|
Tejime
, also called , is a Japanese custom of ceremonial rhythmic hand clapping, typically accompanied by enthusiastic exclamation by the participants, performed at the end of a special event to bring the occasion to a peaceful, lively close. Tejime may be performed at the conclusion of such events as a celebration, meeting of shareholders, or the close of bargaining or other business negotiations. Tejime observes fulfillment, realization, and completion. Tejime begins by a call from the leader, typically "ote wo haishaku" (お手を拝借), after which the participants, just before clapping their hands, usually yell "iyō'o" (イヨーオ), "yo" (ヨッ) or "mō itchō" (もう一丁) in order to synchronize timing. Etymology Tejime is an abbreviated form of , "teuchi" meaning "to strike a deal" or "to come to an agreement" and meaning "to tie" or "to fasten" (in this case, "to close"). ''Teuchi'' is used synonymously with tejime, with the former preferred in the Kansai Region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tejime 01
, also called , is a Japanese custom of ceremonial rhythmic hand clapping, typically accompanied by enthusiastic exclamation by the participants, performed at the end of a special event to bring the occasion to a peaceful, lively close. Tejime may be performed at the conclusion of such events as a celebration, meeting of shareholders, or the close of bargaining or other business negotiations. Tejime observes fulfillment, realization, and completion. Tejime begins by a call from the leader, typically "ote wo haishaku" (お手を拝借), after which the participants, just before clapping their hands, usually yell "iyō'o" (イヨーオ), "yo" (ヨッ) or "mō itchō" (もう一丁) in order to synchronize timing. Etymology Tejime is an abbreviated form of , "teuchi" meaning "to strike a deal" or "to come to an agreement" and meaning "to tie" or "to fasten" (in this case, "to close"). ''Teuchi'' is used synonymously with tejime, with the former preferred in the Kansai Region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansai Region
The or the , lies in the southern-central region of Japan's main island Honshū. The region includes the prefectures of Nara, Wakayama, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo and Shiga, often also Mie, sometimes Fukui, Tokushima and Tottori. The metropolitan region of Osaka, Kobe and Kyoto ( Keihanshin region) is the second-most populated in Japan after the Greater Tokyo Area. Name The terms , , and have their roots during the Asuka period. When the old provinces of Japan were established, several provinces in the area around the then-capital Kyoto were collectively named Kinai and Kinki, both roughly meaning "the neighbourhood of the capital". Kansai (literally ''west of the tollgate'') in its original usage refers to the land west of the Osaka Tollgate (), the border between Yamashiro Province and Ōmi Province (present-day Kyoto and Shiga prefectures).Entry for . Kōjien, fifth edition, 1998, During the Kamakura period, this border was redefined to include Ōmi and Iga Provinces. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customs And Etiquette Of Japan
Etiquette in Japan forms common societal expectations of social behavior practiced throughout the nation of Japan. The etiquette of Japan has changed greatly over the millennia as different civilizations influenced its culture. Modern Japanese etiquette has a strong influence from that of China and the Western world, but retains many of its unique traditional elements. Bathing Bathing is an important part of the daily routine in Japan, where bath tubs are for relaxing, not cleaning the body. Therefore, the body must be cleaned and scrubbed before entering the bathtub or . This is done in the same room as the tub, while seated on a small stool and using a hand-held shower. Soap, a wash cloth, and shampoo are provided; and the bather is expected to wash and rinse thoroughly twice before stepping into the . It is very important that no soap residue be transferred to the because the heated water is not drained after each person's use, and several hours (and the expense of a consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
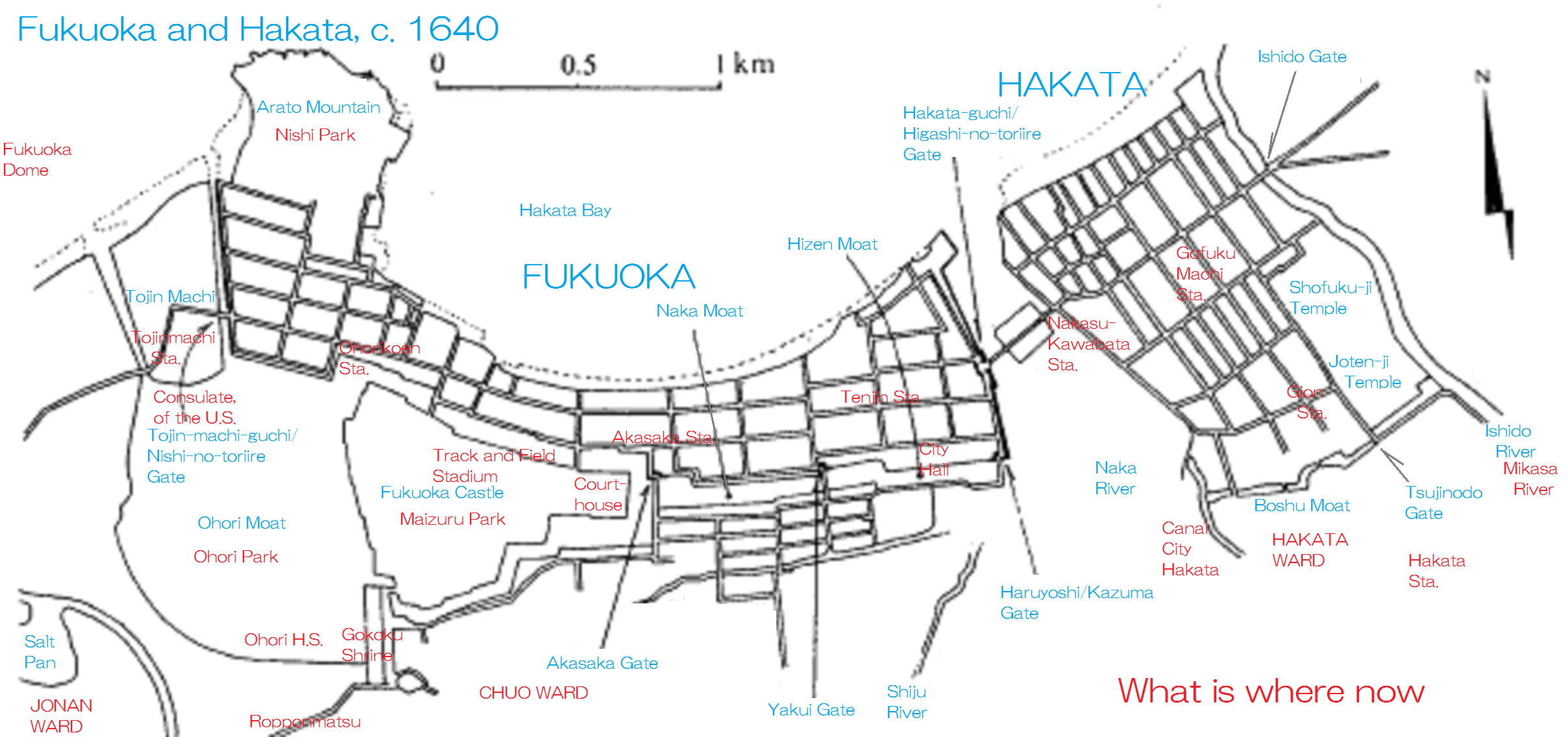
Fukuoka, Fukuoka
is the sixth-largest city in Japan, the second-largest port city after Yokohama, and the capital city of Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. The city is built along the shores of Hakata Bay, and has been a center of international commerce since ancient times. The area has long been considered the gateway to the country, as it is the nearest point among Japan's main islands to the Asian mainland. Although humans occupied the area since the Jomon period, some of the earliest settlers of the Yayoi period arrived in the Fukuoka area. The city rose to prominence during the Yamato period. Because of the cross-cultural exposure, and the relatively great distance from the social and political centers of Kyoto, Osaka, and later, Edo (Tokyo), Fukuoka gained a distinctive local culture and dialect that has persisted to the present. Fukuoka is the most populous city on Kyūshū island, followed by Kitakyushu. It is the largest city and metropolitan area west of Keihanshin. The city was des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakata Gion Yamakasa
is a Japanese festival celebrated from the 1st until the 15th of July in Hakata, Fukuoka. The festivities are centered on the Kushida Jinja. The festival is famous for the Kakiyama, that weigh around one ton and are carried around the city as an act of float-racing. The festival is believed to be over 770 years old and attracts up to a million spectators each year. It was designated an Important Intangible Folk Cultural Property of Japan in 1979. The sound of the Yamakasa has also been selected by the Ministry of the Environment as one of the 100 Soundscapes of Japan. Floats The floats, called Yamakasa, are divided into two groups. The Kakiyama are the smaller, carryable floats, that are raced through the town, while the Kazariyama are stationary floats, that are built up to 13 metres high and often depict historic or mythical events of Japanese culture. Originally the Kakiyama and Kazariyama were one and the same, with the large floats being carried through the city. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakata-ku, Fukuoka
is a ward of the city of Fukuoka in Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. Many of Fukuoka Prefecture and Fukuoka City's principal government, commercial, retail and entertainment establishments are located in the district. Hakata-ku is also the location of Fukuoka's main train station, Hakata Station, Fukuoka Airport and the Hakata Port international passenger ship terminal. Geography Hakata-ku is a ward of Fukuoka City located on its eastern edge. It is 31.47 km2 with a population of 206,629 (current January 1, 2009). Much of the ward consists of low-lying plains beside the . The northwestern end of the ward faces Hakata Bay, which includes both ferry and international cruise ship terminals . The northeast end of the ward is slightly elevated, and is named , with nearby Fukuoka Airport. Around Hakata Station is downtown; is the main dining and entertainment district of the ward along the . Hakata-ku also houses the Fukuoka Prefectural office. Economy Many Japanese companies have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2.7 million in the 2020 census, it is also the largest component of the Keihanshin Metropolitan Area, which is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan and the 10th largest urban area in the world with more than 19 million inhabitants. Osaka was traditionally considered Japan's economic hub. By the Kofun period (300–538) it had developed into an important regional port, and in the 7th and 8th centuries, it served briefly as the imperial capital. Osaka continued to flourish during the Edo period (1603–1867) and became known as a center of Japanese culture. Following the Meiji Restoration, Osaka greatly expanded in size and underwent rapid industrialization. In 1889, Osaka was officially established as a municipality. The construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all synonyms of one another: they are ''synonymous''. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words are considered synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, ''long'' and ''extended'' in the context ''long time'' or ''extended time'' are synonymous, but ''long'' cannot be used in the phrase ''extended family''. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms. Lexicograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention (norm)
A convention is a set of agreed, stipulated, or generally accepted standards, norms, social norms, or criteria, often taking the form of a custom. In a social context, a convention may retain the character of an "unwritten law" of custom (for example, the manner in which people greet each other, such as by shaking each other's hands). Certain types of rules or customs may become law and sometimes they may be further codified to formalize or enforce the convention (for example, laws that define on which side of the road vehicles must be driven). In outline of physical science, physical sciences, numerical values (such as constants, quantities, or scales of measurement) are called conventional if they do not represent a measured property of nature, but originate in a convention, for example an average of many measurements, agreed between the scientists working with these values. General A convention is a selection from among two or more alternatives, where the rule or alternativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negotiation
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more people or parties to reach the desired outcome regarding one or more issues of conflict. It is an interaction between entities who aspire to agree on matters of mutual interest. The agreement can be beneficial for all or some of the parties involved. The negotiators should establish their own needs and wants while also seeking to understand the wants and needs of others involved to increase their chances of closing deals, avoiding conflicts, forming relationships with other parties, or maximizing mutual gains. The goal of negotiation is to resolve points of difference, gain an advantage for an individual or collective, or craft outcomes to satisfy various interests. Distributive negotiations, or compromises, are conducted by putting forward a position and making concessions to achieve an agreement. The degree to which the negotiating parties trust each other to implement the negotiated solution is a major factor in determining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bargaining
In the social sciences, bargaining or haggling is a type of negotiation in which the buyer and seller of a good or service debate the price or nature of a transaction. If the bargaining produces agreement on terms, the transaction takes place. Although the most apparent aspect of bargaining in markets is as an alternative pricing strategy to fixed prices, it can also include making arrangements for credit or bulk purchasing, as well as serving as an important method of clienteling. Bargaining has largely disappeared in parts of the world where retail stores with fixed prices are the most common place to purchase goods. However, for expensive goods such as homes, antiques and collectibles, jewellery and automobiles, bargaining can remain commonplace. Dickering and "haggling" refer to the same process. Where it takes place Haggling is associated commonly with bazaars and other markets where centralized regulation is difficult or impossible. Both religious beliefs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |