|
Tympanostomy Tubes
Tympanostomy tube, also known as a grommet or myringotomy tube, is a small tube inserted into the eardrum in order to keep the middle ear aerated for a prolonged period of time, and to prevent the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. The operation to insert the tube involves a myringotomy and is performed under local or general anesthesia. The tube itself is made in a variety of designs. The most commonly used type is shaped like a grommet. When it is necessary to keep the middle ear ventilated for a very long period, a "T"-shaped tube may be used, as these "T-tubes" can stay in place for 2–4 years. Materials used to construct the tube are most often plastics such as silicone or Teflon. Stainless steel tubes exist, but are no longer in frequent use. Medical uses Inserting grommets is a common surgical procedure for treating children around the world. Grommets are most commonly used to help improve hearing for children who have a condition commonly called "glue ear" (pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum (tympanic membrane). Structure Auricle The ... from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and then to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. Hence, it ultimately converts and amplifies vibration in the air to vibration in cochlear fluid. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles. Rupture or perforation of the eardrum can lead to conductive hearing loss. Collapse or tympanic membrane retraction, retraction of the eardrum can cause conductive hearing loss or cholesteatoma. Structure Orientation and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbaric Chamber
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of breathing gas for the occupants. There are two main functions for diving chambers: * as a simple form of submersible vessel to transport divers underwater and to provide a temporary base and retrieval system in the depths; * as a land, ship or offshore platform-based hyperbaric chamber or system, to artificially reproduce the hyperbaric conditions under the sea. Internal pressures above normal atmospheric pressure are provided for diving-related applications such as saturation diving and diver decompression, and non-diving medical applications such as hyperbaric medicine. Basic types of diving chambers There are two basic types of submersible diving chambers, differentiated by the way in which the pressure in the diving chamber is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diseases Of Middle Ear And Mastoid
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergies and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, dysfunction, distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injuries, disabilities, disorders, syndromes, infections, isolated symptoms, deviant behaviors, and atypical variations of structure and fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audiology
Audiology (from Latin , "to hear"; and from Greek , ''-logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiologic tests), audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing (high, middle, or low frequencies) are affected, to what degree (severity of loss), and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation (e.g. hearing aids, cochlear implants, appropriate medical referrals). In addition to diagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, that is, local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. It allows patients to undergo surgical and dental procedures with reduced pain and distress. In many situations, such as cesarean section, it is safer and therefore superior to general anesthesia. The following terms are often used interchangeably: * ''Local anesthesia'', in a strict sense, is anesthesia of a small part of the body such as a tooth or an area of skin. * ''Regional anesthesia'' is aimed at anesthetizing a larger part of the body such as a leg or arm. * ''Conduction anesthesia'' encompasses a great variety of local and regional anesthetic techniques. Medical A local anesthetic is a drug that causes reversible local anesthesia and a loss of nociception. When it is used on specific nerve pathways (nerve block), effects such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tympanic Membrane
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and then to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. Hence, it ultimately converts and amplifies vibration in the air to vibration in cochlear fluid. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles. Rupture or perforation of the eardrum can lead to conductive hearing loss. Collapse or retraction of the eardrum can cause conductive hearing loss or cholesteatoma. Structure Orientation and relations The tympanic membrane is oriented obliquely in the anteroposterior, mediolateral, and superoinferior planes. Consequently, its superoposterior end lies lateral to its anteroinferior end. Anatomically, it relates superiorly to the middle cranial fossa, posteriorly to the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Anaesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general anaesthetic medications, which often act in combination with an analgesic and neuromuscular blocking agent. Spontaneous ventilation is often inadequate during the procedure and intervention is often necessary to protect the airway. General anaesthesia is generally performed in an operating theater to allow surgical procedures that would otherwise be intolerably painful for a patient, or in an intensive care unit or emergency department to facilitate endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients. A variety of General anesthetic, drugs may be administered, with the overall goal of achieving unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, loss of reflexes of the autonomic nervous system, and in some cases paralysis of ske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
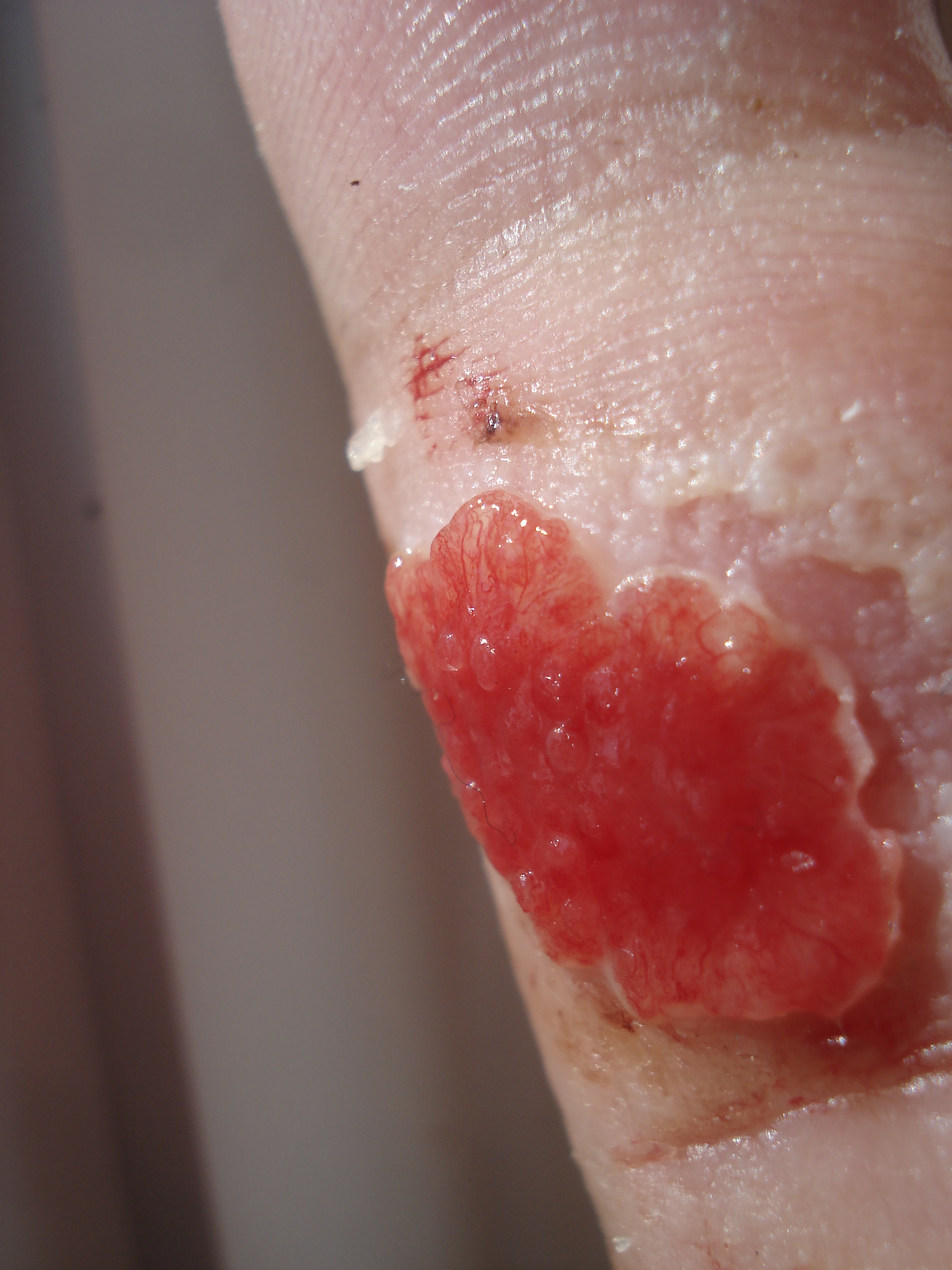
Granulation Tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in pyogenic granulomas and pulp polyps. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and new thin-walled, delicate capillaries (angiogenesis), infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix. Appearance During the migratory phase of wound healing, granulation tissue is: * light red or dark pink, being perfused with new capillary loops or "buds"; * soft to the touch; * moist; * bumpy (granular) in appearance, due to punctate hemorrhages; * pulsatile on palpation; * painless when healthy; Structure Granulation tissue is composed of tissue matrix supporting a variety of cell types, most of which can be associated with one of the following functions: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
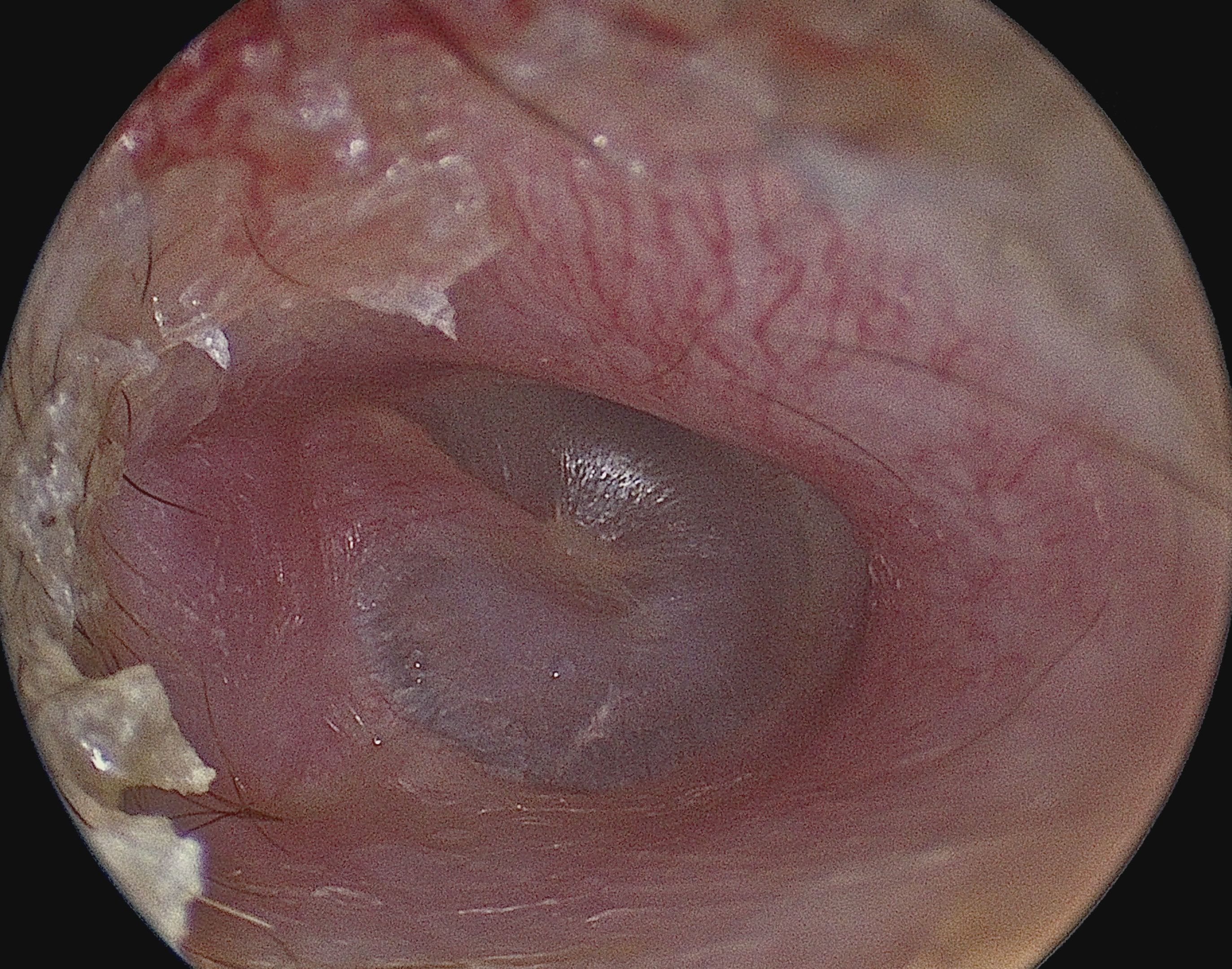
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
A perforated eardrum (tympanic membrane perforation) is a hole in the eardrum. It can be caused by infection (otitis media), trauma, overpressure (loud noise), inappropriate ear clearing, and changes in middle ear pressure. An otoscope can be used to view the eardrum to diagnose a perforation. Perforations may heal naturally, or require surgery. Presentation A perforated eardrum leads to conductive hearing loss, which is usually temporary. Other symptoms may include tinnitus, ear pain, vertigo, or a discharge of mucus. Nausea and/or vomiting secondary to vertigo may occur. Causes A perforated eardrum can have one of many causes, such as: * infection (otitis media). This infection may then spread through the middle ear, and may reoccur. * trauma. This may be caused by trying to clean ear wax with sharp instruments. It may also occur due to surgical complications. * overpressure (loud noise or shockwave from an explosion). * inappropriate ear clearing. * flying with a sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otorrhea
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. The other main type is otitis media with effusion (OME), typically not associated with symptoms, although occasionally a feeling of fullness is described; it is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear which may persist for weeks or months often after an episode of acute otitis media. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation that results in a perforated tympanic membrane with discharge from the ear for more than six weeks. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three types of otitis media may be associated with hearing loss. If children with hearing loss due to OME do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Academy Of Otolaryngology–Head And Neck Surgery
The American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS) is one of the largest of the world's many professional associations for medical specialists, with nearly 12,000 specialists in the area of otolaryngology (otorhinolaryngology) - caring for the ears, nose, and throat and surgery of the head and neck. The medical disorders treated by these physicians are among the most common that afflict all Americans, young and old. They include chronic ear infection, sinusitis, snoring and sleep apnea, hearing loss, allergies and hay fever, swallowing disorders, nosebleeds, hoarseness, dizziness, and head and neck cancer. Membership The Academy represents the interests of more than 12,000 ENT physicians worldwide and their patients. Membership categories range from board certified Physicians to Residents. Special rates are available for Military/Government and International Members. Membership benefits include a subscription to a scientific peer-monthly journal, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |