|
Telephone Wiring
A telephone line or telephone circuit (or just line or circuit industrywide) is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. It is designed to reproduce speech of a quality that is understandable. It is the physical wire or other signaling medium connecting the user's telephone apparatus to the telecommunications network, and usually also implies a single telephone number for billing purposes reserved for that user. Telephone lines are used to deliver landline telephone service and Digital subscriber line (DSL) phone cable service to the premises. Telephone overhead lines are connected to the public switched telephone network. The voltage at a subscriber's network interface is typically 48 V between the ring and tip wires, with tip near ground and ring at -48 V. In the United States In 1878, the Bell Telephone Company began to use two-wire circuits, called the local loop, from each user's telephone to end offices which performed any necessary electrical swi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phone Pole3
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into electronic signals that are transmitted via cables and other communication channels to another telephone which reproduces the sound to the receiving user. The term is derived from el, τῆλε (''tēle'', ''far'') and φωνή (''phōnē'', ''voice''), together meaning ''distant voice''. A common short form of the term is ''phone'', which came into use early in the telephone's history. In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was the first to be granted a United States patent for a device that produced clearly intelligible replication of the human voice at a second device. This instrument was further developed by many others, and became rapidly indispensable in business, government, and in households. The essential elements of a telephone are a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Pole
A utility pole is a column or post typically made out of wood used to support overhead power lines and various other public utilities, such as electrical cable, optical fiber, fiber optic cable, and related equipment such as Distribution transformer, transformers and street lights. It can be referred to as a transmission pole, telephone pole, telecommunication pole, power pole, hydro pole, telegraph pole, or telegraph post, depending on its application. A Stobie pole is a multi-purpose pole made of two steel joists held apart by a slab of concrete in the middle, generally found in South Australia. Electrical wires and cables are routed overhead on utility poles as an inexpensive way to keep them insulated from the ground and out of the way of people and vehicles. Utility poles can be made of wood, metal, concrete, or composites like fiberglass. They are used for two different types of power lines: ''sub transmission lines'', which carry higher voltage power between substations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Connector
A modular connector is a type of electrical connector for cords and cables of electronic devices and appliances, such as in computer networking, telecommunication equipment, and audio headsets. Modular connectors were originally developed for use on specific Bell System telephone sets in the 1960s, and similar types found use for simple interconnection of customer-provided telephone subscriber premises equipment to the telephone network. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) mandated in 1976 an interface registration system, in which they became known as registered jacks. The convenience of prior existence for designers and ease of use led to a proliferation of modular connectors for many other applications. Many applications that originally used bulkier, more expensive connectors have converted to modular connectors. Probably the best-known applications of modular connectors are for telephone and Ethernet. Accordingly, various electronic interface specifications exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
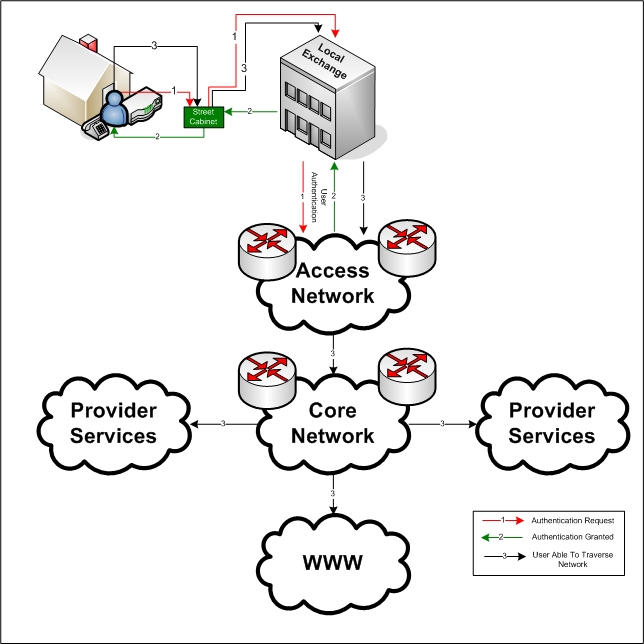
Access Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality of the records which describe the network. In 2006, according t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junction Box
An electrical junction box (also known as a "jbox") is an enclosure housing electrical connections. Junction boxes protect the electrical connections from the weather, as well as protecting people from accidental electric shocks. Construction A small metal or plastic junction box may form part of an electrical conduit or thermoplastic-sheathed cable (TPS) wiring system in a building. If designed for surface mounting, it is used mostly in ceilings, under floors or concealed behind an access panel—particularly in domestic or commercial buildings. An appropriate type (such as that shown in the gallery) may be buried in the plaster of a wall (although full concealment is no longer allowed by modern codes and standards) or cast into concrete—with only the cover visible. It sometimes includes built-in terminals for the joining of wires. A similar, usually wall mounted, container used mainly to accommodate switches, sockets and the associated connecting wiring is called a pattr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital systems to establish telephone calls between subscribers. In historical perspective, telecommunication terms have been used with different semantics over time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. Often, a ''central office'' is defined as a building used to house the inside plant equipment of potentially several telephone exchanges, each serving a certain geographical area. Such an area has also been referred to as the exchange or exchange area. In North America, a central office location may also be identified as a ''wire center'', designating a facility to which a telephone is connected and obtains dial tone. For business and billing purposes, telecommunication carriers defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tip And Ring
Tip and ring are the two conductors or sides of a telephone line. Their names are derived from the telephone plugs used for connecting telephone calls in manual switchboards. One side of the line is connected to the metal ''tip'' of the plug, and the second is connected to a metal ''ring'' behind the tip, separated and insulated from the tip by a non-conducting material. When inserted into a jack, the plug's tip conductor connects first, followed by the ring conductor. In many European countries, tip and ring are referred to as the ''A'' and ''B'' wires. Neither of the tip and ring conductors is permanently connected to earth ground, but may be connected to ground during signaling operations. Typically, the ring conductor has a direct current (DC) potential of to with respect to the tip conductor when the line is in the on-hook (idle) state. Floating both conductors, not referencing either one to ground, minimizes the pickup of hum from any nearby alternating current (AC) power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Wire
Copper has been used in electrical wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s. The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor. Copper is the electrical conductor in many categories of electrical wiring.Pops, Horace, 2008, Processing of wire from antiquity to the future, Wire Journal International, June, pp 58-66 Copper wire is used in power generation, power transmission, power distribution, telecommunications, electronics circuitry, and countless types of electrical equipment. Copper and its alloys are also used to make electrical contacts. Electrical wiring in buildings is the most important market for the copper industry. Roughly half of all copper mined is used to manufacture electrical wire and cable conductors. Properties of copper Electrical conductivity Electrical conductivity is a measure of how well a material transports an electric charge. This is an essential propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
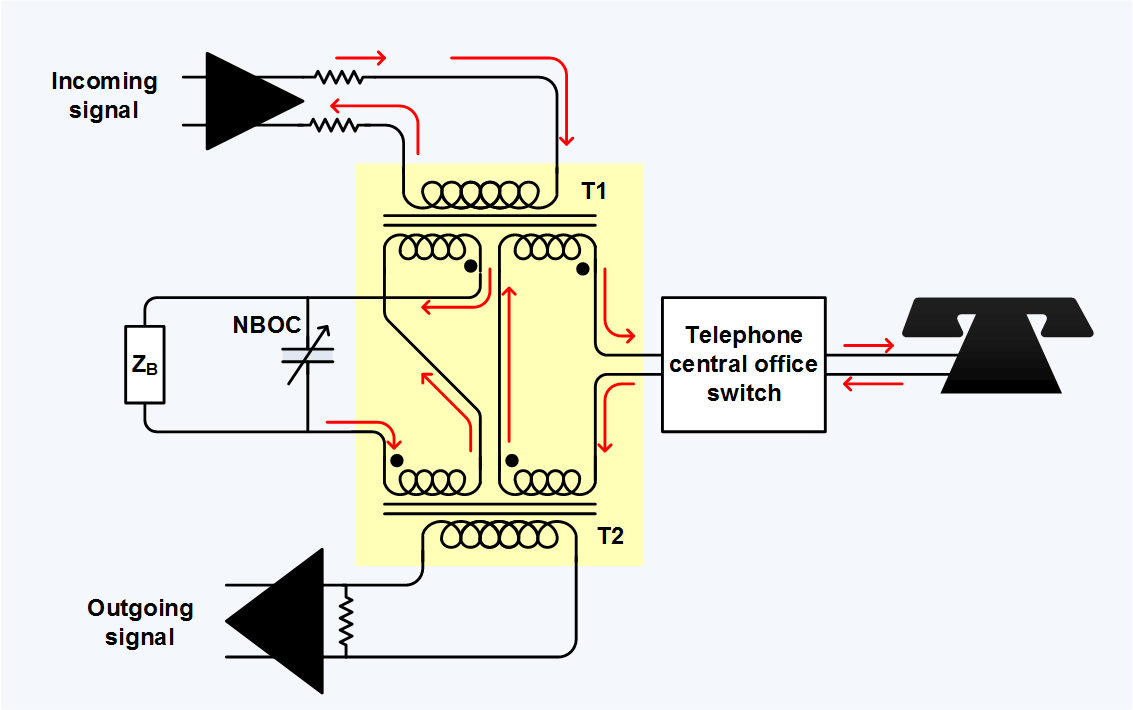
Telephone Hybrid
A telephone hybrid is the component at the ends of a subscriber line of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) that converts between two-wire and four-wire forms of bidirectional audio paths. When used in broadcast facilities to enable the airing of telephone callers, the broadcast-quality telephone hybrid is known as a broadcast telephone hybrid or telephone balance unit. The need for hybrids comes from the nature of analog plain old telephone service (POTS) home or small business telephone lines, where the two audio directions are combined on a single two-wire pair. Within the telephone network, switching and transmission are almost always four-wire circuits with the two signals being separated. Hybrids perform the necessary conversion. In older analog networks, conversion to four-wire was required so that repeater amplifiers could be inserted in long-distance links. In today's digital systems, each speech direction must be processed and transported independently. The line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Access Arrangement
The term data access arrangement (DAA) has the following meanings: #In public switched telephone networks, a single item or group of items at the customer side of the network interface device for data transmission purposes, including all equipment that may affect the characteristics of the interface. #A data circuit-terminating equipment ( DCE) supplied or approved by a common carrier that permits a DCE or data terminal equipment ( DTE) to be attached to the common carrier network. Data access arrangements are an integral part of all modems built for the public telephone network. In view of mixed voice and data access, DAAs are more generally referred to as direct access arrangements. Requirement for DAAs While DAA now describes an integral component of a device that connects to the telephone network, during the 60s and 70s it described a separate device mandated by the Bell System, connected between the telephone line and non-Bell equipment, typically a modem. Following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrier System
A carrier system is a telecommunications system that transmits information, such as the voice signals of a telephone call and the video signals of television, by modulation of one or multiple carrier signals above the principal voice frequency or data rate.Western Electric (1969) ''Fundamentals of Telephone Communication Systems'', p.16.2 Carrier systems typically transmit multiple channels of communication simultaneously over the shared medium using various forms of multiplexing. Prominent multiplexing methods of the carrier signal are time-division multiplexing (TDM) and frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). A cable television system is an example of frequency-division multiplexing. Many television programs are carried simultaneously on the same coaxial cable by sending each at a different frequency. Multiple layers of multiplexing may ultimately be performed upon a given input signal. For example, in the public switched telephone network, many telephone calls are sent over sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission (telecom)
In telecommunications, transmission is the process of sending or propagating an analog or digital signal via a medium that is wired, wireless, or fiber-optic. Transmission technologies typically refer to physical layer protocol duties such as modulation, demodulation, line coding, equalization, error control, bit synchronization and multiplexing, but it may also involve higher-layer protocol duties, for example, digitizing an analog signal, and data compression. Transmission of a digital message, or of a digitized analog signal, is known as data transmission. Examples of transmission are the sending of signals with limited duration, for example, a block or packet of data, a phone call, or an email. See also *Radio transmitter In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)