|
Tyranneutes Stolzmanni
The dwarf tyrant-manakin or dwarf tyranneutes (''Tyranneutes stolzmanni'') is a species of bird in the family Pipridae. Distribution and habitat It is found throughout most of the Amazon Basin, except the area east of the Rio Negro. Rarely found at the edges of the forest, it prefers being at the mid-strata level deep in the forest. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...s. Description The dwarf tyrant-manakin is dull olive above, but lightens to a yellow-olive below. It has a short tail. Behavior These birds rarely move, but produce a distinctive two-note call, which readily identifies them. References dwarf tyrant-manakin Birds of the Amazon Basin dwarf tyrant-manakin Taxonomy articles crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Eduard Hellmayr
Carl Eduard Hellmayr (29 January 1878 in Vienna, Austria – 24 February 1944 in Orselina, Switzerland) was an Austrian ornithologist. Biography Hellmayr was born in Vienna and studied at the University of Vienna, although he did not complete his degree. After his studies he worked in Vienna, Munich, Berlin, Paris, Tring (England), and Chicago. He spent the years 1905–1908 studying Baron Rothschild's private collection of natural history specimens at Tring, near London. There he received guidance from the German ornithologist Ernst Hartert. In 1908, Hellmayr was appointed Curator of the Bird Department at the Bavarian State Museum, which he had helped organize in 1903 and where he became a specialist in Neotropical birds, studying Johann Baptist von Spix's collection of Brazilian birds. In 1922, he was made Curator in Zoology at the Field Museum in Chicago. He stayed there until 1931. His books included 13 of the 15 volumes of the ''Catalogue of Birds of the Americas'' (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipridae
The manakins are a family, Pipridae, of small suboscine passerine birds. The group contains some 54 species distributed through the American tropics. The name is from Middle Dutch ''mannekijn'' "little man" (also the source of the different bird name '' mannikin''). Description Manakins range in size from and in weight from . Species in the genus ''Tyranneutes'' are the smallest manakins, those in the genus ''Antilophia'' are believed to be the largest (since the genus ''Schiffornis'' are no longer considered manakins). They are compact stubby birds with short tails, broad and rounded wings, and big heads. The bill is short and has a wide gap. Females and first-year males have dull green plumage; most species are sexually dichromatic in their plumage, the males being mostly black with striking colours in patches, and in some species having long, decorative tail or crown feathers or erectile throat feathers. In some species, males from two to four years old have a distinctive sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
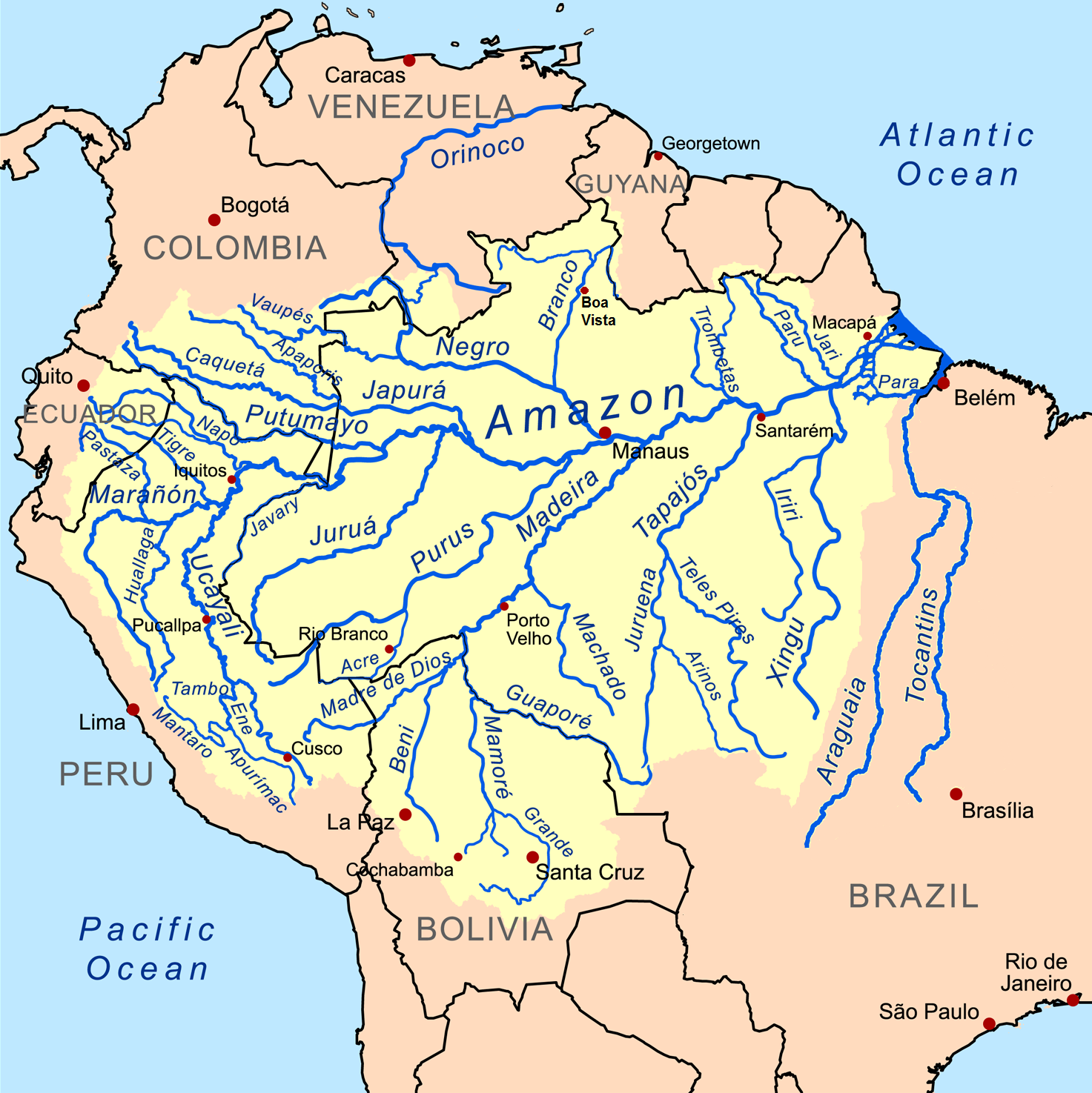
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Negro (Amazon)
The Rio Negro ( pt, Rio Negro, br ; es, Río Negro} "''Black River''"), or Guainía as it is known in its upper part, is the largest left tributary of the Amazon River (accounting for about 14% of the water in the Amazon basin), the largest blackwater river in the world, and one of the world's ten largest rivers by average discharge. Geography Upper course The source of the Rio Negro lies in Colombia, in the Department of Guainía where the river is known as the ''Guainía River''. The young river generally flows in an east-northeasterly direction through the Puinawai National Reserve, passing several small indigenous settlements on its way, such as Cuarinuma, Brujas, Santa Rosa and Tabaquén. After roughly 400 km the river starts forming the border between Colombia's Department of Guainía and Venezuela's Amazonas State. After passing the Colombian community of Tonina and Macanal the river turns Southwest. Maroa is the first Venezuelan town the river passes. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical zone#Temperate zones, temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost. Most subtropical climates fall into two basic types: humid subtropical climate, humid subtropical (Köppen climate classification, Koppen climate Cfa), where rainfall is often concentrated in the warmest months, for example list of regions of China, Southeast China and the Southeastern United States, and Mediterranean climate, dry summer or Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification, Koppen climate Csa/Csb), where seasonal rainfall is concentrated in the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). In terms of climate, the tropics receive sunlight that is more direct than the rest of Earth and are generally hotter and wetter as they aren't affected as much by the solar seasons. The word "tropical" sometimes refers to this sort of climate in the zone rather than to the geographical zone itself. The tropical zone includes deserts and snow-capped mountains, which are not tropical in the climatic sense. The tropics are distinguished from the other climatic and biomatic regions of Earth, which are the middle latitudes and the polar regions on either side of the equatorial zone. The tropics constitute 40% of Earth's surface area and contain 36% of Earth's landmass. , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland. Definitions Upland and lowland are portions of plain that are conditionally categorized by their elevation above the sea level. Lowlands are usually no higher than , while uplands are somewhere around to . On unusual occasions, certain lowlands such as the Caspian Depression lie below sea level. Upland habitats are cold, clear and rocky whose rivers are fast-flowing in mountainous areas; lowland habitats are warm with slow-flowing rivers found in relatively flat lowland areas, with water that is frequently colored by sediment and organic matter. These classifications overlap with the geological definitions of "upland" and "lowland". In geology an "upland" is generally considered to be land that is at a higher elevation than the alluvial plain or stream terrace, which are considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyranneutes
''Tyranneutes'' is a genus of South American birds in the family Pipridae. Both genders somewhat resemble females of other manakins, but are even smaller. They are native to the humid forests in the Amazon and the Guianas. The two species are entirely allopatric Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from ... (their distributions separated by major rivers). Etymology ''Tyranneutes'': gr, τυραννευω ''turanneuō'' “to be a tyrant”, from τυραννος ''turannos'' “tyrant”. Species References * Restall, R. L., Rodner, C., & Lentino, M. (2006). ''Birds of Northern South America.'' Christopher Helm, London. (vol. 1). (vol. 2). Bird genera Taxa named by Philip Sclater Taxa named by Osbert Salvin Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Piprida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of The Amazon Basin
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Birds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)