|
Two-photon Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Time-resolved two-photon photoelectron (2PPE) spectroscopy is a time-resolved spectroscopy technique which is used to study electronic structure and electronic excitations at surfaces. The technique utilizes femtosecond to picosecond laser pulses in order to first photoexcite an electron. After a time delay, the excited electron is photoemitted into a free electron state by a second pulse. The kinetic energy and the emission angle of the photoelectron are measured in an electron energy analyzer. To facilitate investigations on the population and relaxation pathways of the excitation, this measurement is performed at different time delays. This technique has been used for many different types of materials to study a variety of exotic electron behaviors, including image potential states at metal surfaces, and electron dynamics at molecular interfaces. Basic physics The final kinetic energy of the electron can be modeled by :E_\text= E_\text+E_\text-E_\text-\Phi where the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibronic Coupling
Vibronic coupling (also called nonadiabatic coupling or derivative coupling) in a molecule involves the interaction between electronic and nuclear vibrational motion. The term "vibronic" originates from the combination of the terms "vibrational" and "electronic", denoting the idea that in a molecule, vibrational and electronic interactions are interrelated and influence each other. The magnitude of vibronic coupling reflects the degree of such interrelation. In theoretical chemistry, the vibronic coupling is neglected within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. Vibronic couplings are crucial to the understanding of nonadiabatic processes, especially near points of conical intersections. The direct calculation of vibronic couplings is not common due to difficulties associated with its evaluation. Definition Vibronic coupling describes the mixing of different electronic states as a result of small vibrations. : \mathbf_\equiv\langle\,\chi_(\mathbf;\mathbf)\,, \, \hat_\ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Spectroscopy
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an electron making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of the emitted photon is equal to the energy difference between the two states. There are many possible electron transitions for each atom, and each transition has a specific energy difference. This collection of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the emission spectra of molecules can be used in chemical analysis of substances. Emission In physics, emission is the process by which a higher energy quantum mechanical state of a particle becomes converted to a lower one through the emission of a photon, resulting in the production of light. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
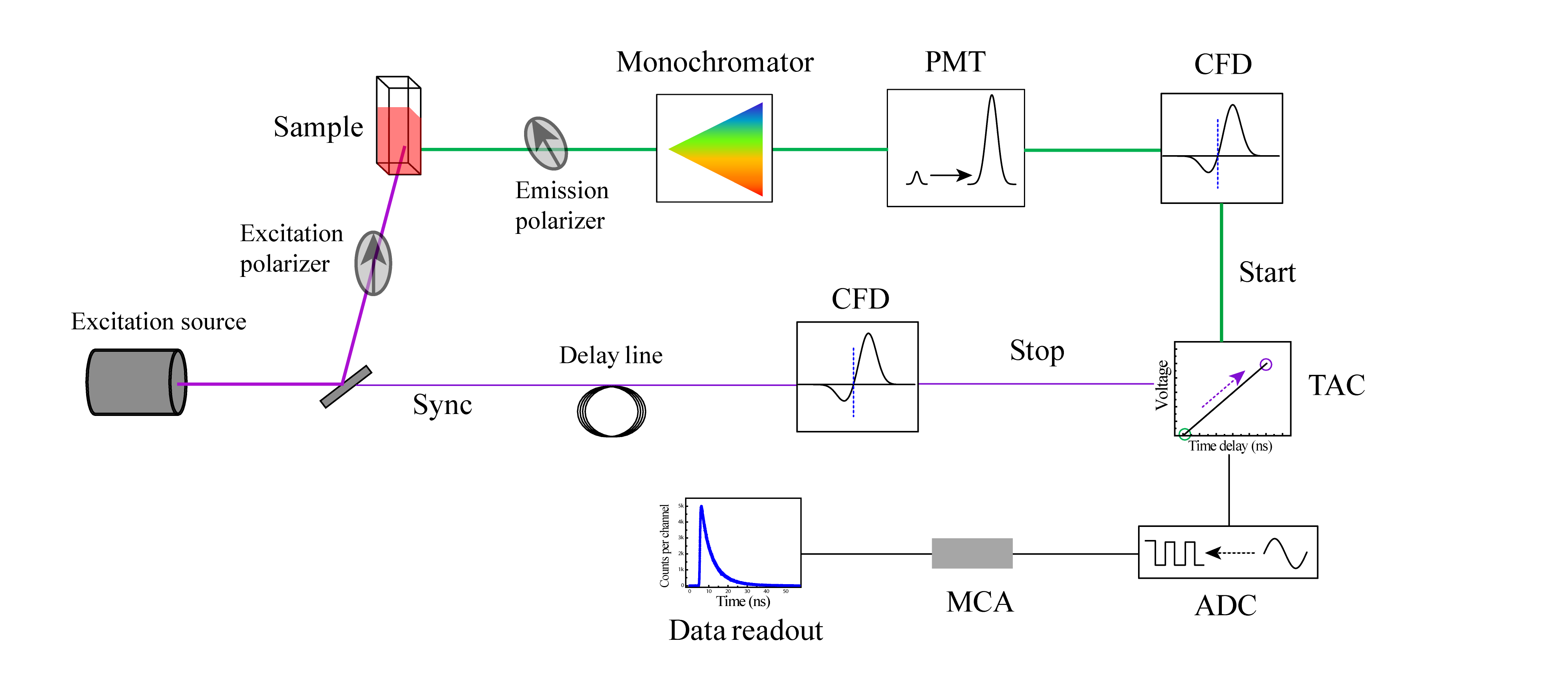
Time-resolved Spectroscopy
In physics and physical chemistry, time-resolved spectroscopy is the study of dynamic processes in materials or chemical compounds by means of spectroscopic techniques. Most often, processes are studied after the illumination of a material occurs, but in principle, the technique can be applied to any process that leads to a change in properties of a material. With the help of pulsed lasers, it is possible to study processes that occur on time scales as short as 10−16 seconds. All time-resolved spectra are suitable to be analyzed using the two-dimensional correlation method for a correlation map between the peaks. Transient-absorption spectroscopy Transient-absorption spectroscopy (TAS), also known as flash photolysis, is an extension of absorption spectroscopy. Ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy, an example of non-linear spectroscopy, measures changes in the absorbance/transmittance in the sample. Here, the absorbance at a particular wavelength or range of wavelengths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrafast Laser Spectroscopy
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique that uses ultrashort pulse lasers for the study of dynamics on extremely short time scales ( attoseconds to nanoseconds). Different methods are used to examine the dynamics of charge carriers, atoms, and molecules. Many different procedures have been developed spanning different time scales and photon energy ranges; some common methods are listed below. Attosecond-to-picosecond spectroscopy Dynamics on the as to fs time scale are in general too fast to be measured electronically. Most measurements are done by employing a sequence of ultrashort light pulses to initiate a process and record its dynamics. The temporal width (duration) of the light pulses has to be on the same scale as the dynamics that are to be measured or even shorter. Light sources Titanium-sapphire laser Ti-sapphire lasers are tunable lasers that emit red and near-infrared light (700 nm- 1100 nm).Ti-sapphire laser oscillators use Ti doped-sapphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser-based Angle-resolved Photoemission Spectroscopy
Laser-based angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy is a form of angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy that uses a laser as the light source. Photoemission spectroscopy is a powerful and sensitive experimental technique to study surface physics. It is based on the photoelectric effect originally observed by Heinrich Hertz in 1887 and later explained by Albert Einstein in 1905 that when a material is shone by light, the electrons can absorb photons and escape from the material with the kinetic energy: E = hf-\phi, where hf is the incident photon energy, \phi the work function of the material. Since the kinetic energy of ejected electrons are highly associated with the internal electronic structure, by analyzing the photoelectron spectroscopy one can realize the fundamental physical and chemical properties of the material, such as the type and arrangement of local bonding, electronic structure and chemical composition. In addition, because electrons with different momentum wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle-resolved Photoemission Spectroscopy
Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) is an experimental technique used in condensed matter physics to probe the allowed energies and momenta of the electrons in a material, usually a crystalline solid. It is based on the photoelectric effect, in which an incoming photon of sufficient energy ejects an electron from the surface of a material. By directly measuring the kinetic energy and emission angle distributions of the emitted photoelectrons, the technique can map the electronic band structure and Fermi surfaces. ARPES is best suited for the study of one- or two-dimensional materials. It has been used by physicists to investigate high-temperature superconductors, graphene, Topological insulator, topological materials, quantum well states, and materials exhibiting charge density waves. ARPES systems consist of a monochromatic light source to deliver a narrow beam of photons, a sample holder connected to a manipulator used to position the sample of a material, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with three spatial dimensions. Time has long been an important subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars. Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems. 108 pages. Time in physics is operationally defined as "what a clock reads". The physical nature of time is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Technology
Optical engineering is the field of science and engineering encompassing the physical phenomena and technologies associated with the generation, transmission, manipulation, detection, and utilization of light. Optical engineers use optics to solve problems and to design and build devices that make light do something useful. They design and operate optical equipment that uses the properties of light using physics and chemistry, such as lenses, microscopes, telescopes, lasers, sensors, fiber optic communication systems and optical disc systems (e.g. CD, DVD). Optical engineering metrology uses optical methods to measure either micro-vibrations with instruments like the laser speckle interferometer, or properties of masses with instruments that measure refraction Nano-measuring and nano-positioning machines are devices designed by optical engineers. These machines, for example microphotolithographic steppers, have nanometer precision, and consequently are used in the fabrication of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoemission Spectroscopy
Photoemission spectroscopy (PES), also known as photoelectron spectroscopy, refers to energy measurement of electrons emitted from solids, gases or liquids by the photoelectric effect, in order to determine the binding energies of electrons in the substance. The term refers to various techniques, depending on whether the ionization energy is provided by X-ray, XUV or UV photons. Regardless of the incident photon beam, however, all photoelectron spectroscopy revolves around the general theme of surface analysis by measuring the ejected electrons. Types X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was developed by Kai Siegbahn starting in 1957 and is used to study the energy levels of atomic core electrons, primarily in solids. Siegbahn referred to the technique as "electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis" (ESCA), since the core levels have small chemical shifts depending on the chemical environment of the atom that is ionized, allowing chemical structure to be determined. Siegb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schematic 2PPE-setup Pdf
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the schematic is intended to convey, and may include oversimplified elements in order to make this essential meaning easier to grasp, as well as additional organization of the information. For example, a subway map intended for passengers may represent a subway station with a dot. The dot is not intended to resemble the actual station at all but aims to give the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols in place of detailed representations of the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment that compose the system, thus emphasizing the functions of the individual elements and the interconnections among them and suppresses their physical details. In an electronic circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |