|
Type II Hair Keratin
Hair keratin is a type of keratin found in hair and nails. There are two types of hair keratin: * the acidic In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a ... ''type I hair keratin'' ** type I hair keratin 1, ** type I hair keratin 2, ** type I hair keratin 3A, ** type I hair keratin 3B, ** type I hair keratin 4, ** type I hair keratin 5, ** type I hair keratin 6, ** type I hair keratin 7, ** type I hair keratin 8, * the basic ''type II hair keratin'' ** type II hair keratin 1, ** type II hair keratin 2, ** type II hair keratin 3, ** type II hair keratin 4, ** type II hair keratin 5, ** type II hair keratin 6, External links * * Keratins {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT37
Keratin 37 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT37 gene. KRT37 is a member of the keratin gene family. Clinical significance KRT37 is the only keratin that is regulated by androgens. This sensitivity to androgens was acquired by Homo sapiens and is not shared with their great ape cousins. Although Winter et al. found that KRT37 is expressed in all the hair follices of chimpanzees, it was not detected in the head hair of modern humans. As androgens are known to grow hair on the body but decrease it on the scalp, this lack of scalp KRT37 may help explain the paradoxical nature of Androgenic alopecia Pattern hair loss (also known as androgenetic alopecia (AGA)) is a hair loss condition that primarily affects the top and front of the scalp. In male-pattern hair loss (MPHL), the hair loss typically presents itself as either a receding front ha ... as well as the fact that head hair anagen cycles are extremely long. Moreover, variations in the gene may account for et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT85
Keratin, type II cuticular Hb5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT85'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. As a type II hair keratin, it is a basic protein which heterodimerizes with type I keratins to form hair and nails. The type II hair keratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q13 and are grouped into two distinct subfamilies based on structure similarity. One subfamily, consisting of KRTHB1, KRTHB3, and KRTHB6, is highly related. The other less-related subfamily includes KRTHB2, KRTHB4, and KRTHB5. References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT84
KRT84 is a keratin gene, for a type II hair keratin Hair keratin is a type of keratin found in hair and nails. There are two types of hair keratin: * the acidic ''type I hair keratin'' ** type I hair keratin 1, ** type I hair keratin 2, ** type I hair keratin 3A, ** type I hair keratin 3B, ** ... contained primarily in the filiform tongue papilla. {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT83
Keratin 83, also known as KRT83, is a protein which humans is encoded by the ''KRT83'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. As a type II hair keratin, it is a basic protein which heterodimerizes with type I keratins to form hair and nails. The type II hair keratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q13 and are grouped into two distinct subfamilies based on structure similarity. One subfamily, consisting of KRTHB1 (KRT81), KRTHB3 (KRT83, this protein), and KRTHB6 (KRT86), is highly related. The other less-related subfamily includes KRTHB2 (KRT82), KRTHB4 (KRT84), and KRTHB5 (KRT85). All hair keratins are expressed in the hair follicle; this hair keratin, as well as KRTHB1 and KRTHB6, is found primarily in the hair cortex. Clinical significance Mutations in the ''KRT83'' gene have been associated with monilethrix Monilethrix (also referred to as beaded hair) is a rare autosomal dominant hair disease that results in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT82
KRT82 is a keratin Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ... gene. This is a type II keratin and appears to be a hair cuticle-specific. References {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT81
Keratin, type II cuticular Hb1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT81'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. As a type II hair keratin, it is a basic protein which heterodimerizes with type I keratins to form hair and nails. The type II hair keratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q13 and are grouped into two distinct subfamilies based on structure similarity. One subfamily, consisting of KRTHB1, KRTHB3, and KRTHB6, is highly related. The other less-related subfamily includes KRTHB2, KRTHB4, and KRTHB5. All hair keratins are expressed in the hair follicle; this hair keratin, as well as KRTHB3 and KRTHB6, is found primarily in the hair cortex. Mutations in this gene a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. They are slippery to the touch, can taste bitter and change the color of pH indicators (e.g., turn red litmus paper blue). In water, by altering the autoionization equilibrium, bases yield solutions in which the hydrogen ion activity is lower than it is in pure water, i.e., the water has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT38 gene.
{{Cytoskeletal proteins ...
KRT38 is a keratin Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT36
Keratin, type I cuticular Ha6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT36'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. This type I hair keratin is an acidic protein which heterodimerizes with type II keratins to form hair and nails. The type I hair keratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 17q12-q21 and have the same direction of transcription. References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
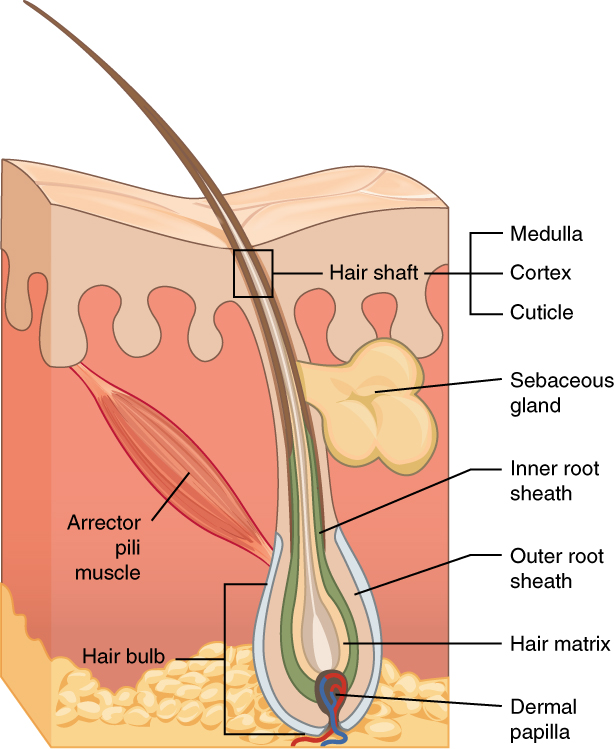
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls out, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT35
Keratin, type I cuticular Ha5 is a keratin Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ... protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT35'' gene. References {{Cytoskeletal proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |