|
Tynagh
Tynagh () is a village and electoral division in south-east County Galway in Ireland. The village is in a townland and civil parish of the same name. Origin of the name Recorded as ''Tyneaach'' (1565), ''Teacneaghe'' (1543), ''Theaneac'' (1541), its current name is a contraction of Teach nEachach, 'Eochu's house'. In medieval Irish sources it is referred to as Teach nEachach, or 'the house of Eochu'. It was originally associated with the townland of Lecarrow, one mile east of the village, now named a Billew Burial Ground, the word Billew derived from ''Bileadha'', plural of ''bile'', denoting a sacred tree. The element ''Eachach'' refers to Dagda, the supreme deity of the pagan Irish. He is cited as the father of the founder of the church, Brandubh of Tynagh. This suggests that Tynagh was originally a cult centre for the festival of Lughnasa, later Christianised by Brandubh, who was cited as Lugh's son, thus betraying its true origins. Geographic area and notable industry F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brandubh Of Tynagh
Brandubh of Tynagh, fl. c. 500 AD, Irish missionary. Brandubh is listed the Irish genealogies as ''Brandamh Tighe nEathach m. Eachach m. Ainmireach m. Aengusa m. Lomáin'' (Brandugh of Tynagh son of Eochu son of Ainmire son of Aonghus son of Lomáin'). He founded the church of Tynagh sometime around 500 AD. Evidence suggests that Tynagh was originally a cult centre for the festival of Lughnasa, later Christianised by Brandubh, who was cited as Lugh's son, thus betraying its true origins. From about the 8th to the 17th centuries the region Tynagh is located was known as Síol Anmchadha. See also * Conainne * St Connell * Kerrill * Téach * Martyrology of Tallaght References * ''The Christian impact on early Ireland;placename evidence'', Deirdre Flannagan in ''Irland un Europa'', ed. P Ni Cathain and Michael Richter, Stuttgart, 1984, pp. 25–51. * ''Early Ecclesiastical Settlement Names of County Galway'', Dónall Mac Giolla Easpaig Dónall Mac Giolla Easpaig, M.A., is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallas Castle
Pallas Castle is a tower house and National Monument located in County Galway, Ireland. According to ''visitgalway.ie'', it is "one of the best-preserved examples of a tower house in Ireland", surrounded as it is by a bawn wall with four corner towers and a gatehouse. Location Pallas Castle is located to the west of Pallas House, south of Tynagh, 1.6 km (1 mile) north of the Duniry River. History The castle was built by the Burkes c. 1500. In 1574 it was owned by Jonyck Fitzthomas Burke, but after the restoration it passed to the Nugent Earls of Westmeath. Near the tower at the west end, there is a rectangular flanker, an 18th-century malt house and the remains of a large 17th-century gabled house. Some buildings in the southwest corner probably date from the 19th century. The Burke family name lives on with the Burke family descendants living down the road and in surrounding areas. Building The tower is 5 storeys high, with the third storey vaulted. The thick en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loughrea
Loughrea ( ; ), is a town in County Galway, Ireland. It lies to the north of a range of wooded hills, the Slieve Aughty Mountains and Lough Rea, the lake from which it takes its name. The town's cathedral, St Brendan's, dominates the urban skyline. The town is in a townland and civil parish of the same name. The town increased in population in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Although Loughrea serves as a commuter town for the city of Galway, it remains an independent market town. Loughrea is the fourth most populous settlement in County Galway, with a population of 6,322 as of 2022. Name The town takes its name from Lough Rea, ( being a variant of meaning grey or speckled). It is situated on the northern shore of the lake. The lake's Irish name is used in the name of the local Irish-language multi-faith primary school: Gaelscoil Riabhach. The town is located within an area that was historically called Trícha Máenmaige, and a barony called Loughrea. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dónall Mac Giolla Easpaig
Dónall Mac Giolla Easpaig, M.A., is the former Chief Placenames Officer in the Placenames Branch in the Department of Community, Equality and Gaeltacht Affairs (''An Roinn Gnóthaí Pobail, Comhionannais agus Gaeltachta'') in Ireland. He is a leading authority on Irish placenames. Select bibliography * "Aspects of variant word order in Early Irish." ''Ériu'' 31 (1980). pp. 28–38. * "Noun + noun compounds in Irish placenames." ''Études Celtiques ''Études Celtiques'' (EC) (, ''Celtic studies, Celtic Studies'') is a French academic journal based in Paris. It started life under the name ''Revue Celtique'', which was founded in 1870 by Henri Gaidoz. Between 1870 and 1934, 52 volumes were p ...'' 18 (1981). pp. 151–163. * "Lough Neagh and Tynagh Revisited." '' Ainm'' 1 (1986). pp. 14–40. * "The place-names of Rathlin Island." ''Ainm'' 4 (1989). pp. 3–89. * "Placenames and early settlement in county Donegal." In ''Donegal: History and Society'', edite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns And Villages In The Republic Of Ireland
This is a link page for cities, towns and villages in the Republic of Ireland, including townships or urban centres in Dublin, Cork, Limerick, Galway, Waterford and other major urban areas. Cities are shown in bold; see City status in Ireland for an independent list. __NOTOC__ A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y See also * List of places in Ireland ** List of places in the Republic of Ireland **List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland as defined by the Central Statistics Office. Includes non-municipal towns and suburbs outside municipal boundaries *** List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland/2011 census *** List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland/2006 census *** List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland/2002 census ** List of cities, boroughs and towns in the Republic of Ireland, with municipal councils and legally defined boundaries up to 2014 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
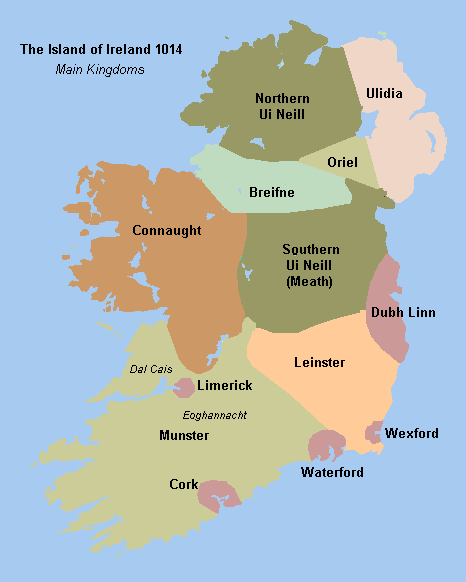
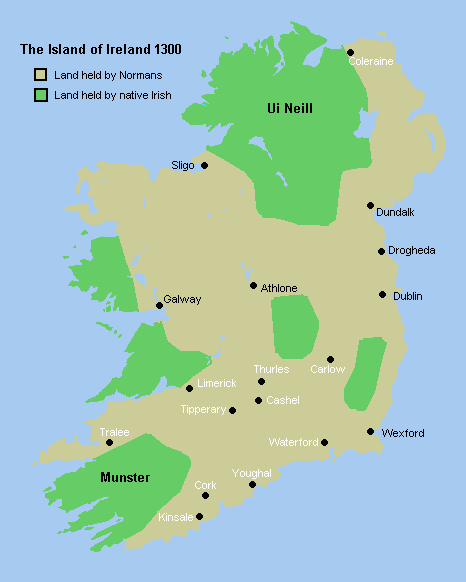
Síol Anmchadha
Síol Anmchadha () was a sub-kingdom or lordship of Uí Maine, and ruled by an offshoot of the Uí Maine called the Síol Anmchadha (''"the seed of Anmchadh"''), from whom the territory took its name. It was located in Connacht, Ireland. History At its largest extent, the Kings of Síol Anmchadha ruled all the land on the west shore of Lough Derg (Shannon) as far south as Thomond; the land between the Shannon and Suck rivers; and a corridor of land, known as Lusmagh, across the Shannon in Munster, in the direction of Birr. It was centred around the barony of Longford. The ruling dynasty later took the surname Ó Madadháin, anglicised as Maddan or Madden. In the later medieval era, they were sometimes vassals of the Earls of Ulster and their successors, the Clanricardes. Legacy In 1651, after the area had been incorporated into the Kingdom of Ireland, land belonging to the Madden, Kelly, Burke and other families was appropriated during the Cromwellian conquest of Irela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Standard Time
Ireland uses Irish Standard Time (IST, UTC+01:00; ) in the summer months and Greenwich Mean Time ( UTC+00:00; ) in the winter period. Roughly two-thirds of the Republic is located west of the 7.5°W meridian. Thus the local mean time in most of Ireland is closer to UTC-01:00 time than to GMT. The Standard Time Act 1968 legally established that "the time for general purposes in the State (to be known as standard time) shall be one hour in advance of Greenwich mean time throughout the year". This act was amended by the Standard Time (Amendment) Act 1971, which legally established Greenwich Mean Time as a winter time period. Ireland therefore operates one hour behind its statutory standard time during the winter period, and reverts to standard time in the summer months. This definition contrasts with the practice of other states in the European Union, which operate one hour ahead of their standard time during the summer period, but produces the same result. The net effect is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
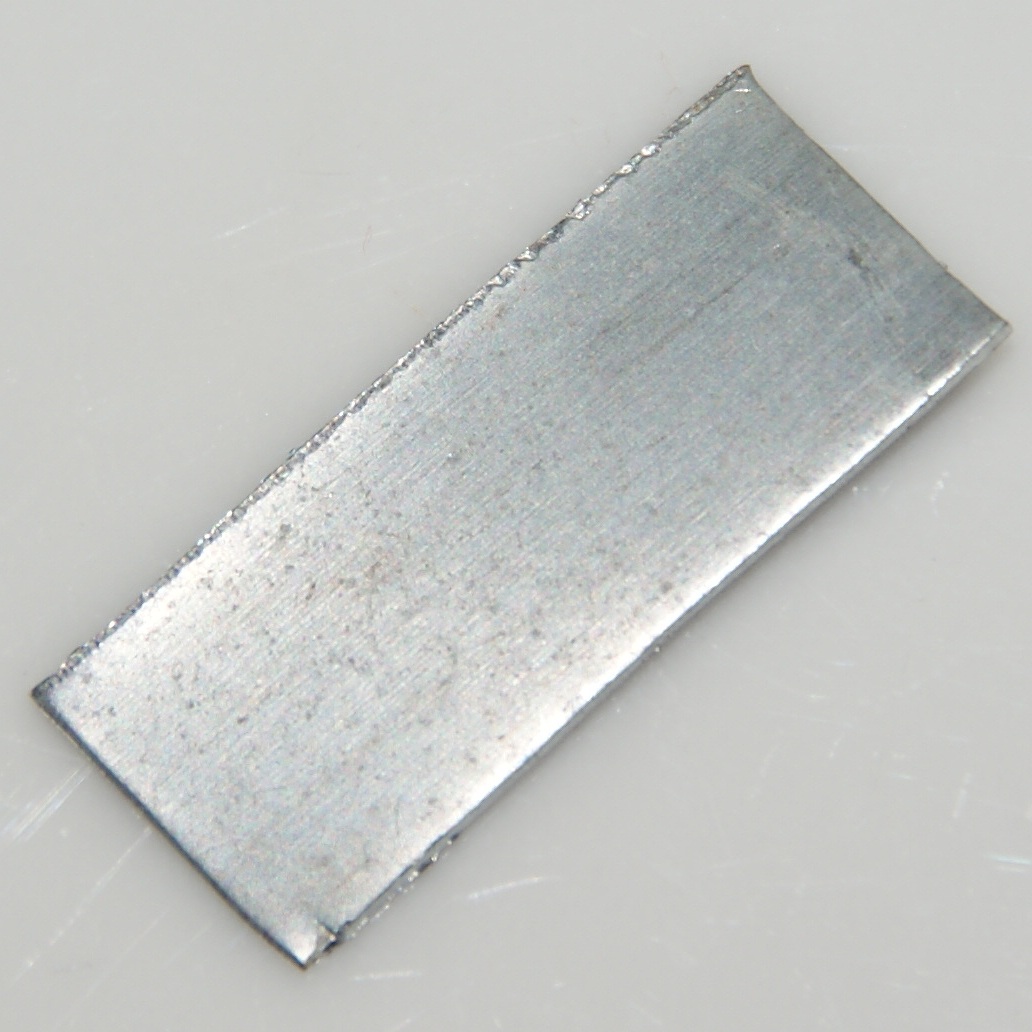
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It is the second most abundant trace metal in humans after iron, an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lough Neagh
Lough Neagh ( ; ) is a freshwater lake in Northern Ireland and is the largest lake on the island of Ireland and in the British Isles. It has a surface area of and is about long and wide. According to Northern Ireland Water, it supplies 40.7% of Northern Ireland's drinking water. Its main inflows are the Upper River Bann and Blackwater, and its main outflow is the Lower Bann. There are several small islands, including Ram's Island, Coney Island and Derrywarragh Island. The lake bed is owned by the 12th Earl of Shaftesbury and the lake is managed by Lough Neagh Partnership. Its name comes from Irish , meaning " Eachaidh's lake".Deirdre Flanagan and Laurance Flanagan, Irish Placenames, (Gill & Macmillan Ltd, 1994) Geography With an area of , it is the British Isles' largest lake by area and is ranked 34th in the list of largest lakes of Europe. Located west of Belfast, it is about long and wide. It is very shallow around the margins and the average depth in the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connacht
Connacht or Connaught ( ; or ), is the smallest of the four provinces of Ireland, situated in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna). Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland. The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of Ireland
The counties of Ireland (Irish language, Irish: ) are historic administrative divisions of the island. They began as Normans in Ireland, Norman structures, and as the powers exercised by the Cambro-Norman barons and the Old English (Ireland), Old English nobility waned over time, new offices of political control came to be established at a county level. The number of counties varied depending on the time period, however thirty-two is the traditionally accepted and used number. Upon the partition of Ireland in 1921, six of the traditional counties became part of Northern Ireland. In Northern Ireland, Counties of Northern Ireland, counties ceased to be used for local government in 1973; Local government in Northern Ireland, districts are instead used. In the Republic of Ireland, some counties have been split resulting in the creation of new counties: there are currently 26 counties, 3 cities and 2 cities and counties that demarcate areas of local government in the Republic of Ire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Aloysius Lyons
Joseph Aloysius Lyons (15 September 1879 – 7 April 1939) was an Australian politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Australia, from 1932 until his death in 1939. He held office as the inaugural leader of the United Australia Party (UAP), having previously led the Tasmanian branch of the Australian Labor Party (ALP) before the Australian Labor Party split of 1931. He served as the 26th premier of Tasmania from 1923 to 1928. Lyons was born in Stanley, Tasmania, and before entering politics worked as a schoolteacher. He was active in the Labor Party from a young age and won election to the Tasmanian House of Assembly in 1909. He was Treasurer of Tasmania (1914–1916) under John Earle, before replacing Earle as party leader in 1916. After two elections that ended in hung parliaments, Lyons was appointed premier in 1923 at the head of a minority government. He pursued moderate reforms and successfully negotiated a constitutional crisis over the powers of the Legisla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |