|
Tensor Product Of Line Bundles
In differential geometry, the tensor product of vector bundles ''E'', ''F'' (over same space X) is a vector bundle, denoted by ''E'' ⊗ ''F'', whose fiber over a point x \in X is the tensor product of vector spaces ''E''''x'' ⊗ ''F''''x''.To construct a tensor-product bundle over a paracompact base, first note the construction is clear for trivial bundles. For the general case, if the base is compact, choose ''E'' such that ''E'' ⊕ ''E'' is trivial. Choose ''F'' in the same way. Then let ''E'' ⊗ ''F'' be the subbundle of (''E'' ⊕ ''E'') ⊗ (''F'' ⊕ ''F'') with the desired fibers. Finally, use the approximation argument to handle a non-compact base. See Hatcher for a general direct approach. Example: If ''O'' is a trivial line bundle, then ''E'' ⊗ ''O'' = ''E'' for any ''E''. Example: ''E'' ⊗ ''E'' ∗ is canonically isomorphic to the endomorphism bundle End(''E''), where ''E'' ∗ is the dual bundle of ''E''. Example: A line bundle ''L'' has tensor inverse: in fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Field
In mathematics and physics, a tensor field assigns a tensor to each point of a mathematical space (typically a Euclidean space or manifold). Tensor fields are used in differential geometry, algebraic geometry, general relativity, in the analysis of stress and strain in materials, and in numerous applications in the physical sciences. As a tensor is a generalization of a scalar (a pure number representing a value, for example speed) and a vector (a pure number plus a direction, like velocity), a tensor field is a generalization of a scalar field or vector field that assigns, respectively, a scalar or vector to each point of space. If a tensor is defined on a vector fields set over a module , we call a tensor field on . Many mathematical structures called "tensors" are also tensor fields. For example, the Riemann curvature tensor is a tensor ''field'' as it is defined on a manifold: it is named after Bernhard Riemann, and associates a tensor to each point of a Riemannian manif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Geometry
Differential geometry is a mathematical discipline that studies the geometry of smooth shapes and smooth spaces, otherwise known as smooth manifolds. It uses the techniques of differential calculus, integral calculus, linear algebra and multilinear algebra. The field has its origins in the study of spherical geometry as far back as antiquity. It also relates to astronomy, the geodesy of the Earth, and later the study of hyperbolic geometry by Lobachevsky. The simplest examples of smooth spaces are the plane and space curves and surfaces in the three-dimensional Euclidean space, and the study of these shapes formed the basis for development of modern differential geometry during the 18th and 19th centuries. Since the late 19th century, differential geometry has grown into a field concerned more generally with geometric structures on differentiable manifolds. A geometric structure is one which defines some notion of size, distance, shape, volume, or other rigidifying structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
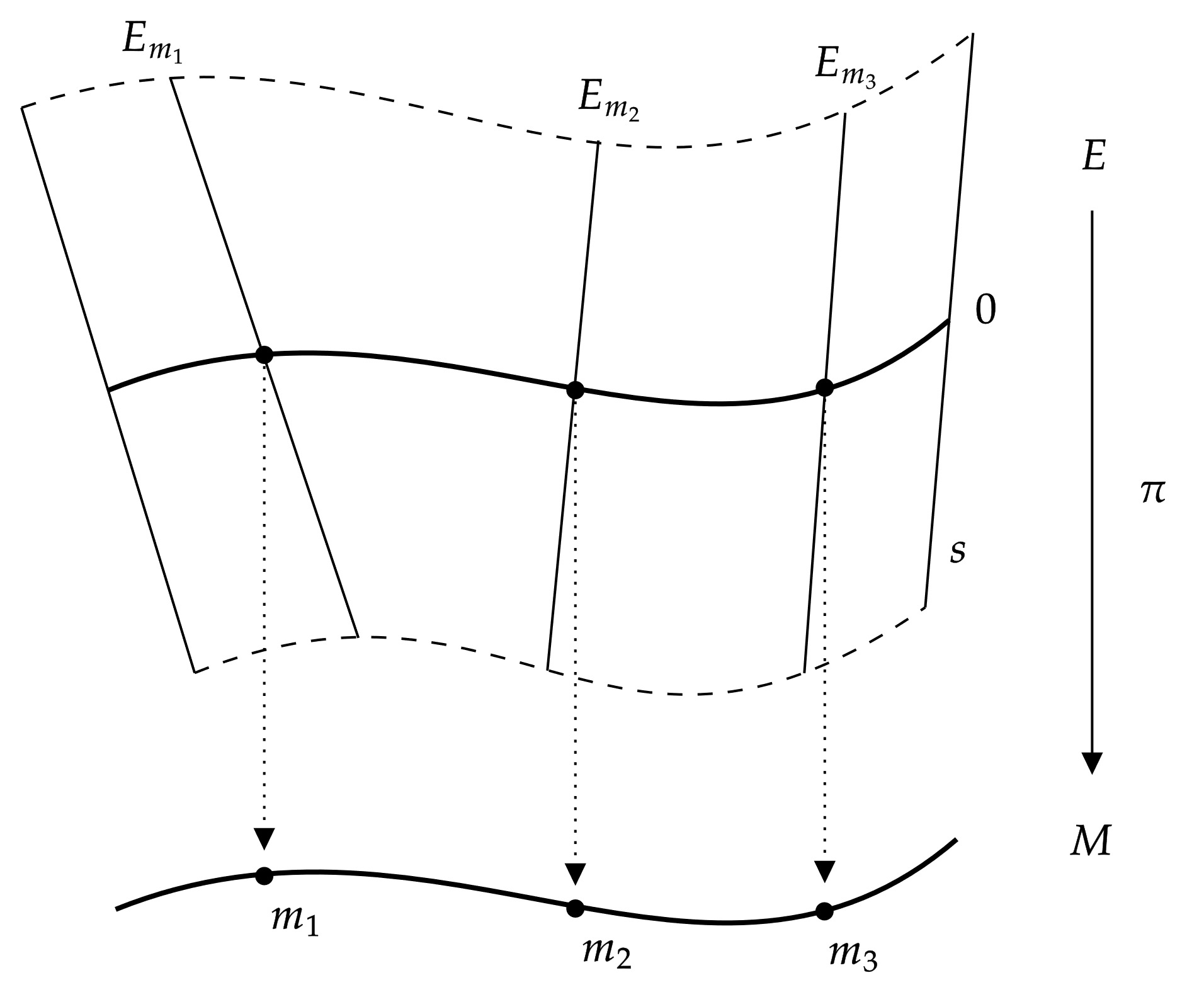
Vector Bundle
In mathematics, a vector bundle is a topological construction that makes precise the idea of a family of vector spaces parameterized by another space X (for example X could be a topological space, a manifold, or an algebraic variety): to every point x of the space X we associate (or "attach") a vector space V(x) in such a way that these vector spaces fit together to form another space of the same kind as X (e.g. a topological space, manifold, or algebraic variety), which is then called a vector bundle over X. The simplest example is the case that the family of vector spaces is constant, i.e., there is a fixed vector space V such that V(x)=V for all x in X: in this case there is a copy of V for each x in X and these copies fit together to form the vector bundle X\times V over X. Such vector bundles are said to be ''trivial''. A more complicated (and prototypical) class of examples are the tangent bundles of smooth (or differentiable) manifolds: to every point of such a manifold w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Product Of Vector Spaces
In mathematics, the tensor product V \otimes W of two vector spaces and (over the same field) is a vector space to which is associated a bilinear map V\times W \to V\otimes W that maps a pair (v,w),\ v\in V, w\in W to an element of V \otimes W denoted v \otimes w. An element of the form v \otimes w is called the tensor product of and . An element of V \otimes W is a tensor, and the tensor product of two vectors is sometimes called an ''elementary tensor'' or a ''decomposable tensor''. The elementary tensors span V \otimes W in the sense that every element of V \otimes W is a sum of elementary tensors. If bases are given for and , a basis of V \otimes W is formed by all tensor products of a basis element of and a basis element of . The tensor product of two vector spaces captures the properties of all bilinear maps in the sense that a bilinear map from V\times W into another vector space factors uniquely through a linear map V\otimes W\to Z (see Universal property). Tens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endomorphism Bundle
In mathematics, a vector bundle is a topological construction that makes precise the idea of a family of vector spaces parameterized by another space X (for example X could be a topological space, a manifold, or an algebraic variety): to every point x of the space X we associate (or "attach") a vector space V(x) in such a way that these vector spaces fit together to form another space of the same kind as X (e.g. a topological space, manifold, or algebraic variety), which is then called a vector bundle over X. The simplest example is the case that the family of vector spaces is constant, i.e., there is a fixed vector space V such that V(x)=V for all x in X: in this case there is a copy of V for each x in X and these copies fit together to form the vector bundle X\times V over X. Such vector bundles are said to be ''trivial''. A more complicated (and prototypical) class of examples are the tangent bundles of smooth (or differentiable) manifolds: to every point of such a manifold w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Bundle
In mathematics, the dual bundle is an operation on vector bundles extending the operation of duality for vector spaces. Definition The dual bundle of a vector bundle \pi: E \to X is the vector bundle \pi^*: E^* \to X whose fibers are the dual spaces to the fibers of E. Equivalently, E^* can be defined as the Hom bundle ''\mathrm(E,\mathbb \times X),'' that is, the vector bundle of morphisms from ''E'' to the trivial line bundle ''\R \times X \to X.'' Constructions and examples Given a local trivialization of ''E'' with transition functions t_, a local trivialization of E^* is given by the same open cover of ''X'' with transition functions t_^* = (t_^T)^ (the inverse of the transpose). The dual bundle E^* is then constructed using the fiber bundle construction theorem. As particular cases: * The dual bundle of an associated bundle is the bundle associated to the dual representation of the structure group. * The dual bundle of the tangent bundle of a differentiable manifold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Bundle
In mathematics, a line bundle expresses the concept of a line that varies from point to point of a space. For example, a curve in the plane having a tangent line at each point determines a varying line: the ''tangent bundle'' is a way of organising these. More formally, in algebraic topology and differential topology, a line bundle is defined as a ''vector bundle'' of rank 1. Line bundles are specified by choosing a one-dimensional vector space for each point of the space in a continuous manner. In topological applications, this vector space is usually real or complex. The two cases display fundamentally different behavior because of the different topological properties of real and complex vector spaces: If the origin is removed from the real line, then the result is the set of 1×1 invertible real matrices, which is homotopy-equivalent to a discrete two-point space by contracting the positive and negative reals each to a point; whereas removing the origin from the complex plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picard Group
In mathematics, the Picard group of a ringed space ''X'', denoted by Pic(''X''), is the group of isomorphism classes of invertible sheaves (or line bundles) on ''X'', with the group operation being tensor product. This construction is a global version of the construction of the divisor class group, or ideal class group, and is much used in algebraic geometry and the theory of complex manifolds. Alternatively, the Picard group can be defined as the sheaf cohomology group :H^1 (X, \mathcal_X^).\, For integral schemes the Picard group is isomorphic to the class group of Cartier divisors. For complex manifolds the exponential sheaf sequence gives basic information on the Picard group. The name is in honour of Émile Picard's theories, in particular of divisors on algebraic surfaces. Examples * The Picard group of the spectrum of a Dedekind domain is its '' ideal class group''. * The invertible sheaves on projective space P''n''(''k'') for ''k'' a field, are the twisting shea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetric Power
In mathematics, the ''n''-th symmetric power of an object ''X'' is the quotient of the ''n''-fold product X^n:=X \times \cdots \times X by the permutation action of the symmetric group \mathfrak_n. More precisely, the notion exists at least in the following three areas: *In linear algebra, the ''n''-th symmetric power of a vector space ''V'' is the vector subspace of the symmetric algebra of ''V'' consisting of degree-''n'' elements (here the product is a tensor product). *In algebraic topology, the ''n''-th symmetric power of a topological space ''X'' is the quotient space X^n/\mathfrak_n, as in the beginning of this article. *In algebraic geometry, a symmetric power is defined in a way similar to that in algebraic topology. For example, if X = \operatorname(A) is an affine variety, then the GIT quotient In algebraic geometry, an affine GIT quotient, or affine geometric invariant theory quotient, of an affine scheme X = \operatorname A with an action by a group scheme ''G'' is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exterior Power
In mathematics, the exterior algebra, or Grassmann algebra, named after Hermann Grassmann, is an algebra that uses the exterior product or wedge product as its multiplication. In mathematics, the exterior product or wedge product of vectors is an algebraic construction used in geometry to study areas, volumes, and their higher-dimensional analogues. The exterior product of two vectors u and v, denoted by u \wedge v, is called a bivector and lives in a space called the ''exterior square'', a vector space that is distinct from the original space of vectors. The magnitude of u \wedge v can be interpreted as the area of the parallelogram with sides u and v, which in three dimensions can also be computed using the cross product of the two vectors. More generally, all parallel plane surfaces with the same orientation and area have the same bivector as a measure of their oriented area. Like the cross product, the exterior product is anticommutative, meaning tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Form
In mathematics, differential forms provide a unified approach to define integrands over curves, surfaces, solids, and higher-dimensional manifolds. The modern notion of differential forms was pioneered by Élie Cartan. It has many applications, especially in geometry, topology and physics. For instance, the expression is an example of a -form, and can be integrated over an interval contained in the domain of : :\int_a^b f(x)\,dx. Similarly, the expression is a -form that can be integrated over a surface : :\int_S (f(x,y,z)\,dx\wedge dy + g(x,y,z)\,dz\wedge dx + h(x,y,z)\,dy\wedge dz). The symbol denotes the exterior product, sometimes called the ''wedge product'', of two differential forms. Likewise, a -form represents a volume element that can be integrated over a region of space. In general, a -form is an object that may be integrated over a -dimensional manifold, and is homogeneous of degree in the coordinate differentials dx, dy, \ldots. On an -dimensional manifold, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector-valued Differential Form
In mathematics, a vector-valued differential form on a manifold ''M'' is a differential form on ''M'' with values in a vector space ''V''. More generally, it is a differential form with values in some vector bundle ''E'' over ''M''. Ordinary differential forms can be viewed as R-valued differential forms. An important case of vector-valued differential forms are Lie algebra-valued forms. (A connection form is an example of such a form.) Definition Let ''M'' be a smooth manifold and ''E'' → ''M'' be a smooth vector bundle over ''M''. We denote the space of smooth sections of a bundle ''E'' by Γ(''E''). An ''E''-valued differential form of degree ''p'' is a smooth section of the tensor product bundle of ''E'' with Λ''p''(''T'' ∗''M''), the ''p''-th exterior power of the cotangent bundle of ''M''. The space of such forms is denoted by :\Omega^p(M,E) = \Gamma(E\otimes\Lambda^pT^*M). Because Γ is a strong monoidal functor, this can also be interpreted as :\Gamma(E\otimes\Lambd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |