|
Tanzanian Sign Languages
Around seven Tanzanian sign languages were developed independently among deaf students in separate Tanzanian schools for the deaf starting in 1963, though use of several are forbidden by their schools. In 1984, a standardized Tanzanian Sign Language was proposed by the Tanzania Association for the Deaf, using common or similar signs where these exist in the schools which allowed research, but it has not been officially implemented, and there remains little influence between the languages. A dictionary has been produced. Lexically, the variety that developed in the oralist deaf school in Tabora is significantly different from the dictionary, and is under investigation. The common Swahili term in Tanzania for these languages is ''lugha ya alama (ya Tanzania)'', lit. '(Tanzanian) sign language'. The term ''lugha ya bubu'' 'mute/dumb language' is also used, but is pejorative and offensive. References Sign language isolates Languages of Tanzania Endangered sign language isola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus ''Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of '' Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deaf-community Sign Language
A deaf-community or urban sign language is a sign language that emerges when deaf people who do not have a common language come together and form a community. This may be a formal situation, such as the establishment of a school for deaf students, or informal, such as migration to cities for employment and the subsequent gathering of deaf people for social purposes. An example of the first is Nicaraguan Sign Language, which emerged when deaf children in Nicaragua were brought together for the first time, and received only oral education; of the latter, Bamako Sign Language, which emerged among the tea circles of the uneducated deaf in the capital of Mali. Nicaraguan SL is now a language of instruction and is recognized as the national sign language; Bamako SL is not, and is threatened by the use of American Sign Language in schools for the deaf. Deaf-community sign languages contrast with village sign language in that they tend to be used only by the deaf, at least at first, and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language Isolates
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or medical symptoms a sign of disease. A conventional sign signifies by agreement, as a full stop signifies the end of a sentence; similarly the words and expressions of a language, as well as bodily gestures, can be regarded as signs, expressing particular meanings. The physical objects most commonly referred to as signs (notices, road signs, etc., collectively known as signage) generally inform or instruct using written text, symbols, pictures or a combination of these. The philosophical study of signs and symbols is called semiotics; this includes the study of semiosis, which is the way in which signs (in the semiotic sense) operate. Nature Semiotics, epistemology, logic, and philosophy of language are concerned about the nature of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
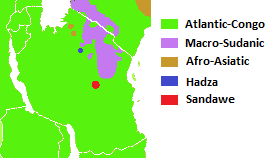
Languages Of Tanzania
Tanzania is a multilingual country. There are many languages spoken in the country, but no one language is spoken natively by a majority or a large plurality of the population. Swahili and English, the latter of which was inherited from colonial rule (''see Tanganyika Territory''), are widely spoken as lingua francas. They serve as working languages in the country, with Swahili being the official national language. There are more speakers of Swahili than of English in Tanzania. Overview According to ''Ethnologue'', there are a total of 126 languages spoken in Tanzania. Two are institutional, 18 are developing, 58 are vigorous, 40 are endangered, and 8 are dying. There are also three languages that recently became extinct. Most languages spoken locally belong to two broad language families: Niger-Congo ( Bantu branch) and Nilo-Saharan ( Nilotic branch), spoken by the country's Bantu and Nilotic populations, respectively. Additionally, the Hadza and Sandawe hunter-gatherers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |