|
Amrum M Suessen-3567-2
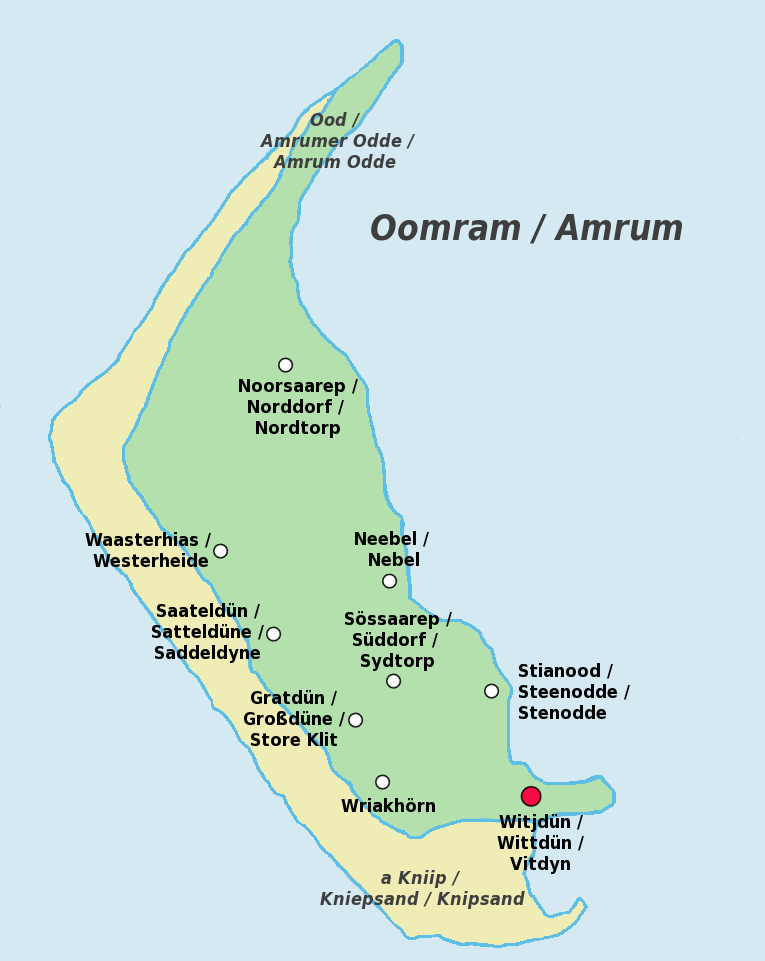
Amrum (; Öömrang, ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the Germany, German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants. The island is made up of a sandy core of geestland and features an extended beach all along its west coast, facing the open North Sea. The east coast borders to mudflats of the Wadden Sea. Sand dunes are a characteristic part of Amrum's landscape, resulting in a vegetation that is largely made up of heath and shrubs. The island's only forest was planted in 1948. Amrum is a refuge for many species of birds and a number of marine mammals including the grey seal and harbour porpoise. Settlements on Amrum have been traced back to the Neolithic period when the area was still a part of the mainland of the Jutland peninsula. During the Middle Ages, Frisians, Frisian settlers arrived at Amrum and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galiot
A galiot, galliot or galiote, was a small galley boat propelled by sail or oars. There are three different types of naval galiots that sailed on different seas. A ''galiote'' was a type of French flat-bottom river boat or barge and also a flat-bottomed boat with a simple sail for transporting wine. Naval vessels * Mediterranean, (16th–17th centuries) : Historically, a galiot was a type of ship with oars, also known as a half-galley, then, from the 17th century forward, a ship with sails and oars. As used by the Barbary pirates against the Republic of Venice, a galiot had two masts and about 16 pairs of oars. Warships of the type typically carried between two and ten cannons of small caliber, and between 50 and 150 men. It was a Barbary galiot, captained by Barbarossa I, that captured two Papal vessels in 1504. * North Sea (17th–19th centuries) : A galiot was a type of Dutch or German merchant ship of 20 to 400 tons ( bm), similar to a ketch, with a rounded fore and aft like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern History Of Germany
The German-speaking states of the early modern period (c. 1500–1800) were divided politically and religiously. Religious tensions between the states comprising the Holy Roman Empire had existed during the preceding period of the Late Middle Ages (c. 1250–1500)—notably erupting in Bohemia with the Hussite Wars (1419–1434). However, the defining religious movement of this period, the Reformation, would result in unprecedented levels of violence and political upheaval for the region. Usually considered to have begun with the publication of the ''Ninety-five Theses'' (1517) by Martin Luther in the city of Wittenberg (then within the Electorate of Saxony, now located within the modern German state of Saxony-Anhalt), the progression of the Reformation would divide the German states among new religious lines: the north, the east, and many of the major cities—Strasbourg, Frankfurt, and Nuremberg—becoming Protestant while the southern and western regions largely remained Catho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amrum M Suessen-4003
Amrum (; ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants. The island is made up of a sandy core of geestland and features an extended beach all along its west coast, facing the open North Sea. The east coast borders to mudflats of the Wadden Sea. Sand dunes are a characteristic part of Amrum's landscape, resulting in a vegetation that is largely made up of heath and shrubs. The island's only forest was planted in 1948. Amrum is a refuge for many species of birds and a number of marine mammals including the grey seal and harbour porpoise. Settlements on Amrum have been traced back to the Neolithic period when the area was still a part of the mainland of the Jutland peninsula. During the Middle Ages, Frisian settlers arrived at Amrum and engaged in salt making a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro
The euro ( symbol: €; code: EUR) is the official currency of 19 out of the member states of the European Union (EU). This group of states is known as the eurozone or, officially, the euro area, and includes about 340 million citizens . The euro is divided into 100 cents. The currency is also used officially by the institutions of the European Union, by four European microstates that are not EU members, the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, as well as unilaterally by Montenegro and Kosovo. Outside Europe, a number of special territories of EU members also use the euro as their currency. Additionally, over 200 million people worldwide use currencies pegged to the euro. As of 2013, the euro is the second-largest reserve currency as well as the second-most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar. , with more than €1.3 trillion in circulation, the euro has one of the highest combined values of banknotes and coins in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravestones In Amrum373
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, date of birth, and date of death inscribed on it, along with a personal message, or prayer, but may contain pieces of funerary art, especially details in stone relief. In many parts of Europe, insetting a photograph of the deceased in a frame is very common. Use The stele (plural stelae), as it is called in an archaeological context, is one of the oldest forms of funerary art. Originally, a tombstone was the stone lid of a stone coffin, or the coffin itself, and a gravestone was the stone slab that was laid over a grave. Now, all three terms are also used for markers placed at the head of the grave. Some graves in the 18th century also contained footstones to demarcate the foot end of the grave. This sometimes developed into full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelmine
The Wilhelmine Period () comprises the period of German history between 1890 and 1918, embracing the reign of Kaiser Wilhelm II in the German Empire from the resignation of Chancellor Otto von Bismarck until the end of World War I and Wilhelm's abdication during the November Revolution. It affected the society, politics, culture, art and architecture of Germany and roughly coincided with the Belle Époque era of Western Europe. Overview The term "Wilhelminism" (''Wilhelminismus'') is not meant as a conception of society associated with the name Wilhelm and traceable to an intellectual initiative of the German Emperor. Rather, it relates to the image presented by Wilhelm II and his demeanour, as manifested by the public presentation of grandiose military parades and self-aggrandisement on his part. The latter tendency had already been noticed by his grandfather, Emperor Wilhelm I, while the latter's father, later Frederick III, was Crown Prince. Wilhelminism also characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. The region is called ''Slesvig-Holsten'' in Danish and pronounced . The Low German name is ''Sleswig-Holsteen'', and the North Frisian name is ''Slaswik-Holstiinj''. In more dated English, it is also known as ''Sleswick-Holsatia''. Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Schleswig was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it escaped full control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary empire led by an emperor, although has been used in German to denote the Roman Empire because it had a weak hereditary tradition. In the case of the German Empire, the official name was , which is properly translated as "German Empire" because the official position of head of state in the constitution of the German Empire was officially a "presidency" of a confederation of German states led by the King of Prussia who would assume "the title of German Emperor" as referring to the German people, but was not emperor of Germany as in an emperor of a state. –The German Empire" ''Harper's New Monthly Magazine''. vol. 63, issue 376, pp. 591–603; here p. 593. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Schleswig War
The Second Schleswig War ( da, Krigen i 1864; german: Deutsch-Dänischer Krieg) also sometimes known as the Dano-Prussian War or Prusso-Danish War was the second military conflict over the Schleswig-Holstein Question of the nineteenth century. The war began on 1 February 1864, when Prussian and Austrian forces crossed the border into the Danish fief Schleswig. Denmark fought the Kingdom of Prussia and the Austrian Empire. Like the First Schleswig War (1848–1852), it was fought for control of the duchies of Schleswig, Holstein and Lauenburg. Succession disputes concerning the duchies arose when the Danish king died without an heir acceptable to the German Confederation. The war started after the passing of the History of Schleswig-Holstein#The November Constitution, November Constitution of 1863, which tied Duchy of Schleswig more closely to the Denmark, Danish kingdom, which was viewed by the German side as a violation of the London Protocol (1852), London Protocol. The war en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales. Terminology The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japan, still dedicates a single factory ship for the industry. The vessels used by aboriginal whaling communities are much smaller and are used for various purposes over the course of the year. The ''whale catcher'' was developed during the age of steam, and then driven by diesel engines throughout much of the twentieth century. It was designed with a harpoon gun mounted at its bow and was fast enough to chase and catch rorquals such as the fin whale. At first, whale catchers either brought the whales they killed to a whaling station, a settlement ashore where the carcasses could be processed, or to its factory ship anchored in a sheltered bay or inlet. With the later development of the slipway at the ship's stern, whale catchers were able ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |