|
Tasuku Honjo
is a Japanese physician-scientist and immunologist. He won the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and is best known for his identification of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). He is also known for his molecular identification of cytokines: IL-4 and IL-5, as well as the discovery of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) that is essential for class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation. He was elected as a foreign associate of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States (2001), as a member of German Academy of Natural Scientists Leopoldina (2003), and also as a member of the Japan Academy (2005). In 2018, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine along with James P. Allison. He and Allison together had won the 2014 Tang Prize in Biopharmaceutical Science for the same achievement. Life and career Honjo was born in Kyoto in 1942. He completed his M.D. degree in 1966 from the Faculty of Medicine, Kyoto Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin, Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the city had a population of 1.46 million. The city is the cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Kyoto, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 3.8 million people. Kyoto is one of the oldest municipalities in Japan, having been chosen in 794 as the new seat of Japan's imperial court by Emperor Kanmu. The original city, named Heian-kyō, was arranged in accordance with traditional Chinese feng shui following the model of the ancient Chinese capital of Chang'an/Luoyang. The emperors of Japan ruled from Kyoto in the following eleven centuries until 1869. It was the scene of several key events of the Muromachi period, Sengoku period, and the Boshin War, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren Alpert Foundation Prize
The Warren Alpert Foundation Prize is awarded annually to scientist(s) whose scientific achievements have led to the prevention, cure or treatment of human diseases or disorders, and/or whose research constitutes a seminal scientific finding that holds great promise of ultimately changing our understanding of or ability to treat disease. The prize was established in 1987 by the late philanthropist and businessman Warren Alpert and the Warren Alpert Foundation. The Warren Alpert Prize is given internationally and since its inception, 10 winners have gone on to win Nobel Prizes. The prize is administered in concert with Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts and the Warren Alpert Foundation, located in Providence, Rhode Island. An annual symposium is held at Harvard Medical School each fall where the recipient(s) present their work. The prize currently includes $500,000, a citation and plaque. Warren Alpert Foundation Prize Recipients See also * List of biomedical scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve ''pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
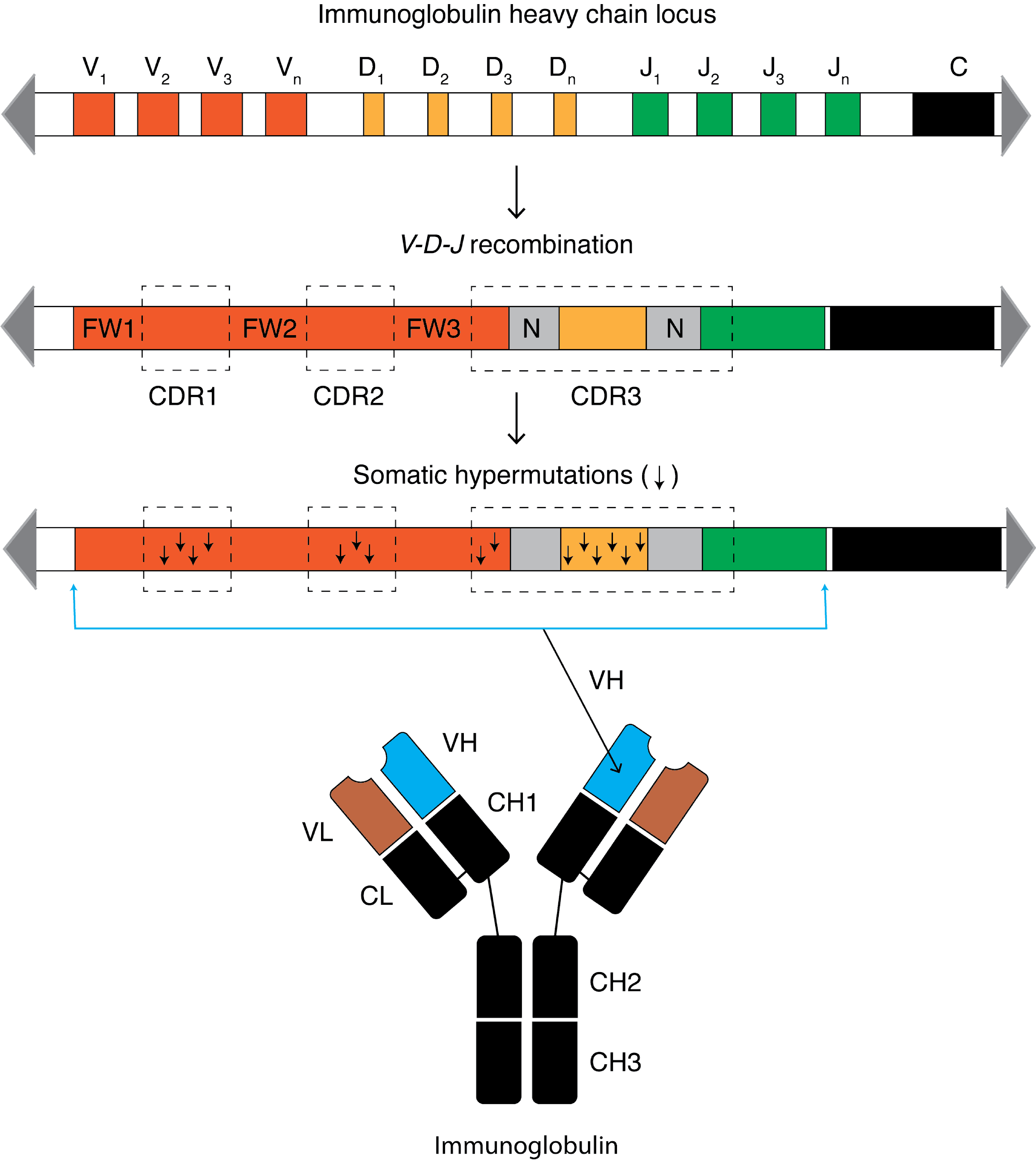
Somatic Hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes), as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM diversifies B cell receptors used to recognize foreign elements (antigens) and allows the immune system to adapt its response to new threats during the lifetime of an organism. Somatic hypermutation involves a programmed process of mutation affecting the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes. Unlike germline mutation, SHM affects only an organism's individual immune cells, and the mutations are not transmitted to the organism's offspring.Oprea, M. (1999''Antibody Repertoires and Pathogen Recognition:'' The Role of Germline Diversity and Somatic Hypermutation'' (Thesis) University of Leeds.'' Because this mechanism is merely selective and not precisely targeted, somatic hypermutation has been strongly implicated in the development of B-cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class Switch Recombination
Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the isotype IgM to the isotype IgG. During this process, the constant-region portion of the antibody heavy chain is changed, but the variable region of the heavy chain stays the same (the terms ''variable'' and ''constant'' refer to changes or lack thereof between antibodies that target different epitopes). Since the variable region does not change, class switching does not affect antigen specificity. Instead, the antibody retains affinity for the same antigens, but can interact with different effector molecules. Mechanism Class switching occurs after activation of a mature B cell via its membrane-bound antibody molecule (or B cell receptor) to generate the different classes of antibody, all with the same variable domains as the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase, also known as AICDA, AID and single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminase, is a 24 kDa enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ''AICDA'' gene. It creates mutations in DNA by deamination of cytosine base, which turns it into uracil (which is recognized as a thymine). In other words, it changes a C:G base pair into a U:G mismatch. The cell's DNA replication machinery recognizes the U as a T, and hence C:G is converted to a T:A base pair. During germinal center development of B lymphocytes, AID also generates other types of mutations, such as C:G to A:T. The mechanism by which these other mutations are created is not well understood. It is a member of the APOBEC family. In B cells in the lymph nodes, AID causes mutations that produce antibody diversity, but that same mutation process leads to B cell lymphoma. Function This gene encodes a DNA-editing deaminase that is a member of the cytidine deaminase family. The protein is involved in somat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine signaling, autocrine, paracrine signaling, paracrine and endocrine signaling as Immunomodulation, immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some growth factor#cytokine, overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as Endothelium, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Cell Death Protein 1
Programmed cell death protein 1, also known as PD-1 and CD279 (cluster of differentiation 279), is a protein on the surface of T and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's response to the cells of the human body by down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T cell inflammatory activity. This prevents autoimmune diseases, but it can also prevent the immune system from killing cancer cells. PD-1 is an immune checkpoint and guards against autoimmunity through two mechanisms. First, it promotes apoptosis (programmed cell death) of antigen-specific T-cells in lymph nodes. Second, it reduces apoptosis in regulatory T cells (anti-inflammatory, suppressive T cells). PD-1 inhibitors, a new class of drugs that block PD-1, activate the immune system to attack tumors and are used to treat certain types of cancer. The PD-1 protein in humans is encoded by the ''PDCD1'' gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the immunoglob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician-scientist
A physician-scientist is traditionally a holder of a medical degree and a doctor of philosophy also known as an MD-PhD. Compared to other clinicians, physician-scientists invest significant time and professional effort in scientific research and spend correspondingly less time in direct clinical practice with ratios of research to clinical time ranging from 50/50 to 80/20. Physician-scientists are often employed by academic or research institutions where they drive innovation across a wide range of medical specialties and may also use their extensive training to focus their clinical practices on specialized patient populations, such as those with rare genetic diseases or cancers. Although they are a minority of both practicing physicians and active research scientists, physician-scientists are often cited as playing a critical roles in translational medicine and clinical research by adapting biomedical research findings to health care applications. Over time, the term physician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shizuo Akira
(born January 27, 1953 in Higashiōsaka) is a professor at the Department of Host Defense, Osaka University, Japan. He has made ground-breaking discoveries in the field of immunology, most significantly in the area of innate host defense mechanisms. Education Shizuo Akira gained a M.D. in School of Medicine from Osaka University in 1977. In 1984 he earned a PhD from Osaka University. Till 1987, he did post-doctoral research at University of California, Berkeley. Research Besides being one of the world's most-cited scientists, he has also been recognised, in the years 2006 and 2007, for having published the greatest number of ‘Hot Papers’ (11 papers) over the preceding two years. He is the recipient of several international awards, including the Gairdner Foundation International Award (2011), Robert Koch Prize, the Milstein Award (2007), and the William B. Coley Award. Among his greatest discoveries is the demonstration, through the ablation of toll-like receptor (TLR)s gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)