|
TNNC1
Troponin C, also known as TN-C or TnC, is a protein that resides in the troponin complex on actin thin filaments of striated muscle (cardiac, fast-twitch skeletal, or slow-twitch skeletal) and is responsible for binding calcium to activate muscle contraction. Troponin C is encoded by the ''TNNC1'' gene in humans for both cardiac and slow skeletal muscle. Structure Cardiac troponin C (cTnC) is a 161-amino acid protein organized into two domains: the regulatory N-terminal domain (cNTnC, residues 1-86), the structural C-terminal domain (cCTnC, residues 93-161), and a flexible linker connecting the two domains (residues 87-92). Each domain contains two EF-hands, Ca2+-binding helix-loop-helix motifs exemplified by proteins like parvalbumin and calmodulin. In cCTnC the two EF-hand motifs constitute two high affinity Ca2+-binding sites. that are occupied at all physiologically relevant calcium concentrations. In contrast, only the second EF-hand in cNTnC binds Ca2+ with low affinity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D145E
D145E is a point mutation on troponin C that leads to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disease. This mutation is caused by the change of nucleotide C to A at nucleotide 435, switching the amino acid aspartic acid to glutamic acid, which is located at the C-terminal The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ... tail. Patients with this mutation have different structure on the thin filament and alter the binding of Ca2+ at the troponin C site IV. Further, D145E causes increase in development of force and activation of ATPase in the presence of Ca2+. References Mutation Troponin {{Gene-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
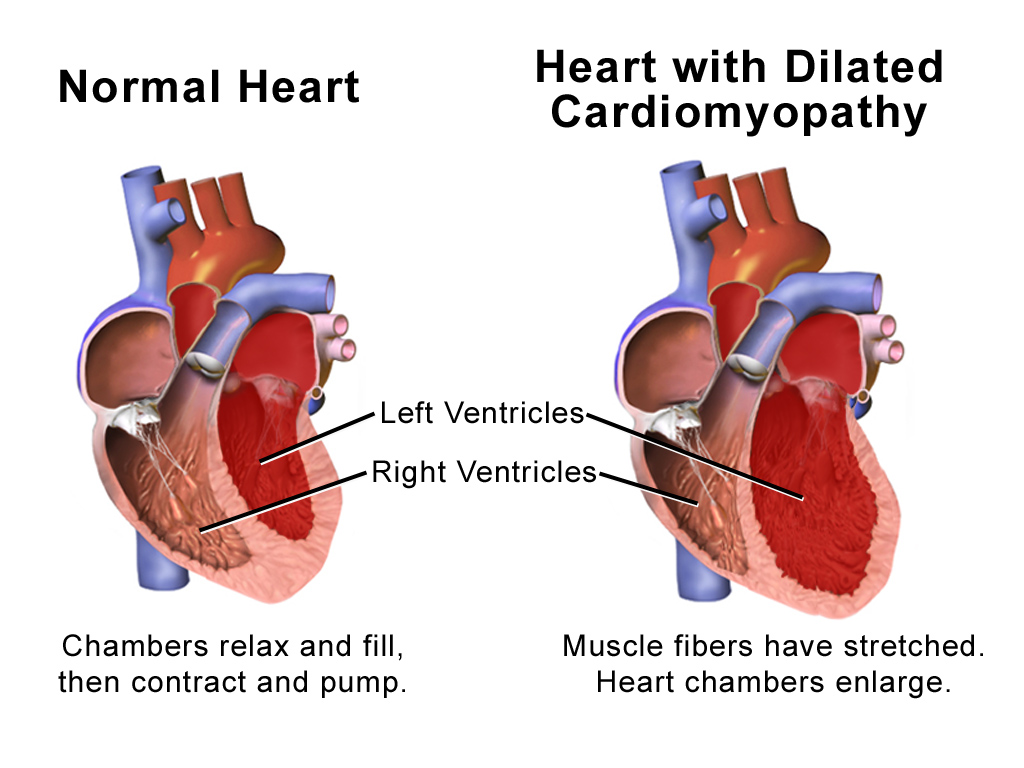
Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EF-hand
The EF hand is a helix–loop–helix structural domain or ''motif'' found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins. The EF-hand motif contains a helix–loop–helix topology, much like the spread thumb and forefinger of the human hand, in which the Ca2+ ions are coordinated by ligands within the loop. The motif takes its name from traditional nomenclature used in describing the protein parvalbumin, which contains three such motifs and is probably involved in muscle relaxation via its calcium-binding activity. The EF-hand consists of two alpha helices linked by a short loop region (usually about 12 amino acids) that usually binds calcium ions. EF-hands also appear in each structural domain of the signaling protein calmodulin and in the muscle protein troponin-C. Calcium ion binding site The calcium ion is coordinated in a pentagonal bipyramidal configuration. The six residues involved in the binding are in positions 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 12; these residues are denoted b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send blood to the larger, lower ventricle chambers. This flow fills the ventricles with blood, and the resulting pressure closes the valves to the atria. The ventricles now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bepridil
Bepridil (trade name Vascor) is an diamine calcium channel blocker once used to treat angina pectoris. It is no longer sold in the United States. It is nonselective. It has been discussed as a possible option in the treatment of atrial fibrillation. It has been implicated in causing ventricular arrhythmia (torsades de pointes). Ebola research In June 2015 a research paper was published finding bepridil to result in a 100% survival rate for mice exposed to ebola during an experiment searching for potential pharmaceutical ebola treatments; indicating its potential use in future ebola research and therapy. SARS-CoV-2 research A research paper showed that Bepridil inhibited cytopathogenic effects induced by SARS-CoV-2 Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a ... in Vero E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resveratrol
Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-''trans''-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts. Although commonly used as a dietary supplement and studied in laboratory models of human diseases, there is no high-quality evidence that resveratrol improves lifespan or has a substantial effect on any human disease. Research Resveratrol has been studied for its potential therapeutic use, with little evidence of anti-disease effects or health benefits in humans. Cardiovascular disease There is no evidence of benefit from resveratrol in people who already have heart disease. A 2018 meta-analysis found no effect on systolic or diastolic blood pressure; a sub-analysis revealed a 2 mmHg decrease in systolic pressure only from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levosimendan
Levosimendan (INN) is a calcium sensitizer used in the management of acutely decompensated congestive heart failure. It is marketed under the trade name Simdax (Orion Corporation). Overall the drug has a two fold mechanism of action. It leads to greater ionotrophy by increasing the calcium sensitivity as it binds to Troponin and this results in a greater positive iontrophic force. Secondly, the drug is able to open ATP sensitive potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells, and the vascular dilatory effects of the drug lead to a decreased pre-load and afterload, putting less work on the heart. This drug is in the process of review by the FDA but has not been approved yet. Mechanism of action Levosimendan is a calcium sensitizer — it increases the sensitivity of the heart to calcium, thus increasing cardiac contractility without a rise in intracellular calcium. Levosimendan exerts its positive inotropic effect by increasing calcium sensitivity of myocytes by binding to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed during embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma. Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long, fibrous tail and a globular head, which binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to ATP, which is the source of energy for muscle movement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventricular Septum
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior interventricular sulci. The lower part of the septum, which is the major part, is thick and muscular, and its much smaller upper part is thin and membraneous. During each cardiac cycle the interventricular septum contracts by shortening longitudinally and becoming thicker. Structure The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another. The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior longitudinal sulci. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which the heart becomes thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited from a person's parents in an autosomal dominant pattern. It is often due to mutations in certain genes involved with making heart muscle proteins. Other inherited causes of left ventricular hypertrophy may include Fabry disease, Friedreich's ataxia, and certain me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)