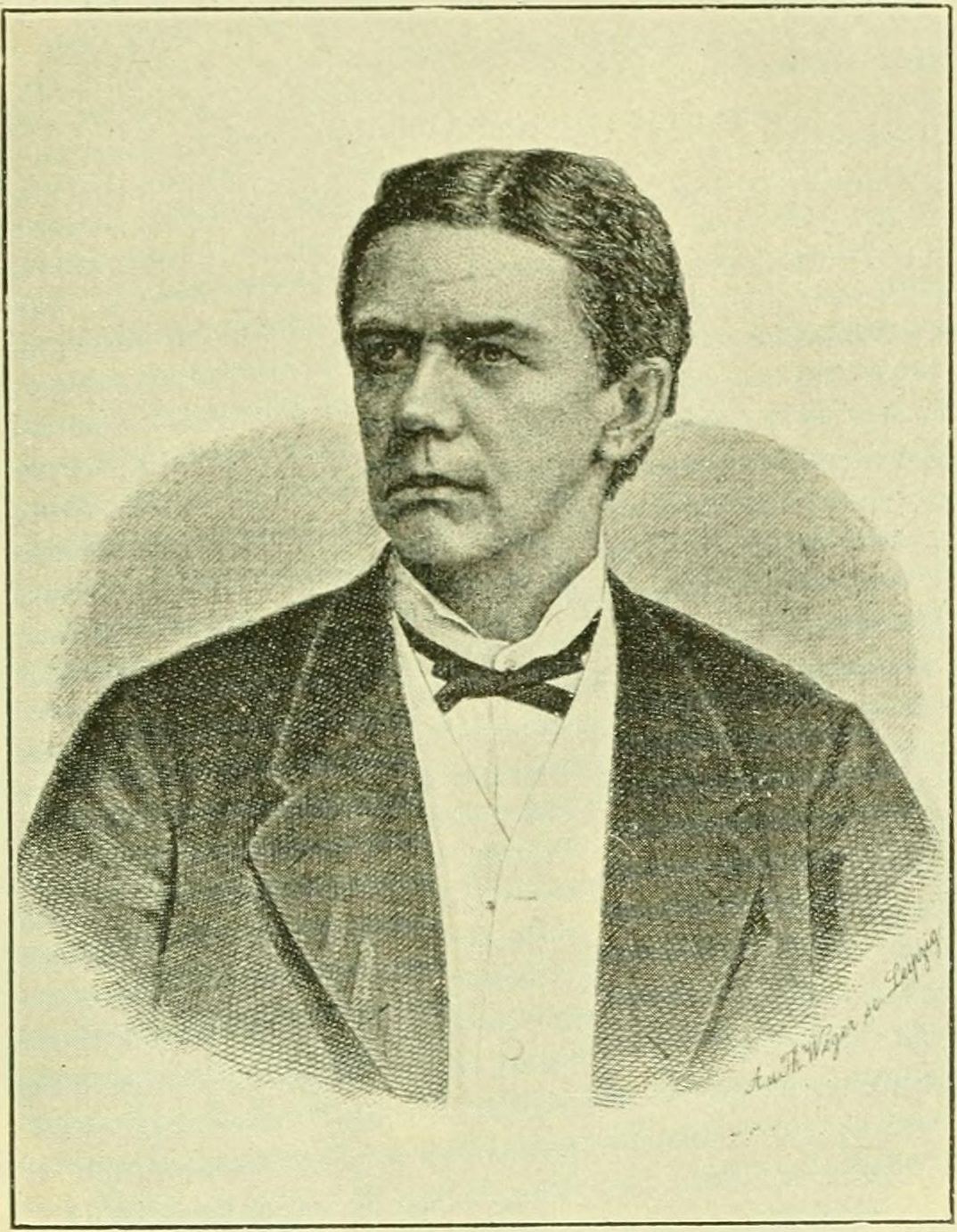
Theodor Kjerulf
Theodor Kjerulf (30 March 182525 October 1888) was a Norwegian geologist and professor at the University of Oslo. He also served as director of the Norwegian Geological Survey. Biography He was born in Christiania (now Oslo), Norway. He was the son of Peder Kjerulf (1781–1841) and Elisabet Maria Lasson (1791–1873). He was the brother of composer Halfdan Kjerulf. He was educated in the Royal Frederick University (now University of Oslo) and subsequently studied in Germany, working with Karl Georg Bischof in Bonn and Robert Wilhelm Bunsen in Heidelberg. In 1858, he was hired as a lecturer at the Royal Frederick University. In 1866 he was promoted to professor of geology. His contributions to the geology of Norway were numerous. From 1858 to 1888, he served as the first director of the Norwegian Geological Survey (''Norges geologiske undersøkelse''), which he had been instrumental in establishing. He also contributed to the systematic and detailed mapping of Norway's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Kjerulf
Theodor Kjerulf (30 March 182525 October 1888) was a Norwegian geologist and professor at the University of Oslo. He also served as director of the Norwegian Geological Survey. Biography He was born in Christiania (now Oslo), Norway. He was the son of Peder Kjerulf (1781–1841) and Elisabet Maria Lasson (1791–1873). He was the brother of composer Halfdan Kjerulf. He was educated in the Royal Frederick University (now University of Oslo) and subsequently studied in Germany, working with Karl Georg Bischof in Bonn and Robert Wilhelm Bunsen in Heidelberg. In 1858, he was hired as a lecturer at the Royal Frederick University. In 1866 he was promoted to professor of geology. His contributions to the geology of Norway were numerous. From 1858 to 1888, he served as the first director of the Norwegian Geological Survey (''Norges geologiske undersøkelse''), which he had been instrumental in establishing. He also contributed to the systematic and detailed mapping of Norway's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of St
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of different ways * Hierarchy, an arrangement of items that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another * an action or inaction that must be obeyed, mandated by someone in authority People * Orders (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Order'' (album), a 2009 album by Maroon * "Order", a 2016 song from '' Brand New Maid'' by Band-Maid * ''Orders'' (1974 film), a 1974 film by Michel Brault * ''Orders'', a 2010 film by Brian Christopher * ''Orders'', a 2017 film by Eric Marsh and Andrew Stasiulis * ''Jed & Order'', a 2022 film by Jedman Business * Blanket order, purchase order to allow multiple delivery dates over a period of time * Money order or postal order, a financial instrument usually i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartvig Caspar Christie (physicist)
Hartvig Caspar Christie (1 December 1826 – 3 March 1873) was a Norwegian mineralogist and physicist. Personal life He was born in Trondhjem as a son of naval commander Hartvig Caspar Christie (1788–1869) and Martha Sophia Sylow. He was a grandnephew of Werner Hosewinckel Christie, a nephew of Wilhelm Frimann Koren Christie and Edvard Eilert Christie and a first cousin of Hans Langsted Christie, Christian Christie and Johan Koren Christie. In January 1859 in Christiania he married Margaretha Sophie Bonnevie (1831–1913). The couple had eight children, and they were grandparents of politician Hartvig Caspar Christie. Through his wife, Christie was a brother-in-law of politician Jacob Aall Bonnevie, a son-in-law of politician Honoratus Bonnevie and an uncle of professor Kristine Bonnevie, judge Thomas Bonnevie and politician Carl Emil Christian Bonnevie. Career He finished secondary school at Trondheim Cathedral School in 1844, and took the cand.miner. degree in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norsk Polarinstitutt
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Georgia Island
South Georgia ( es, Isla San Pedro) is an island in the South Atlantic Ocean that is part of the British Overseas Territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. It lies around east of the Falkland Islands. Stretching in the east–west direction, South Georgia is around long and has a maximum width of . The terrain is mountainous, with the central ridge rising to at Mount Paget. The northern coast is indented with numerous bays and fjords, serving as good harbours. Discovered by Europeans in 1675, South Georgia had no indigenous population due to its harsh climate and remoteness. Captain James Cook in made the first landing, survey and mapping of the island, and on 17 January 1775 he claimed it a British possession, naming it "Isle of Georgia" after King George III. Through its history, it served as a whaling and seal hunting base, with intermittent population scattered in several whaling bases, the most important historically being Grytviken. The main settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kjerulf Glacier
Kjerulf Glacier, , () is a glacier long flowing west from Mount Sugartop to the east side of Newark Bay, on the south coast of South Georgia. It was mapped by Olaf Holtedahl during his visit to South Georgia in 1927–28, and named by him for Norwegian geologist Theodor Kjerulf, Professor of Mineralogy at the University of Christiania. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, c ... References Glaciers of South Georgia {{SouthGeorgia-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by a wide isthmus. It lies northeast of Iceland (495 km 05 miNE of Kolbeinsey), east of central Greenland, and west of the North Cape, Norway. The island is mountainous, the highest summit being the Beerenberg volcano in the north. The isthmus is the location of the two largest lakes of the island, Sørlaguna (South Lagoon) and Nordlaguna (North Lagoon). A third lake is called Ullerenglaguna (Ullereng Lagoon). Jan Mayen was formed by the Jan Mayen hotspot and is defined by geologists as a separate continent. Although administered separately, in the ISO 3166-1 standard, Jan Mayen and Svalbard are collectively designated as ''Svalbard and Jan Mayen'', with the two-letter country code " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kjerulf Glacier (Jan Mayen)
Kjerulf Glacier ( no, Kjerulfbreen) is a glacier in Jan Mayen. It begins at the Hakluyttoppen slope, in the outer crater edge of the Beerenberg. The Kjerulf Glacier and both its neighbors, the Weyprecht Glacier in the west and the Svend-Foyn Glacier in the east, are the most active glaciers in the island. The glacier was named after Norwegian geologist Theodor Kjerulf (1825–88), founder of the Geological Survey of Norway, during the Norwegian North-Atlantic Expedition 1876-1878 led by Henrik Mohn.''Kjerulfbreen'' - Stadnamn i norske polarområde, Norsk polarinstitutt. See also *List of glaciers in Norway *Svalbard and Jan Mayen Svalbard and Jan Mayen ( no, Svalbard og Jan Mayen, ISO 3166-1 alpha-2: SJ, ISO 3166-1 alpha-3: SJM, ISO 3166-1 numeric: 744) is a statistical designation defined by ISO 3166-1 for a collective grouping of two remote jurisdictions of Norway: ... References External links Glaciers of Jan Mayen Glaciers of Jan Mayen {{JanMayen-geo-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kjerulføya
Kjerulføya is an island north of Nordaustlandet in Svalbard, Norway. It is named for Theodor Kjerulf. The island is located within Nordaust-Svalbard Nature Reserve Nordaust-Svalbard Nature Reserve ( no, Nordaust-Svalbard naturreservat) is located in the north-eastern part of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. The nature reserve covers all of Nordaustlandet, Kong Karls Land, Kvitøya, Sjuøyane, Storøya, .... In the film ''Orion's Belt'', Kjerulfsøya is the location of the Soviet bearing station. References Islands of Svalbard {{Svalbard-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kjerulfbreen
Kjerulfbreen (Kjerulf Glacier) is a glacier in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a length of about 7.5 kilometers, and is debouching into the Trygghamna bay at the northern side of Isfjorden. The glacier is named after Norwegian geologist Theodor Kjerulf Theodor Kjerulf (30 March 182525 October 1888) was a Norwegian geologist and professor at the University of Oslo. He also served as director of the Norwegian Geological Survey. Biography He was born in Christiania (now Oslo), Norway. He was th .... See also * List of glaciers in Svalbard References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is the world's largest island. It is one of three constituent countries that form the Kingdom of Denmark, along with Denmark and the Faroe Islands; the citizens of these countries are all citizens of Denmark and the European Union. Greenland's capital is Nuuk. Though a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe (specifically Norway and Denmark, the colonial powers) for more than a millennium, beginning in 986.The Fate of Greenland's Vikings , by Dale Mackenzie Brown, ''Archaeological Institute of Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |