|
Two-stroke Diesel Engine
A two-stroke diesel engine is a diesel engine that uses compression ignition in a two-stroke combustion cycle. It was invented by Hugo Güldner in 1899.Mau (1984) p.7 In compression ignition, air is first compressed and heated; fuel is then injected into the cylinder, causing it to self-ignite. This delivers a power stroke each time the piston rises and falls, without any need for the additional exhaust and induction strokes of the four-stroke cycle. History According to the engineer who drew up Rudolf Diesel‘s design for one of the first operational diesel engine, Motor 250/400, Imanuel Lauster, Diesel did not originally intend using the two-stroke principle for the diesel engine. Hugo Güldner designed what is believed to be the first operational two-stroke diesel engine in 1899, and he convinced MAN, Krupp and Diesel to fund building this engine with ℳ 10,000 each. Güldner's engine had a 175 mm work cylinder, and a 185 mm scavenging cylinder; both had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordberg Radial Engine 648
Nordberg is a neighbourhood in Nordre Aker in Oslo, the capital of Norway. From 1934 to 1992 it was served by Nordberg (station), Nordberg Station on the Sognsvann Line, but is now served by Østhorn (station), Østhorn and Holstein (station), Holstein on the same line. References Neighbourhoods of Oslo {{Oslo-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Junkers
Hugo Junkers (3 February 1859 – 3 February 1935) was a German aircraft engineer and aircraft designer who pioneered the design of all-metal airplanes and flying wings. His company, Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works), was one of the mainstays of the German aircraft industry in the years between World War I and World War II. His multi-engined, all-metal passenger and freight planes helped establish airlines in Germany and around the world. In addition to aircraft, Junkers also built both diesel and petrol engines and held various thermodynamic and metallurgical patents. He was also one of the main sponsors of the Bauhaus movement and facilitated the move of the Bauhaus from Weimar to Dessau (where his factory was situated) in 1925. Amongst the highlights of his career were the Junkers J 1 of 1915, the world's first practical all-metal aircraft, incorporating a cantilever wing design with virtually no external bracing, the Junkers F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Engine
The Otto engine is a large stationary single-cylinder internal combustion engine, internal combustion four-stroke engine, designed by the German Nicolaus Otto. It was a low-RPM machine, and only fired every other stroke due to the Otto cycle, also designed by Otto. Types Three types of internal combustion engines were designed by German inventors Nicolaus Otto and his partner Eugen Langen. The models were a failed 1862 compression engine, an 1864 atmospheric engine, and the 1876 Otto cycle engine known today as the ''petrol engine''. The engines were initially used for stationary installations, as Otto had no interest in transportation. Other makers such as Daimler perfected the Otto engine for transportation use."Nikolaus August Otto: Inventor Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Air Parts Gemini Diesel 100
The Superior Air Parts Gemini Diesel 100 is a diesel aircraft engine, under development by Superior Air Parts of Coppell, Texas, United States for use in homebuilt aircraft.Tacke, Willi; Marino Boric; et al: ''World Directory of Light Aviation 2015-16'', pages 262-263. Flying Pages Europe SARL, 2015. The company is owned by the Chinese company Superior Aviation Beijing, which is 60% owned by Chairman Cheng Shenzong and 40% owned by Beijing E-Town, an economic development agency of the municipal government of Beijing. Design and development The Gemini Diesel 100 is a three-cylinder two-stroke, in-line, supercharged liquid-cooled, diesel engine design. It produces , with a helical gear mechanical gearbox reduction drive with a reduction ratio of 1.586:1. The engine design uses an opposed-piston engine, with "two-opposing-pistons-per-cylinder", based upon the Second World War 6-cylinder, 12-piston Junkers Jumo 205 engine concept. The engine was originally developed by UK bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
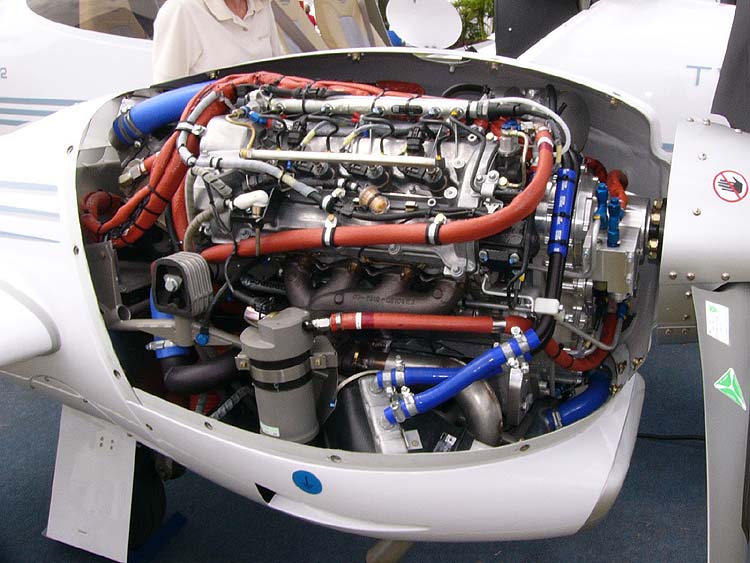
Aircraft Diesel Engine
The aircraft diesel engine or aero diesel is a diesel-powered aircraft engine. They were used in airships and tried in aircraft in the late 1920s and 1930s, but were never widely adopted until recently. Their main advantages are their excellent specific fuel consumption, the reduced flammability and somewhat higher density of their fuel, but these have been outweighed by a combination of inherent disadvantages compared to gasoline-fueled or turboprop engines. The ever-rising cost of avgas and doubts about its future availability have spurred a resurgence in aircraft diesel engine production in the early 2010s. Using diesel engines in aircraft is additionally advantageous from the standpoint of environmental protection as well as the protection of human health, since the tetraethyllead antiknock ingredient of avgas has long been known to be highly toxic as well as polluting. Development Early diesel aircraft A number of manufacturers built diesel aero engines in the 1920s and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieselisation
Dieselisation (US: dieselization) is the process of equipping vehicles with a diesel engine or diesel engines. It can involve replacing an internal combustion engine powered by petrol (US: gasoline) fuel with an engine powered by diesel fuel, as occurred on a large scale with trucks, buses, farm tractors, trains, and building construction machinery after World War II. Alternatively it can involve replacing the entire plant or vehicle with one that is diesel-powered; the term commonly describes the generational replacement between the 1930s to 1970s of railway steam locomotives with diesel locomotives, and associated facilities. Water transport The two-stroke diesel engine for marine applications was introduced in 1908 and remains in use today. It is the most efficient prime mover to date, models such as the Wärtsilä-Sulzer RTA96-C offer a thermal efficiency of 50% and over 100,000 horsepower. First steps towards conversions using diesel engines as means of propulsion (on sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for longer and heavier freight trains, companies are increasingly using distributed power: single or multiple locomotives placed at the front and rear and at intermediate points throughout the train under the control of the leading locomotive. Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing motion', and is a shortened form of the term ''locomotive engine'', which was first used in 1814 to distinguish between self-propelled and stationary steam engines. Classifications Prior to locomotives, the motive force for railways had been generated by various lower-technology methods such as human power, horse power, Gravity railroad, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power-to-weight Ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power source. It is also used as a measurement of performance of a vehicle as a whole, with the engine's power output being divided by the weight (or mass) of the vehicle, to give a metric that is independent of the vehicle's size. Power-to-weight is often quoted by manufacturers at the peak value, but the actual value may vary in use and variations will affect performance. The inverse of power-to-weight, weight-to-power ratio (power loading) is a calculation commonly applied to aircraft, cars, and vehicles in general, to enable the comparison of one vehicle's performance to another. Power-to-weight ratio is equal to thrust per unit mass multiplied by the velocity of any vehicle. Power-to-weight ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland Diesel Engine Division
The Cleveland Diesel Engine Division of General Motors (GM) was a leading research, design and production facility of diesel engines from the 1930s to the 1960s that was based in Cleveland, Ohio. The Cleveland Diesel Engine Division designed several 2 stroke diesel engines for submarines, tugboats, destroyer escorts, s and other marine applications. Emergency generator sets were also built around the Cleveland Diesel and were installed in many US warships. The division was created in 1938 from the GM-owned Winton Engine Corporation and was folded into the GM Electro-Motive Division in 1962. The engines continue in use today on older tugs. History Cleveland Diesel traces it roots to the Winton Gas Engine and Manufacturing Company, which was formed by the early Cleveland automobile manufacturer Alexander Winton in November 1912. Winton soon expanded into production of heavy spark-ignition and diesel engines, introducing the first American diesel in 1913. Renamed the Winton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Motors
General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing four automobile brands: Chevrolet, Buick, GMC (marque), GMC, and Cadillac, each a separate division of GM. By total sales, it has continuously been the largest automaker in the United States, and was the List of manufacturers by motor vehicle production, largest in the world for 77 years before losing the top spot to Toyota in 2008. General Motors operates manufacturing plants in eight countries. In addition to its four core brands, GM also holds interests in Chinese brands Baojun and SAIC-GM-Wuling, Wuling via SAIC-GM-Wuling, SAIC-GM-Wuling Automobile. GM further owns GM Defense, a namesake defense vehicles division which produces military vehicles for the United States government and military, the vehicle safety, security, and information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles F
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was ''Churl, Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinisation of names, Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as ''Carolus (other), Carolus''. Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as wikt:churl, churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its deprecating sense in the Middle English period. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch language, Dutch and German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
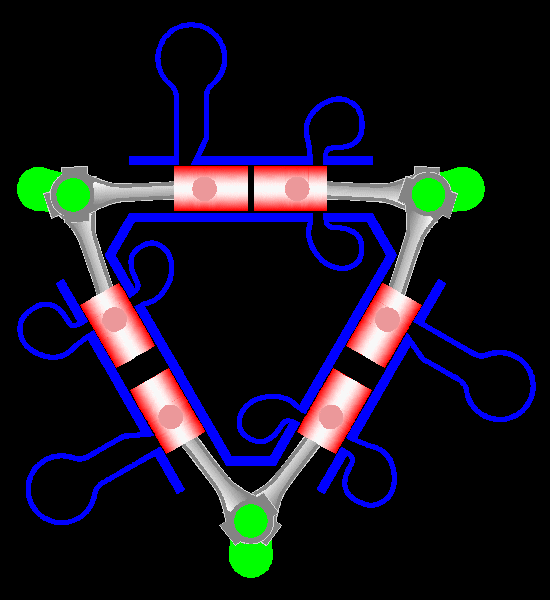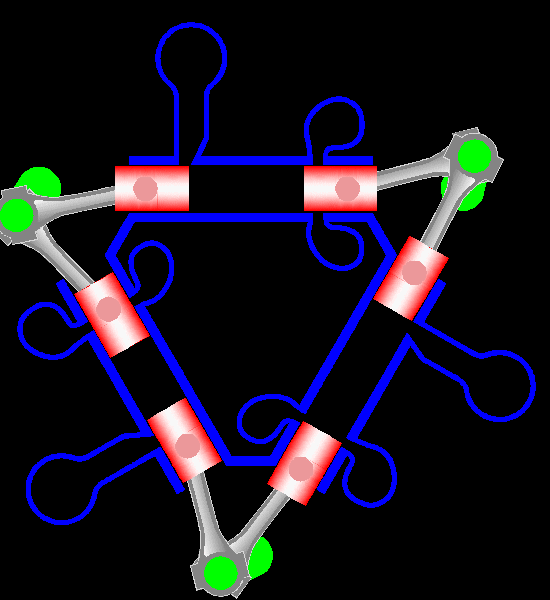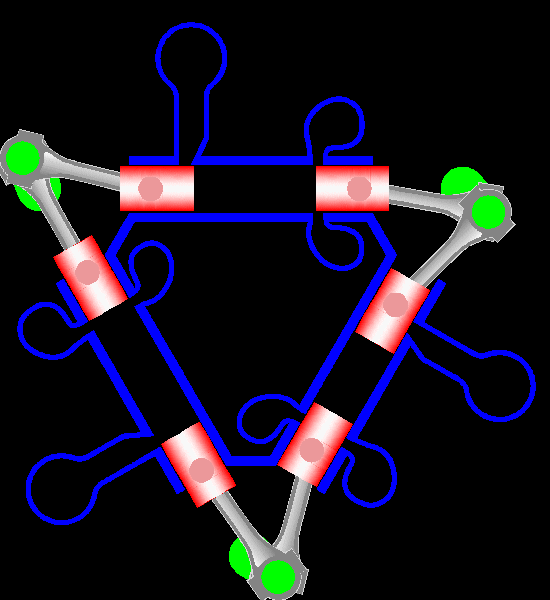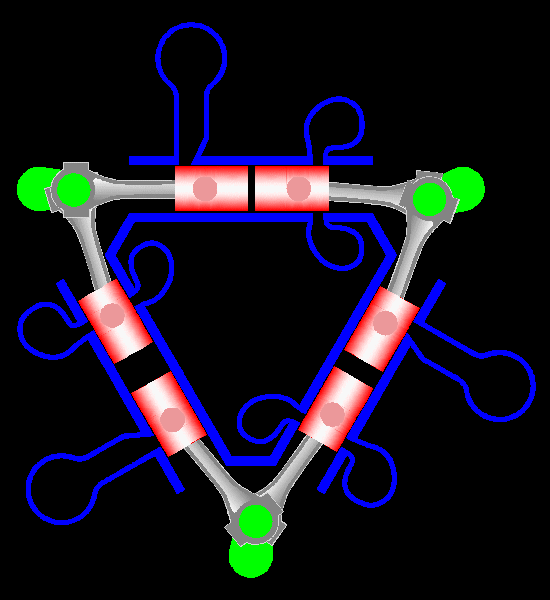
Napier Deltic
The Napier Deltic engine is a British opposed-piston valveless, supercharged uniflow scavenged, two-stroke diesel engine used in marine and locomotive applications, designed and produced by D. Napier & Son. Unusually, the cylinders were disposed in a three-bank triangle, with a crankshaft at each corner of the triangle. The term Deltic (meaning "in the form of the Greek letter (capital) delta") is used to refer to both the Deltic E.130 opposed-piston, high-speed diesel engine and the locomotives produced by English Electric using these engines, including its demonstrator locomotive named ''DELTIC'' and the production version for British Railways, which designated these as the Class 55. A single, half-sized, turbocharged Deltic power unit also featured in the English Electric-built Type 2 locomotive, designated as the Class 23. Both locomotive and engine became better known as the "Baby Deltic". History and design The Deltic story began in 1943 when the British Admiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |