|
Tell Yunatsite
Tell Yunatsite ( bg, Селищна могила Юнаците), also known as ''Ploskata mogila'' ( bg, Плоската могила, "The Flat Mound"), is situated in the Pazardzhik Province of southern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), some to the west of the district capital Pazardzhik. The tell stands above modern ground level and has a diameter of . It is situated on a low terrace at the right bank of the former Topolnitsa riverbed near to its confluence with the Maritsa River (ca. away from the site). Medieval, Roman, Iron Age, Early Bronze Age, and Copper Age periods have all been attested at the site. Parallel to the Maritsa River on the Pazardzhik plain lays the so-called Via Diagonalis, one of the most important ancient European roads, which passes through the Balkans and connects West and Central Europe to Anatolia and the Near East. The former road bears witness to the rich history and importance of the region. The plain slants from west to east (300 m to 100 m asl.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pazardzhik
Pazardzhik ( bg, Пазарджик ) is a city situated along the banks of the Maritsa river, southern Bulgaria. It is the capital of Pazardzhik Province and centre for the homonymous Pazardzhik Municipality. The Tatars founded Pazardzhik in the end of the XIV century, which they named it ''Tatar-Pazardzhik''. The population was predominantly muslim. That provoke an interest to christians, which would allow the first church in the small town in the XVII century and also create the first church ''St. Mary''. The economy grew over the centuries with the prosper trading of iron, leather and rice. During the 19th century, a brief siege was made during the Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812) and the Russians in the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) kicked the Ottomans from the area. Even though undefended, it was spared from massacres, because the Armenian Ovanes Sovadzhiyan prevented the Ottomans from carrying out their plan to burn down and murder the inhabitants the small town by tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and has many mineral springs, such as the Sofia Central Mineral Baths. It has a humid continental climate. Being in the centre of the Balkans, it is midway between the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea, and closest to the Aegean Sea. Known as Serdica in Antiquity and Sredets in the Middle Ages, Sofia has been an area of human habitation since at least 7000 BC. The recorded history of the city begins with the attestation of the conquest of Serdica by the Roman Republic in 29 BC from the Celtic tribe Serdi. During the decline of the Roman Empire, the city was raided by Huns, Visigoths, Avars and Slavs. In 809, Serdica was incorporated into the Bulgarian Empire by Khan Krum and became known as Sredets. In 1018, the Byzantines ended Bulgarian rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solnitsata
Solnitsata ( bg, Солницата, "The Saltworks") was a prehistoric town located in present-day Bulgaria, near the modern city of Provadia. Believed by archaeologists to be the oldest town in Europe, Solnitsata was a fortified stone settlement - citadelle, inner and outer city with pottery production site and the site of a salt production facility approximately six millennia ago; it flourished ca 4700–4200 BC. The settlement was walled to protect the salt, a crucial commodity in antiquity. Although its population has been estimated at only 350, archaeologist Vassil Nikolov argues that it meets established criteria as a prehistoric city. Salt production drove Solnitsata's economy, and the town is believed to have supplied salt throughout the Balkans. A large collection of gold objects nearby has led archaeologists to consider that this trade resulted in great wealth for the town's residents — Varna Necropolis. Nearby is the ancient Anhialos, whose livelihood was the extrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seuthopolis
Seuthopolis (Ancient Greek: Σευθόπολις) was an ancient hellenistic-type city founded by the Thracian king Seuthes III between 325–315 BC and the capital of the Odrysian kingdom. Its ruins are now located at the bottom of the Koprinka Reservoir near Kazanlak, Stara Zagora Province, in central Bulgaria. Several kilometres north of the city is the Valley of the Thracian Rulers where many magnificent royal tombs are located. Seuthopolis was not a true polis, but rather the seat of Seuthes and his court. His palace had a dual role, functioning also as a sanctuary of the Cabeiri, the gods of Samothrace. Most of the space within the city was occupied not by homes but by official structures, the majority of the people living outside the city. It had Thracian and Greek populace. In 281 BC it was sacked by Celts. The dual role of Seuthes' palace (royal court and sanctuary) indicates that Seuthes was a priest–king: the high priest of the Cabeiri among the Odrysian Thracians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perperikon
The ancient Thracian city of Perperikon (also Perpericum; bg, Перперикон, el, Περπερικόν) is located in the Eastern Rhodopes, 15 km northeast of the present-day town of Kardzhali, Bulgaria on a 470 m high rocky hill, which is thought to have been a sacred place. The village of Gorna krepost ("Upper Fortress") is located at the foot of the hill and the gold-bearing Perpereshka River flows nearby. Perperikon is the largest megalith ensemble site in the Balkans. The name "Perperikon" The name Perperikon dates from the Middle Ages – 11th–13th centuries. The original name Hyperperakion was shortened by scribes to Perperakion or Perperikon. There are at least two theories about the origin and meaning of the name, both associating it with gold-mining: The city may have been named after a Medieval high-temperature gold-refining process (Medieval Greek ), or the resumed use of a classical-era name for the site, derived from a word for altar-fire (anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karanovo Culture
The Karanovo culture is a Neolithic culture (Karanovo I-III ca. 62nd to 55th centuries BC) named after the Bulgarian village of (Караново, Sliven Province ). The culture, which is part of the Danube civilization, is considered the largest and most important of the Azmak River Valley agrarian settlements. Discovery Archaeologists discovered the Karanovo settlement in the 1930s when a tell - a settlement mound - was excavated at Karanovo. The hilltop settlement is constituted of 18 buildings, which housed some 100 inhabitants. The site was inhabited more or less continuously from the early 7th to the early 2nd millennia BC. The Karanovo culture served as the foundation of the East Balkan cultural sequence. The layers at Karanovo are employed as a chronological system for Balkans prehistory. This culture had seven major phases: Karanovo I and II, which existed parallel to Starčevo; Karanovo III (Veselinovo); Karanovo IV; Karanovo V (Marica); Karanovo VI (Gumelniţ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Cities In Thrace And Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durankulak (archaeological Site)
Durankulak is a prehistoric archaeological site on the Golemija ostrov (Big Island) in Durankulak lake, Bulgaria. Prehistoric settlement commenced on the small island approximately 7000 BP and lasted for thousands of years. The first inhabitants were the Hamangia culture, dated from the middle of the 6th millennium to the middle of 5th millennium BC, and were the first manifestation of the Neolithic life in Dobrudja. Hamangia people were small-scale cultivators and plant collectors who built houses, made pottery, herded and hunted animals. Around 4700/4600 BC the stone architecture was already in general use and became a characteristic phenomenon that was unique in Europe. The settlement in Durankulak was a well-organized aggregation of buildings of substantial size with several rooms. They were coherently laid out according to a plan that was repeated over successive generations of house reconstructions. Buildings were rectilinear and large, narrow paths separated individual hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Europe (archaeology)
Old Europe is a term coined by the Lithuanian archaeologist Marija Gimbutas to describe what she perceived as a relatively homogeneous pre-Indo-European Neolithic and Copper Age cultural horizon or civilisation in Southeastern Europe and part of Central-Eastern Europe, centred in the Danube River valley. Old Europe is also referred to in some literature as the Danube civilisation. The term 'Danubian culture' was earlier coined by the archaeologist Vere Gordon Childe to describe early farming cultures (e.g. the Linear Pottery culture) which spread westwards and northwards from the Danube valley into Central and Eastern Europe. Old Europe Old Europe, or Neolithic Europe, refers to the time between the Mesolithic and Bronze Age periods in Europe, roughly from 7000 BCE (the approximate time of the first farming societies in Greece) to c. 2000 BCE (the beginning of the Bronze Age in Scandinavia). The duration of the Neolithic varies from place to place: in Southeastern Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
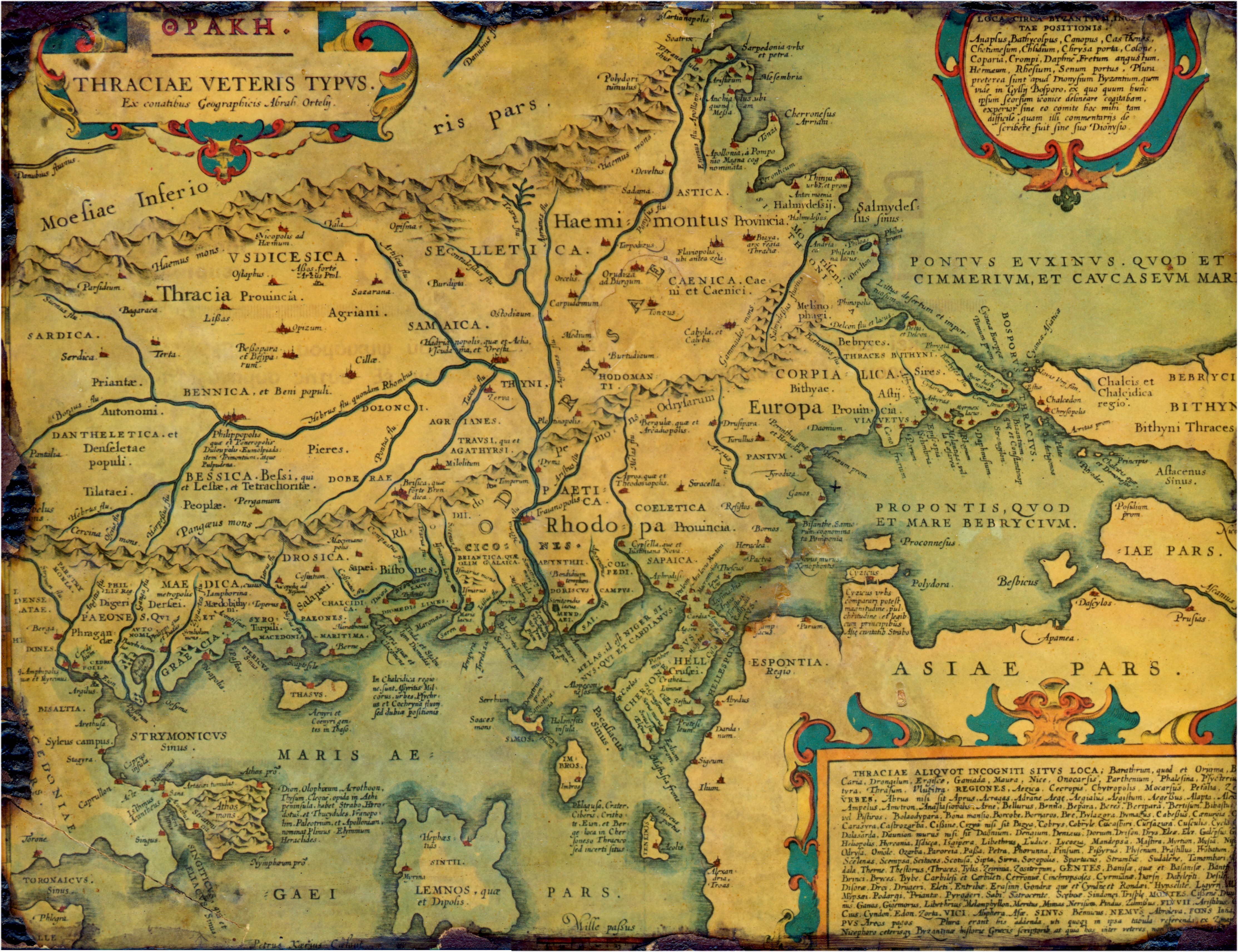
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey ( East Thrace). The region's boundaries are based on that of the Roman Province of Thrace; the lands inhabited by the ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into the region of Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'' was first used by the Greeks when referring to the Thracian tribes, from ancient Greek Thrake (Θρᾴκη), descending from ''Thrāix'' (Θρᾷξ). It referred originally to the Thracians, an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' first referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Yunastite-1
Tell may refer to: *Tell (archaeology), a type of archaeological site *Tell (name), a name used as a given name and a surname *Tell (poker), a subconscious behavior that can betray information to an observant opponent Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Tell'' (2012 film), a short psychological horror film by Ryan Connolly * ''Tell'' (2014 film), a crime thriller starring Katee Sackhoff, Jason Lee and Milo Ventimiglia * '' Tell Magazine'', a Nigerian newsweekly * "The Tell", an episode of ''NCIS'' * "The Tell" (''Teen Wolf''), a television episode * ''The Tell'', a photomural, part of the Laguna Canyon Project Places Middle East *Tel Aviv, Israel *Et-Tell, an archaeological site identified with Bethsaida *Tell, West Bank, a Palestinian village near Nablus *Ancient Tell, Beirut, Lebanon; the Canaanite pre-Phoenician era of Beirut and archaeological site United States *Tell, Texas, unincorporated community in the United States *Tell, Wisconsin, town in the United States *Tell C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Field Research
The Institute for Field Research (IFR) is a nonprofit organization established in 2011 by a group of academic archaeologists. It operates as an independent, nonprofit academic organization that offers field research courses (field schools) at various sites around the world. The IFR worked with different universities to provide students with academic credit units. At present, the IFR school of record is Connecticut College. Through this agreement, students receive 8 semester credit units (equivalent to 12 quarter units) for attending any of the field schools offered by the IFR. These units are transferable to student's home institution through official Connecticut College transcripts. Students receive a letter grade for attending a field school. All field schools provide a minimum of 160 direct instructional hours. The IFR has conducted field schools at numerous sites around the world, including Cahokia, Spike Island and Ribchester Ribchester is a village and civil parish with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |