|
Tyrannosauroid
Tyrannosauroidea (meaning 'tyrant lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that includes the family Tyrannosauridae as well as more basal relatives. Tyrannosauroids lived on the Laurasian supercontinent beginning in the Jurassic Period. By the end of the Cretaceous Period, tyrannosauroids were the dominant large predators in the Northern Hemisphere, culminating in the gigantic ''Tyrannosaurus''. Fossils of tyrannosauroids have been recovered on what are now the continents of North America, Europe and Asia, with fragmentary remains possibly attributable to tyrannosaurs also known from South America and Australia. Tyrannosauroids were bipedal carnivores, as were most theropods, and were characterized by numerous skeletal features, especially of the skull and pelvis. Early in their existence, tyrannosauroids were small predators with long, three-fingered forelimbs. Late Cretaceous genera became much larger, including some of the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaraptora
Megaraptora is a clade of carnivorous tetanuran theropod dinosaurs with controversial relations to other theropods. Its derived members, the Megaraptoridae are noted for their elongated hand claws and proportionally large arms, which are usually reduced in size in other large theropods. Megaraptorans are incompletely known, and no complete megaraptoran skeleton has been found. However, they still possessed a number of unique features. Their forelimbs were large and strongly built, and the ulna bone had a unique shape in members of the family Megaraptoridae, a subset of megaraptorans which excludes ''Fukuiraptor'' and ''Phuwiangvenator''. The first two fingers were elongated, with massive curved claws, while the third finger was small. Megaraptoran skull material is very incomplete, but a juvenile ''Megaraptor'' described in 2014 preserved a portion of the snout, which was long and slender. Leg bones referred to megaraptorans were also quite slender and similar to those of coeluro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
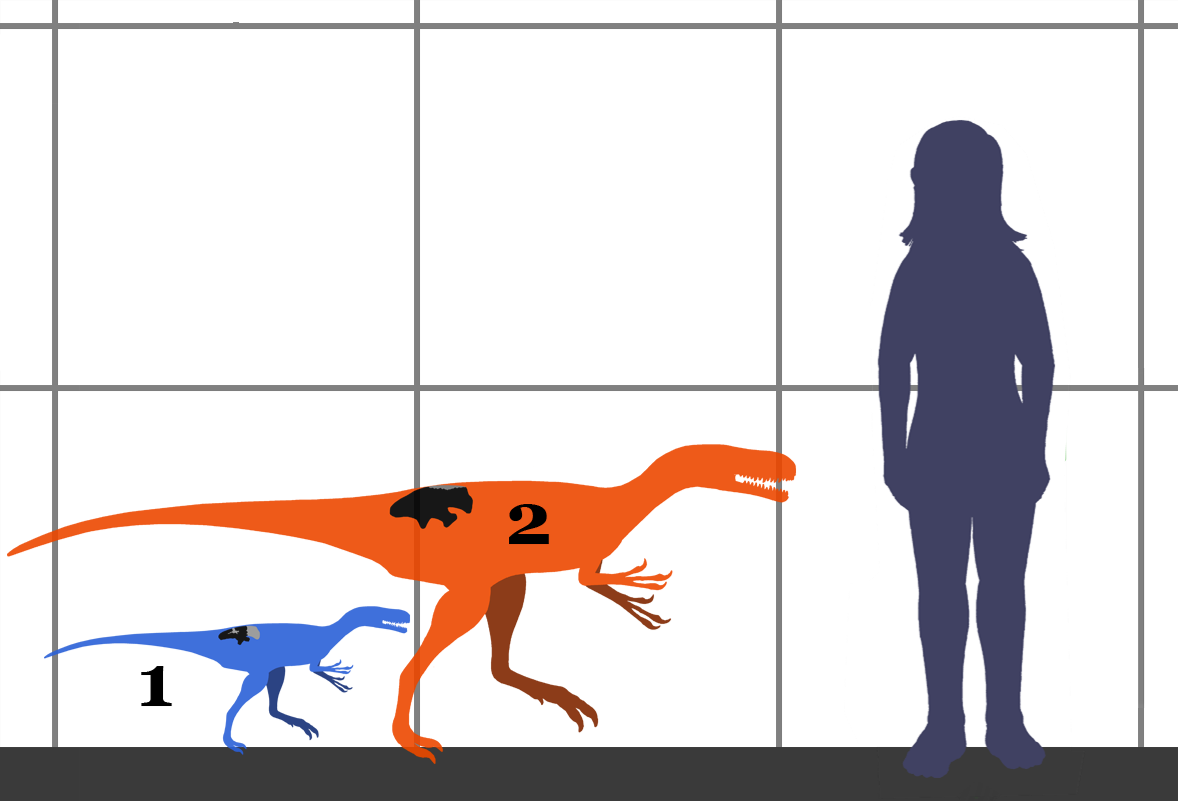
Dilong Paradoxus
''Dilong'' (帝龍, which means 'emperor dragon') is a genus of basal tyrannosauroid dinosaur. The only species is ''Dilong paradoxus''. It is from the Lower Cretaceous Yixian Formation near Lujiatun, Beipiao, in the western Liaoning province of China. It lived about 126 million years ago. Discovery ''Dilong'' was described by Xu Xing and colleagues in 2004. The name is derived from the Chinese 帝 ''dì'' meaning 'emperor' and 龙 / 龍 ''lóng'' meaning 'dragon'. "Di", "emperor", refers to the relationship of this animal to ''Tyrannosaurus rex'', the "king" tyrannosaurid. "Long" is used to name Chinese dinosaurs in much the same way that the Latin ''-saur'' is in the West. The specific name, ''paradoxus'', is a Latinisation of the Ancient Greek παράδοξον meaning 'against received wisdom'. Description The type specimen is IVPP 14243 (Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology in Beijing), a nearly complete, semi-articulated, skull and skeleton. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alectrosaurus
''Alectrosaurus'' (; meaning "alone lizard") is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about some 96 million years ago in what is now the Iren Dabasu Formation. It was a medium-sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, estimated at with a body shape similar to its much larger advanced relative, ''Tyrannosaurus''. ''Alectrosaurus'' was a very fast running tyrannosauroid as indicated by the elongated hindlimbs that likely filled the niche of a pursuit predator, a trait that seems to be lost by the advanced and robust tyrannosaurids, in adulthood. Discovery and naming In 1923, the Third Asiatic Expedition of the American Museum of Natural History, led by chief paleontologist Walter W. Granger, was hunting for dinosaur fossils in Mongolia. On April 25 in the gobi desert, assistant paleontologist George Olsen excavated and recovered the holotype AMNH 6554, a nearly complete right hindlimb. This include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eotyrannus
''Eotyrannus'' (meaning "dawn tyrant") is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur hailing from the Early Cretaceous Wessex Formation beds, included in Wealden Group, located in the southwest coast of the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom. The remains (MIWG1997.550), consisting of assorted skull, axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton elements, from a juvenile or subadult, found in a plant debris clay bed, were described by Hutt ''et al.'' in early 2001. The etymology of the generic name refers to the animal's classification as an early tyrannosaur or "tyrant lizard", while the specific name honors the discoverer of the fossil. Discovery and naming The exact location of the discovery of the holotype specimen has not been revealed due to its importance and the possibility of new material to be collected as the coastline recedes. From what is mentioned in the description, the specimen was found on the southwestern coast of the Isle of Wight, between Atherfield Point and Hanover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosaurus Rex
''Tyrannosaurus'' is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' (''rex'' meaning "king" in Latin), often called ''T. rex'' or colloquially ''T-Rex'', is one of the best represented theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. ''Tyrannosaurus'' had a much wider range than other tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of rock formations dating to the Maastrichtian age of the Upper Cretaceous period, 68 to 66 million years ago. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids and among the last non- avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Like other tyrannosaurids, ''Tyrannosaurus'' was a bipedal carnivore with a massive skull balanced by a long, heavy tail. Relative to its large and powerful hind limbs, the forelimbs of ''Tyrannosaurus'' were short but unusually powerful for their size, and they had t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teihivenator
This list of informally named dinosaurs is a listing of dinosaurs (excluding Aves; birds and their extinct relatives) that have never been given formally published scientific names. This list only includes names that were not properly published ("unavailable names") and have not since been published under a valid name (see list of dinosaur genera for valid names). The following types of names are present on this list: * ''Nomen nudum'', Latin for "naked name": A name that has appeared in print but has not yet been formally published by the standards of the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature. ''Nomina nuda'' (the plural form) are invalid, and are therefore not italicized as a proper generic name would be. * '' Nomen manuscriptum'', Latin for "manuscript name": A name that appears in manuscript but was not formally published. A ''nomen manuscriptum'' is equivalent to a ''nomen nudum'' for everything except the method of publication, and description. * '' Nomen ex d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokesosaurus
''Stokesosaurus'' (meaning "Stokes' lizard") is a genus of small (around in length), carnivorous early tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the late Jurassic period of Utah, United States. History From 1960 onwards Utah geologist William Lee Stokes and his assistant James Henry Madsen excavated thousands of disarticulated ''Allosaurus'' bones at the Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry in Emery County, Utah. During the early 1970s, Madsen began to catalogue these finds in detail, discovering that some remains represented species new to science. In 1974 Madsen named and described the type species ''Stokesosaurus clevelandi''. Its generic name honours Stokes. The specific name refers to the town of Cleveland, Utah. The holotype ( UMNH 2938, also known as UMNH VP 7473 and formerly known as UUVP 2938) was uncovered in the Brushy Basin Member of the Morrison Formation dating from the early Tithonian stage, about 150 million years old. It consists of a left ilium or hip bone, bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juratyrant
''Juratyrant'' (meaning "Jurassic tyrant") is a tyrannosauroid dinosaur genus from the late Jurassic period (early Tithonian age) of England. The genus contains a single species, ''Juratyrant langhami'', which was once classed as a species of ''Stokesosaurus''. Discovery The species is known from a single specimen consisting of an "associated partial skeleton represented by a complete pelvis" as well as a partially complete leg and neck, back and tail vertebrae. This skeleton was discovered in 1984 in Dorset. The specimen was mentioned in several papers, but was not formally described until 2008. The species was named in honor of commercial fossil collector Peter Langham, who uncovered the specimen. The specimen was discovered in strata of the Kimmeridge Clay dating from the Tithonian, the final stage of the Late Jurassic, and belonging to the ''Pectinatites pectinatus'' ammonite zone, indicating the fossil is between 149.3 and 149 million years old. Description Paul (2010) l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moros Intrepidus
''Moros'' is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now Utah, United States. It contains a single species, ''M. intrepidus''. ''Moros'' represents one of the earliest known diagnostic tyrannosauroid material from the North America. Discovery and naming ''Moros'' was first discovered at the Stormy Theropod site located in Emery County in the U.S. state of Utah. Palaeontologists had been researching the area for ten years when in 2013 limb bones were seen jutting out of a hillside, prompting the excavation. The bones were described as of a new species in February, 2019. In 2019, the type species ''Moros intrepidus'' was named and described by Lindsay E. Zanno, Ryan T. Tucker, Aurore Canoville, Haviv M. Avrahami, Terry A. Gates and Peter J. Makovicky. The generic name is derived from the Greek ''Moros'' (an embodiment of impending doom), in reference to the establishment of the tyrannosauroid lineage in North America. The specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceratosauridae
Proceratosauridae is a family or clade of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Distinguishing features Unlike the advanced tyrannosaurids but similar to primitive tyrannosauroids like ''Dilong'', proceratosaurids were generally small (with the exception of the possible proceratosaurids '' Yutyrannus'' and '' Sinotyrannus'') and had fairly long, three-fingered arms capable of grasping prey. In comparison to other members of Tyrannosauroidea, proceratosaurids can be distinguished by the following features according to phylogenetic analyses by Averianov ''et al''. (2010) and Loewen ''et al''. (2013) : * A sagittal cranial crest formed by the nasals starting at the junction of the premaxilla and nasals. * Extremely elongated external nares, with posterior margins posterior to the anterior margin of the antorbital fossa and maxillary fenestrae. * A short ventral margin of the premaxilla. * The depth of the antorbital fossa ventral to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suskityrannus
''Suskityrannus'' (meaning "coyote tyrant", ''suski'' meaning "coyote" in Zuni) is a genus of small tyrannosauroid theropod from the Late Cretaceous in southern Laramidia. It contains a single species, ''Suskityrannus hazelae,'' believed to have lived roughly 92 million years ago. The type specimen was found in the Turonian-age Moreno Hill Formation of the Zuni Basin in western New Mexico. Discovery and naming First mentioned as a small dromaeosaurid by Wolfe and Kirkland in their description of ''Zuniceratops'', ''Suskityrannus'' was informally referred to as the "Zuni coelurosaur", "Zuni tyrannosaur", and by the 2011 documentary ''Planet Dinosaur'' "Zunityrannus" prior to its scientific description. The original fossils were found by Robert Denton, a professional geologist from Virginia, and a native Mesa teen Sterling Nesbitt, who was a museum volunteer that came to a dig with paleontologist Doug Wolfe. In 2019 ''Suskityrannus'' was formally described as a genus of primit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviatyrannis
''Aviatyrannis'' is a genus of carnivorous tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur from the Oxfordian-Tithonian stages of the Late Jurassic found in Portugal. Discovery and naming In 2000 Oliver Walter Mischa Rauhut reported the find of tyrannosauroid material in the lignite coal mine of Guimarota near Leiria, which he referred to ''Stokesosaurus''. Later concluding the distinctiveness of the material justified a separate genus, Rauhut in 2003 named and described it as the type species ''Aviatyrannis jurassica''. The species name was by Rauhut given the intended meaning of "tyrant's grandmother from the Jurassic". The generic name is derived from Latin ''avia'', "grandmother", and ''tyrannus'', "tyrant", on the presumption ''tyrannis'' would be its genitive. The specific name means "Jurassic". The holotype, IPFUB Gui Th 1, was found in a layer of the Alcobaça Formation dating from the early Kimmeridgian, about 155 million years old. It consists of a right ilium. Rauhut in 2003 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |