|
THIQ
THIQ is a drug used in scientific research, which is the first non-peptide agonist developed that is selective for the melanocortin receptor subtype MC4. In animal studies, THIQ stimulated sexual activity in rats, but with little effect on appetite or inflammation. This supports possible application of MC4 selective agonists for the treatment of sexual dysfunction in humans, although THIQ itself has poor oral bioavailability and a short duration of action so improved analogues will need to be developed. See also * Bremelanotide * Melanotan II * PL-6983 * PF-00446687 PF-00446687 is a drug developed by Pfizer for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, which is a non-peptide agonist selective for the melanocortin receptor subtype MC4. It was found to be active in preliminary human trials, with the 200mg do ... References Erectile dysfunction drugs Female sexual dysfunction drugs Melanocortin receptor agonists Triazoles Piperidines Propionamides Chloroarenes Tet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydroisoquinolines
Tetrahydroisoquinoline (TIQ or THIQ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C9H11N. Classified as a secondary amine, it is derived from isoquinoline by hydrogenation. It is a colorless viscous liquid that is miscible with most organic solvents. The tetrahydroisoquinoline skeleton is encountered in a number of bioactive compounds and drugs. Reactions As a secondary amine, tetrahydroisoquinoline has weakly basic properties and forms salts with strong acids. It can be dehydrogenated to give isoquinoline and hydrogenated to decahydroisoquinoline. Like other secondary amines, tetrahydroisoquinoline can be oxidized to the corresponding nitrone using hydrogen peroxide, catalyzed by selenium dioxide. Toxicology Tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives may be formed in the body as metabolites of some drugs, and this was once thought to be involved in the development of alcoholism. This theory has now been discredited and is no longer generally accepted by the scientific community, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin Receptor
Melanocortin receptors are members of the rhodopsin family of 7-transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors. There are five known members of the melanocortin receptor system each with differing specificities for melanocortins: * . MC1R is associated with pigmentation genetics. * . MC2R is also known as the ACTH receptor or corticotropin receptor because it is specific for ACTH alone. * . MC3R is associated with childhood growth, accrual of lean mass and onset of puberty. * . Defects in MC4R are a cause of autosomal dominant obesity, accounting for 6% of all cases of early-onset obesity. * . MC5R These receptors are inhibited by endogenous inverse agonists agouti signalling peptide and agouti-related peptide, and activated by synthetic (i.e. afamelanotide) and endogenous agonist melanocyte-stimulating hormones. Selective ligands Several selective ligands for the melanocortin receptors are known, and some synthetic compounds have been investigated as potential tanning, anti-obesity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin 4 Receptor
Melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) is a melanocortin receptor that in humans is encoded by the gene. It encodes the MC4R protein, a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH). In mouse models, MC4 receptors have been found to be involved in feeding behaviour, the regulation of metabolism, sexual behaviour, and male erectile function. Clinical significance In 2009, two very large genome-wide association studies of body mass index (BMI) confirmed the association of variants about 150 kilobases downstream of the ''MC4R'' gene with insulin resistance, obesity, and other anthropometric traits. ''MC4R'' may also have clinical utility as a biomarker for predicting individual susceptibility to drug-induced adverse effects causing weight gain and related metabolic abnormalities. Another GWAS performed in 2012 identified twenty SNPs located ~190 Kb downstream of ''MC4R'' in association with severe antipsychotic-induced weight gain. This ''locus'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
Bremelanotide
Bremelanotide, sold under the brand name Vyleesi, is a medication used to treat low sexual desire in women. Specifically it is used for low sexual desire which occurs before menopause and is not due to medical problems, psychiatric problems, or problems within the relationship. It is given by an injection just under the skin of the thigh or abdomen. Common side effects include nausea, pain at the site of injection, and headache. It may also cause a temporary increase in blood pressure and decrease in heart rate after each dose, and darkening of the gums, face, and breasts. The medication is a peptide and acts by activating the melanocortin receptors. Bremelanotide was approved for medical use in the United States in 2019. It was developed by Palatin Technologies. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication. Medical uses Bremelanotide is used for the treatment of generalized hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in premenopa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanotan II
Melanotan II is a synthetic analogue of the peptide hormone α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) that stimulates melanogenesis and increases sexual arousal. It was under development as drug candidate for female sexual dysfunction and erectile dysfunction but clinical development ceased by 2003, and as of 2018, no product containing melanotan II was marketed and all commercial development had ceased. Unlicensed, untested, or fraudulent products sold as "melanotan II" are found on the Internet, and purported to be effective as "tanning drugs", though side effects such as uneven pigmentation (it makes already uneven pigmentation more noticeable), new nevi (moles), and darkening or enlargement of existing moles have been reported and have led to medical authorities discouraging its use. There has been no scientific study into the long term and permanent side effects the use of this peptide may cause. Mechanism of action Melanotan II acts as a non-selective agonist of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PL-6983
PL-6983 is a synthetic peptide and selective MC4 receptor agonist which is under development by Palatin Technologies for the treatment of female sexual dysfunction and erectile dysfunction. It was developed as a successor to/replacement of bremelanotide (PT-141) due to concerns of the side effect of increased blood pressure seen with the latter in clinical trials. Relative to bremelanotide, PL-6983 produces significantly lower increases in blood pressure in animal models. The drug has reportedly been in pre-clinical development for all medical indications since 2008. Palatin has stated that "We are focusing development efforts on bremelanotide for emale sexual dysfunction but are continuing evaluation of PL-6983." The chemical structure A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PF-00446687
PF-00446687 is a drug developed by Pfizer for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, which is a non-peptide agonist selective for the melanocortin receptor subtype MC4. It was found to be active in preliminary human trials, with the 200mg dose being of similar effectiveness to 100mg sildenafil, though lower doses were ineffective. While it is unclear whether PF-00446687 itself will be potent and effective enough to be developed for medical use, it has demonstrated that selectively targeting the MC4 subtype can produce similar aphrodisiac effects to older non-selective peptide-based melanocortin receptor agonists like melanotan II and bremelanotide, without the side effects caused by action at the other melanocortin receptor subtypes. See also * PL-6983 * PF-219,061 PF-219,061 is a drug that was under development by Pfizer which acts as a potent and highly selective agonist for the dopamine D3 receptor. It was under development as a potential medication for the tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erectile Dysfunction Drugs
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body with numerous vascular spaces, or cavernous tissue, that may become engorged with blood. However, tissue that is devoid of or otherwise lacking erectile tissue (such as the labia minora, the vestibule/vagina and the urethra) may also be described as engorging with blood, often with regard to sexual arousal. In the clitoris and penis Erectile tissue exists in places such as the corpora cavernosa of the penis, and in the clitoris or in the bulbs of vestibule. During erection, the corpora cavernosa will become engorged with arterial blood, a process called ''tumescence''.Chapter 35 in: This may result from any of various physiological stimuli, also known as sexual arousal. The corpus spongiosum is a single tubular structure located just below the corpora cavernosa. This may also become slightly engorged with blood, but less so than the corpora cavernosa. In the nose Erectile tissue is present in the anterior part of the nasal septum and is atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female Sexual Dysfunction Drugs
Female (symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction. A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes, unlike isogamy where they are the same size. The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown. In species that have males and females, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Female characteristics vary between different species with some species having pronounced secondary female sex characteristics, such as the presence of pronounced mammary glands in mammals. In humans, the word ''female'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Etymology and usage The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin Receptor Agonists
The melanocortins are a family of neuropeptide hormones which are the ligands of the melanocortin receptorsEricson, M.D., et al., ''Bench-top to clinical therapies: A review of melanocortin ligands from 1954 to 2016.'' Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2017. 1863(10 Pt A): p. 2414-2435. The melanocortin system consists of melanocortin receptors, ligands, and accessory proteins. The genes of the melanocortin system are found in chordates. Melanocortins were originally named so because their earliest known function was in melanogenesis. It is now known that the melanocortin system regulates diverse functions throughout the body, including inflammatory response, fibrosis, melanogenesis, steroidogenesis, energy homeostasis, sexual function, and exocrine gland function. There are four endogenous melanocortin agonists which are derived from post-transcriptional processing of the precursor molecule proopiomelanocortin (POMC) (Figure 1). They are Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), a-mel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
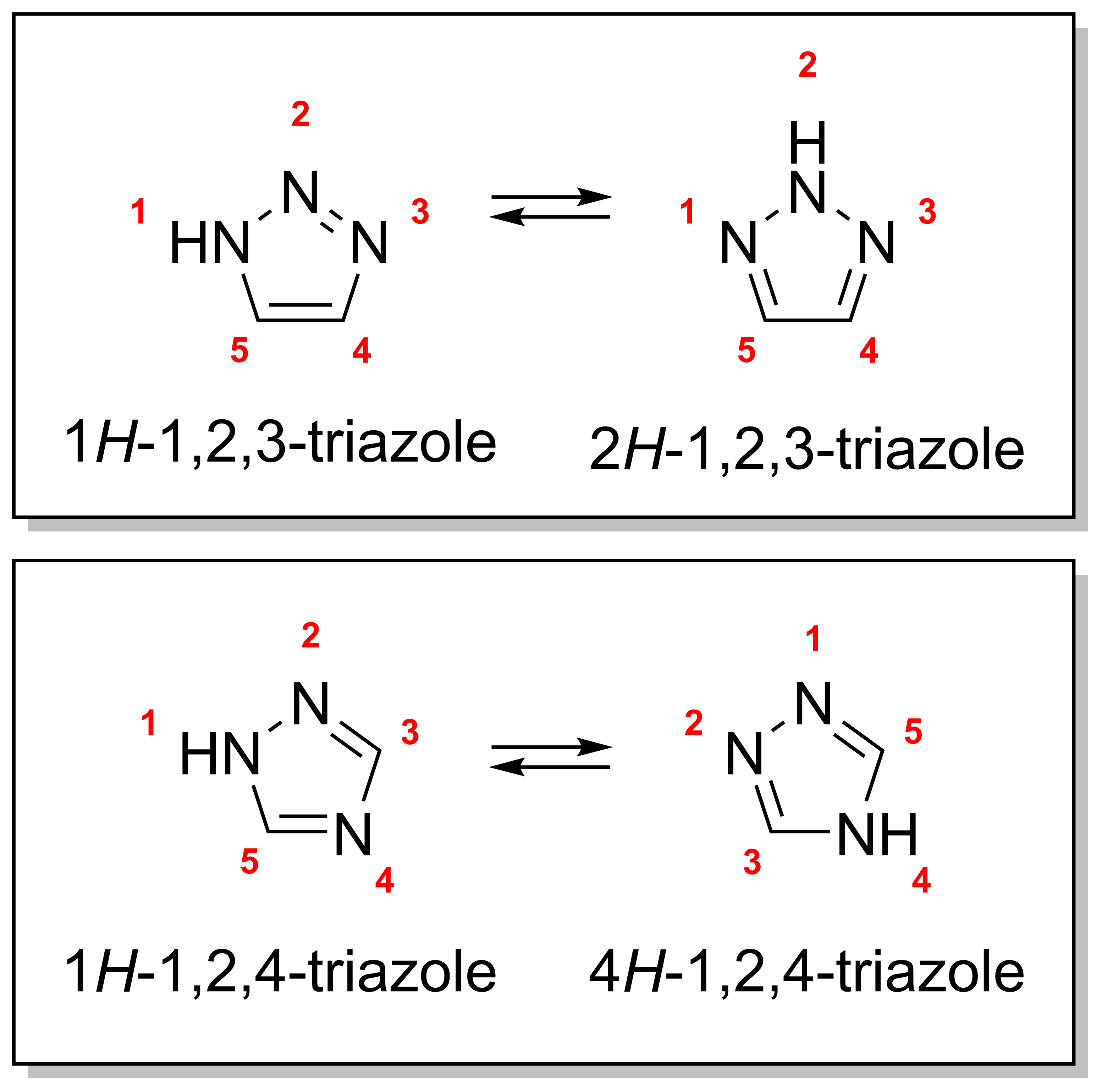
Triazoles
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of tautomers. In the 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category has two tautomers that differ by which nitrogen has a hydrogen bonded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |