|
Tập Đình
Tập Đình ( vi-hantu, 集亭, ?–?) was a general during the Tây Sơn Rebellion. Born Li A-chi () in Chaozhou, Guangdong, Qing China. He went to Qui Nhơn in 1759, and became a merchant there.鄭永瑞, 《試論越南華人在「新舊阮之爭」中所扮演的角色》 After the Tay Son rebellion broke out, he organized an army named ''Trung Nghĩa Quân'' (忠義軍, "Loyal Army") to join in the rebellion.''Việt Nam sử lược'', Quyển 2, Chương 8 He was granted the title Tập Đình Hầu (集亭侯, "Marquess of Tập Đình"), which later became his nick name. The members in this army wore their hair in the Manchu style, though some of them were not Chinese. In battles, they were drunk and bare-chested, and combated bravery.'' Đại Nam chính biên liệt truyện'', vol. 30 The army of Trịnh lord marched south in 1775. Tập Đình fought against Trịnh army together with Lý Tài and Nguyễn Nhạc, but was defeated in Cẩm Sa (a place in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trịnh Lord
Trịnh is a Vietnamese family name, which is also common in some countries such as Korea (Jung, Jeong). A considerable portion of families that bear the surname Trinh are ethnically Vietnamese. Notable people *Trịnh Như Khuê, First Cardinal of the Catholic Church of Vietnam, Archbishop of Archdiocese of Hanoi *Trịnh Văn Căn, Second Cardinal of Catholic Church of Vietnam, Archbishop of Archdiocese of Hanoi * Eugene Huu Chau Trinh, the first Vietnamese-American astronaut *Trinh Xuan Thuan, Big Bang theorist/scientist *Trịnh Công Sơn, Vietnamese musician *Trinh T. Minh-ha, filmmaker *Trịnh lords, family who ruled Northern Vietnam for more than 100 years *François Trinh-Duc, French rugby union player of Vietnamese descent *Trang Trịnh, Vietnamese pianist See also *Chung (Korean surname) *Zheng (surname) Zheng or zhèng ( Hanyu Pinyin) or Cheng ( Wade-Giles) () is a Chinese surname and also the name of an ancient state in today's Henan province. It is written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
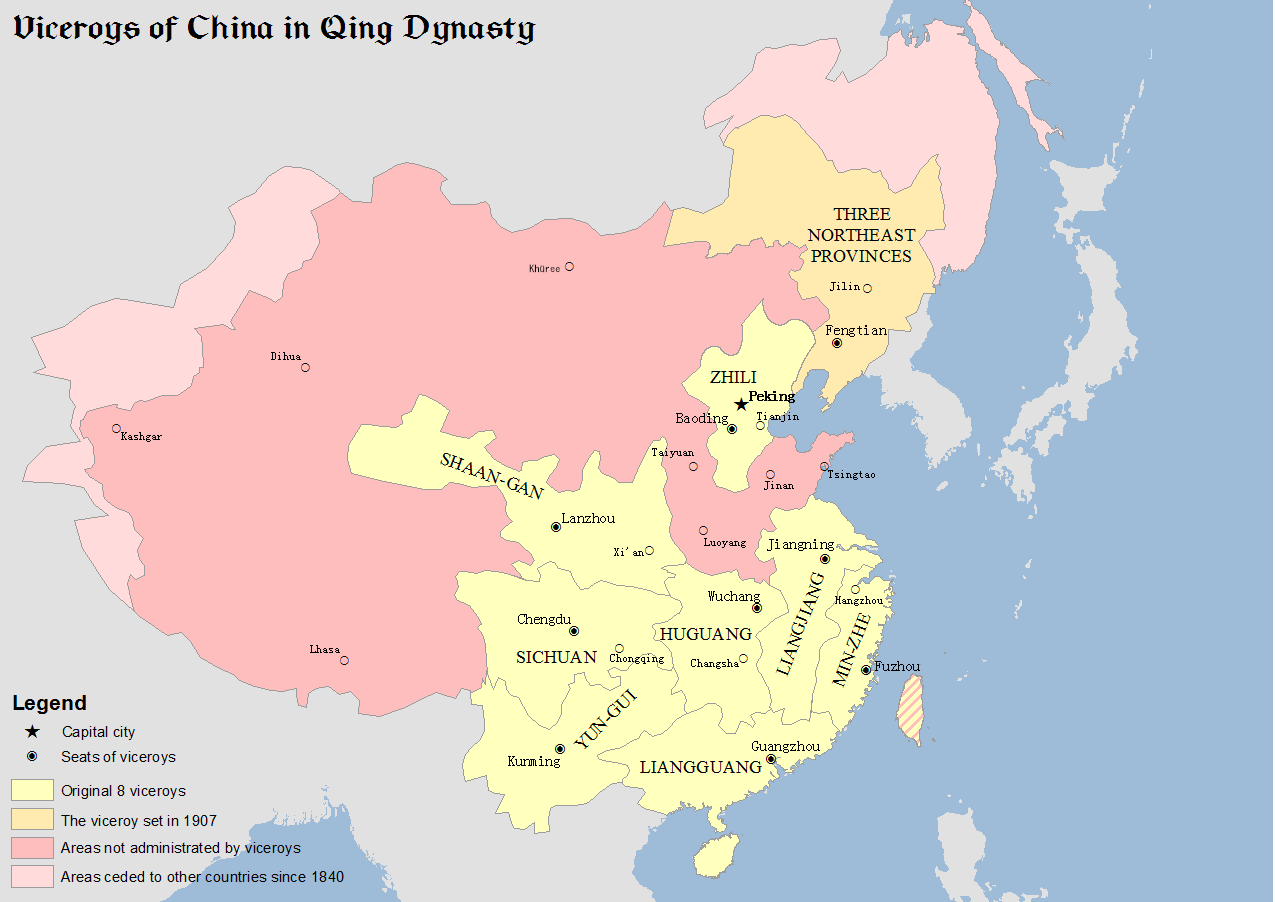
Viceroy Of Liangguang
The Viceroy of Liangguang or Viceroy of the Two Guangs, was one of eight regional Viceroys during the Ming and Qing dynasties. The two ''Guang'' referred to Guangdong and Guangxi provinces. The areas under the Viceroy's jurisdiction included present-day Guangdong and Guangxi provinces, as well as Hainan Province. Name Its full name in Chinese is Governor-General, Commander and Quartermaster, Supervisor of Waterways, and Inspector-General of the Two Expanses and Surrounding Areas. History Ming dynasty The office of the Viceroy of Liangguang originated in 1452 during the Ming dynasty. The Jingtai Emperor accepted Yu Qian's proposal to create the office and appointed Wang Ao (王翱) as the first viceroy. In 1465, the Chenghua Emperor appointed Han Yong (韓雍) as Left Censor-in-Chief and Viceroy of Liangguang. The office was formalised in 1469, with the administrative headquarters fixed in Wuzhou, Guangxi. In 1536, during the reign of the Jiajing Emperor, the viceroy Qia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Nhạc
Nguyễn Nhạc ( vi-hantu, 阮岳, died 1793) was the founder of the Tây Sơn dynasty, reigning from 1778 to 1788. From 1778 to 1788, Nguyễn Nhạc proclaimed himself Emperor Thái Đức ( vi-hantu, 泰德). In 1788 after his younger brother proclaimed himself Emperor Quang Trung, Nguyễn Nhạc resigned his Emperor title and declared himself as King of Tây Sơn. Nguyễn Nhạc and his brothers, namely Nguyễn Lữ and Nguyễn Huệ, known as the Tây Sơn Brothers, ended the centuries-long civil war between the two feudal families, the Trịnh Lords in northern Vietnam and the Nguyễn Lords in southern Vietnam, seizing reigning power from these groups and the Lê dynasty. Early life Born in Tây Sơn District, Quy Nhơn Province (modern Bình Định Province). Vietnamese historian Trần Trọng Kim described him as a courageous and clever man. He had two younger brothers: Nguyễn Lữ and Nguyễn Huệ. Their talents are highly appreciated by their martial ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lý Tài
Lý Tài ( vi-hantu, 李才, Wade–Giles: ''Li Tsai'', ?–1777) was a general during the Tây Sơn Rebellion. Lý was a Chinese merchant. After the Tay Son rebellion broke out, he organized an army named ''Hòa Nghĩa Quân'' (和義軍, "Harmony Army") to join in the rebellion. All members of this army was from Qing China in Chinese costume. The Trịnh lords, who ruled the northern half of the country, sent a large army to attack in 1775, which forced Nguyen king Nguyễn Phúc Thuần to flee to Quảng Nam. Nguyễn Phúc Dương, who was the crown prince of Nguyen, was captured by Lý Tài, and taken to Hội An. Dương was used by Tay Son rebels to gain popularity among Southern Vietnameses. The Tay Son army was defeated by Trinh lord in Cẩm Sa (a place in mordern Hòa Vang District, Quảng Nam). Meanwhile, Nguyễn Phúc Thuần entrenched himself in the south and tried to regain the lost territory. Nguyễn Nhạc had to be reconciled with Trinh, and direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaozhou
Chaozhou (), alternatively Chiuchow, Chaochow or Teochew, is a city in the eastern Guangdong province of China. It borders Shantou to the south, Jieyang to the southwest, Meizhou to the northwest, the province of Fujian to the east, and the South China Sea to the southeast. It is administered as a prefecture-level city with a jurisdiction area of and a total population of 2,568,387. Its built-up (or metro) area encompassing most of Shantou and Jieyang cities was home to 12,543,024 inhabitants on 13 local administrative areas. Along with Shantou and Jieyang, Chaozhou is a cultural center of the Chaoshan region. History In 214 BC, Chaozhou was an undeveloped part of Nanhai Commandery () of the Qin Dynasty. In 331 during the Eastern Jin Dynasty, Haiyang () was established as a part of Dongguan Commandery (). The Dongguan Commandery was renamed Yi'an Commandery () in 413. The commandery became a prefecture in 590 during the early Sui Dynasty, first as Xun Prefecture (), then as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Đại Nam Thực Lục
''Đại Nam thực lục'' ( vi-hantu, 大南寔錄, lit. "Veritable Records of the Great South", "Annals of Đại Nam", "Chronicle of Greater Vietnam") was the official history of Nguyễn dynasty, Vietnam. It contained the royal records of the Nguyễn lords, and the imperial annals of Nguyễn dynasty emperors up until Khải Định. Just like other official histories, ''Đại Nam thực lục'' was written in Classical Chinese. The annals comprised 584 volumes. At first the records were called "''Đại Nam thật lục''" "". During Thiệu Trị's reign however, "" was changed to "", and its pronunciation changed to "thực", because "實" was against the naming taboo of Empress Tá Thiên, Thiệu Trị's mother. ''Đại Nam thực lục'' was the most important primary source regarding the Nguyễn dynasty. It was an important reference of Cao Xuân Dục's ''Quốc triều chính biên toát yếu'' and Trần Trọng Kim's ''Việt Nam sử lược''. History of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queue (hairstyle)
A queue or cue is a hairstyle that was worn by the Jurchen and Manchu peoples of Manchuria, and was later required to be worn by male subjects of Qing China. Hair on top of the scalp is grown long and is often braided, while the front portion of the head is shaved. The distinctive hairstyle led to its wearers being targeted during anti-Chinese riots in Australia and the United States. The requirement that Han Chinese men and others under Manchu rule give up their traditional hairstyles and wear the queue was met with resistance, although opinions about the queue did change over time. Han women were never required to wear their hair in the traditional women's Manchu style, liangbatou, although that too was a symbol of Manchu identity. In the 18th century, both soldiers and sailors of western nations wore their hair pulled back into a queue, but the fashion was abandoned at the start of the next century. Predecessors and origin The Xianbei and Wuhuan were said to shave their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |