|
The Temple Institute
The Temple Institute, known in Hebrew as Machon HaMikdash ( he, מכון המקדש), is an organization in Israel focusing on the endeavor of establishing the Third Temple. Its long-term aims are to build the third Jewish temple on the Temple Mount, on the site occupied by the Dome of the Rock, and to reinstate animal sacrificial worship. It aspires to reach this goal through the study of Temple construction and ritual and through the development of actual Temple ritual objects, garments, and building plans suitable for immediate use in the event conditions permit its reconstruction. It runs a museum in the Jewish Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem in Israel. It was founded and is headed by Rabbi Yisrael Ariel. Its current director general is Dovid Shvartz, and the International Department is headed by Rabbi Chaim Richman. New York billionaire Henry Swieca has supported the institute. The Israeli government has also provided funding. Activities Building of Temple ritual i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukkot
or ("Booths, Tabernacles") , observedby = Jews, Samaritans, a few Protestant denominations, Messianic Jews, Semitic Neopagans , type = Jewish, Samaritan , begins = 15th day of Tishrei , ends = 21st day of Tishrei , date = , date = , date = , date = , observances = Dwelling in '' sukkah'', taking the Four Species, ''hakafot'' and Hallel in Synagogue , significance = One of the three pilgrimage festivals , relatedto = Shemini Atzeret, Simchat Torah , alt=, nickname=, litcolor=, celebrations=, date=15 Tishrei, 16 Tishrei, 17 Tishrei, 18 Tishrei, 19 Tishrei, 20 Tishrei, 21 Tishrei, weekday=, month=, scheduling=, duration=, frequency=, firsttime=, startedby= Sukkot ''Ḥag hasSukkōṯ'', lit. "festival of booths". Also spelled Succot; Ashkenazic: Sukkos. is a Torah-commanded holiday celebrated for seven days, beginning on the 15th day of the month of Tishrei. It is one of the Three Pilgrimage Festivals ( he, שלוש רג ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
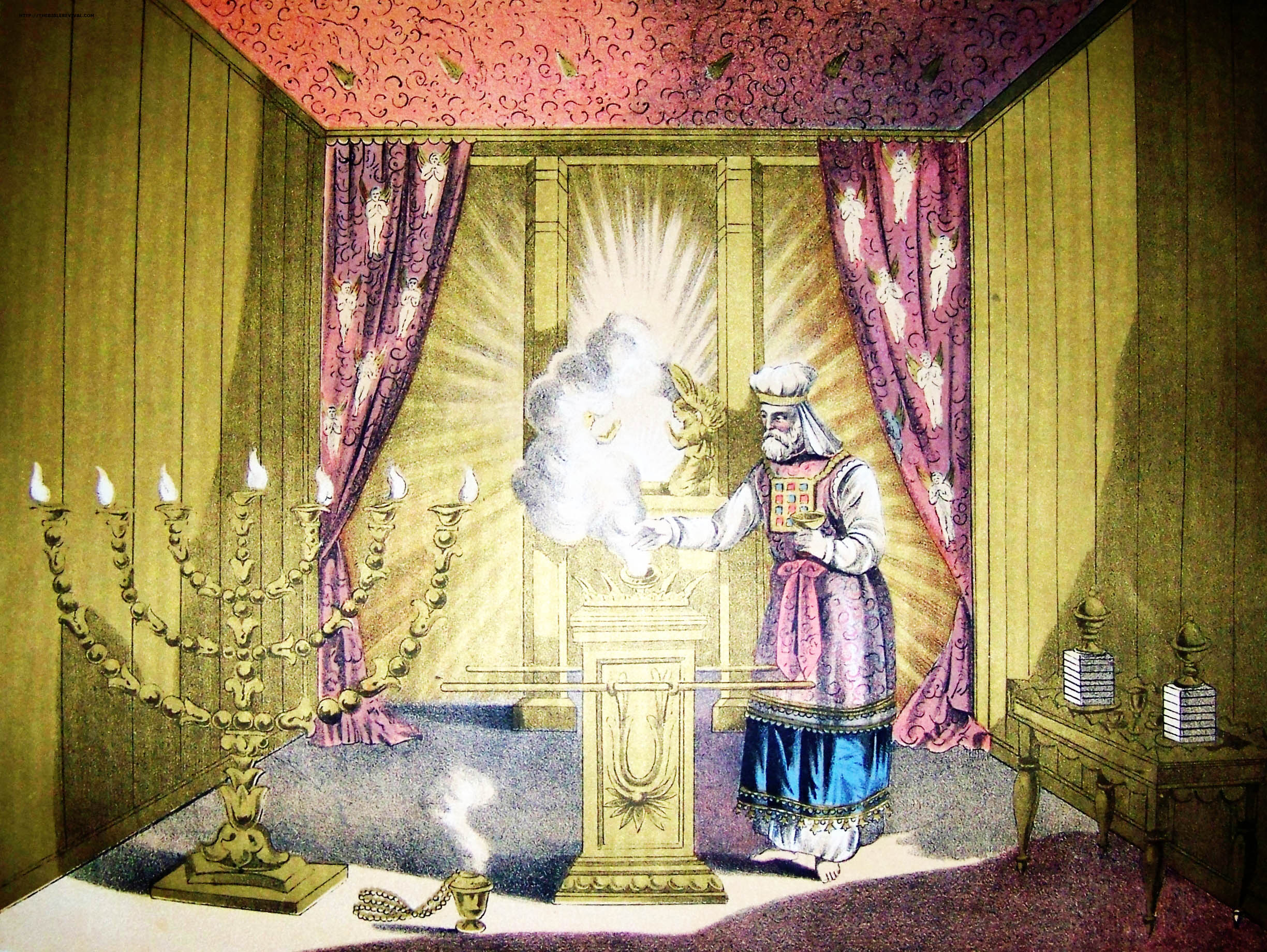
Tzitz
The priestly crown or frontlet (צִיץ ''ṣîṣ''/''tsiyts'') was the golden plate or tiara worn by the Jewish High Priest on his mitre or turban whenever he would minister in the Tabernacle or the Temple in Jerusalem. Etymology The root ''tzitz'' (צִיץ) means “to blossom” or “a flower” and as such is employed by the picturesque metaphors in Isaiah 27:6, 28:1, 40:7-8, floral descriptions of Solomon’s temple (1 Kings 6:18-35) and the blooming of Aaron’s rod (Num. 17:23). This latter instance is particularly interesting, because just as a ''tzitz'' appeared on the Aaron’s rod so is the Aaronide high-priest supposed to wear a ''tzitz'' on his forehead. In addition to this, once in the Hebrew Bible, in Ezekiel 8:3, the word appears in the construction ''tzitzit rosh'' meaning “a mop of hair” and probably deriving from the metaphor of hair as the plants grown from skin. This is furthermore supported by a handful of rabbinic descriptions which compare the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephod
An ephod ( he, אֵפוֹד ''ʾēfōḏ''; or ) was a type of apron, which according to the Hebrew Bible, was worn by the Jewish high priest the kohen gadol, an artifact and an object to be revered in ancient Israelite culture, and was closely connected with oracular practices and priestly ritual. In the Books of Samuel and Books of Chronicles, David is described as wearing an ephod when dancing in the presence of the Ark of the Covenant (2 Samuel 6:14, 1 Chronicles 15:27) and one is described as standing in the sanctuary at Nob, with a sword behind it (1 Samuel 21:9). In the book of Exodus and in Leviticus one is described as being created for the High Priest to wear as part of his official vestments (Exodus 28:4+, 29:5, 39:2+; Leviticus 8:7). Description In the Bible, in the contexts where it is worn, the ephod is usually described as being linen, but did not constitute complete clothing of any kind, as the Books of Samuel describe.Cheyne and Black, ''Encyclopedia Biblica'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoshen
The priestly breastplate or breastpiece of judgment ( he, חֹשֶׁן ''ḥōšen'') was a sacred breastplate worn by the High Priest of the Israelites, according to the Book of Exodus. In the biblical account, the breastplate is termed the ''breastplate of judgment'' ( he, חֹשֶׁן מִשְׁפָּט ''ḥōšen mišpāṭ'' - ), because the Urim and Thummim ( he, הָאוּרִים וְהַתֻּמִּים ''hāʾūrīm wəhattummīm'') were placed upon it.(). These elements of the breastplate are said in the Exodus verse to carry the judgement ( he, מִשְׁפָּט ''mišpāṭ'') of God concerning the Israelites at all times. Hebrew Bible According to the description in Exodus, this breastplate was attached to the tunic-like garment known as an ephod by gold chains/cords tied to the gold rings on the ephod's shoulder straps, and by blue ribbon tied to the gold rings at the belt of the ephod. The biblical description states that the breastplate was also to be made f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived from the Greek translation, (), meaning "instrumental music" and, by extension, "the words accompanying the music". The book is an anthology of individual Hebrew religious hymns, with 150 in the Jewish and Western Christian tradition and more in the Eastern Christian churches. Many are linked to the name of David, but modern mainstream scholarship rejects his authorship, instead attributing the composition of the psalms to various authors writing between the 9th and 5th centuries BC. In the Quran, the Arabic word ‘Zabur’ is used for the Psalms of David in the Hebrew Bible. Structure Benedictions The Book of Psalms is divided into five sections, each closing with a doxology (i.e., a benediction). These divisions were probably intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levites
Levites (or Levi) (, he, ''Lǝvīyyīm'') are Jewish males who claim patrilineal descent from the Tribe of Levi. The Tribe of Levi descended from Levi, the third son of Jacob and Leah. The surname ''Halevi'', which consists of the Hebrew definite article "" ''Ha-'' ("the") plus ''Levi'' (Levite) is not conclusive regarding being a Levite; a titular use of HaLevi indicates being a Levite. The daughter of a Levite is a " ''Bat Levi''" (''Bat'' being Hebrew for "daughter"). The Tribe of Levi served particular religious duties for the Israelites and had political (administering cities of refuge) and educational responsibilities as well. In return, the landed tribes were expected to support the Levites with a tithe (), particularly the tithe known as the First tithe, ''ma'aser rishon''. The Kohanim, a subset of the Levites, were the priests, who performed the work of holiness in the Temple. The Levites, referring to those who were not Kohanim, were specifically assigned to * singi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
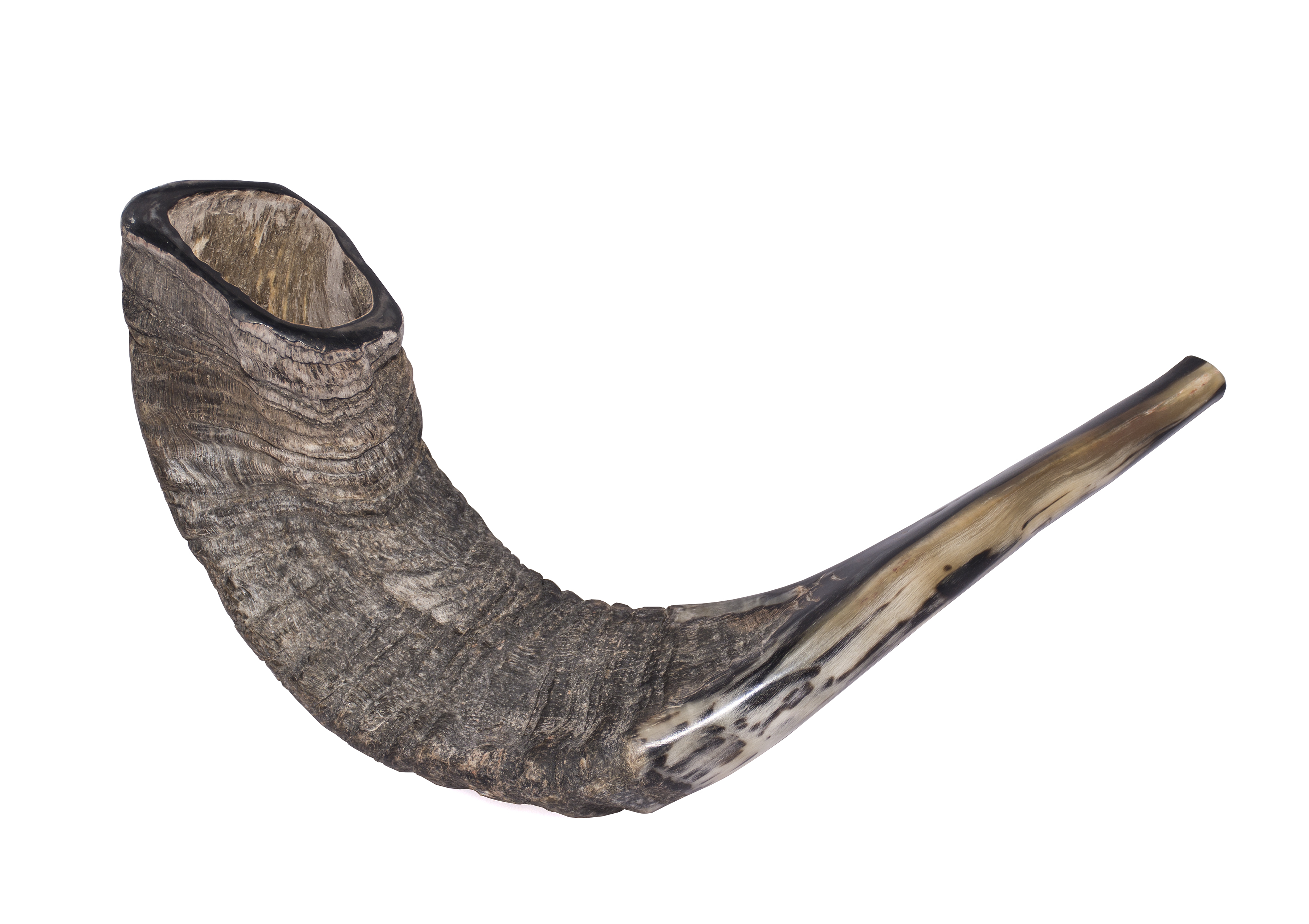
Shofar
A shofar ( ; from he, שׁוֹפָר, ) is an ancient musical horn typically made of a ram's horn, used for Jewish religious purposes. Like the modern bugle, the shofar lacks pitch-altering devices, with all pitch control done by varying the player's embouchure. The shofar is blown in synagogue services on Rosh Hashanah and at the end of Yom Kippur; it is also blown every weekday morning in the month of Elul running up to Rosh Hashanah. Shofars come in a variety of sizes and shapes, depending on the choice of animal and level of finish. Bible and rabbinic literature The shofar is mentioned frequently in the Hebrew Bible, the Talmud and rabbinic literature. In the first instance, in , the blast of a shofar emanating from the thick cloud on Mount Sinai makes the Israelites tremble in awe. The shofar was used to announce the new moon and the Jubilee year. The first day of Tishrei (now known as Rosh Hashana) is termed a "memorial of blowing", or "day of blowing", the shofar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosh Hashanah
Rosh HaShanah ( he, רֹאשׁ הַשָּׁנָה, , literally "head of the year") is the Jewish New Year. The biblical name for this holiday is Yom Teruah (, , lit. "day of shouting/blasting") It is the first of the Jewish High Holy Days (, , "Days of Awe"), as specified by Leviticus 23:23–25, that occur in the late summer/early autumn of the Northern Hemisphere. Rosh Hashanah begins a ten-day period of penitence culminating in Yom Kippur, as well as beginning the cycle of autumnal religious festivals running through Sukkot and ending in Shemini Atzeret. Rosh Hashanah is a two-day observance and celebration that begins on the first day of Tishrei, which is the seventh month of the ecclesiastical year. In contrast to the ecclesiastical lunar new year on the first day of the first month Nisan, the spring Passover month which marks Israel's exodus from Egypt, Rosh Hashanah marks the beginning of the civil year, according to the teachings of Judaism, and is the traditional ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohen Gadol
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post-Babylonian captivity, Exilic times until Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Roman Empire, Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Yahwism, Israelite religion, including during the time of the History of ancient Israel and Judah, kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a List of Jewish states and dynasties, Jewish kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ark Of The Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an elaborately designed lid called the mercy seat. According to the Book of Exodus, the Ark contained the two stone tablets of the Ten Commandments. According to the New Testament Book of Hebrews, it also contained Aaron's rod and a pot of manna. The biblical account relates that approximately one year after the Israelites' exodus from Egypt, the Ark was created according to the pattern given to Moses by God when the Israelites were encamped at the foot of Mount Sinai. Thereafter, the gold-plated acacia chest was carried by its staves by the Levites approximately 2,000 cubits (approximately ) in advance of the people when on the march. God spoke with Moses "from between the two cherubim" on the Ark's cover. Biblical account Construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Showbread
Showbread ( he, לחם הפנים ''Leḥem haPānīm'', literally: "Bread of the Faces"), in the King James Version: shewbread, in a biblical or Jewish context, refers to the cakes or loaves of bread which were always present, on a specially-dedicated table, in the Temple in Jerusalem as an offering to God. An alternative, and more appropriate, translation would be ''presence bread'',''Jewish Encyclopedia'' since the Bible requires that the bread be constantly in the presence of God (). Biblical references Within the Torah, the showbread is mentioned exclusively by the Priestly Code and Holiness Code, but certain sections of the Bible, including the Books of Chronicles, Books of Samuel, and Books of Kings, also describe aspects of them. In the Holiness Code, the showbread is described as twelve cakes baked from fine flour, arranged in two rows on a table; each cake was to contain "two tenth parts of an ephah" of flour () (approx 4.9 pounds). The biblical regulations specify tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |