|
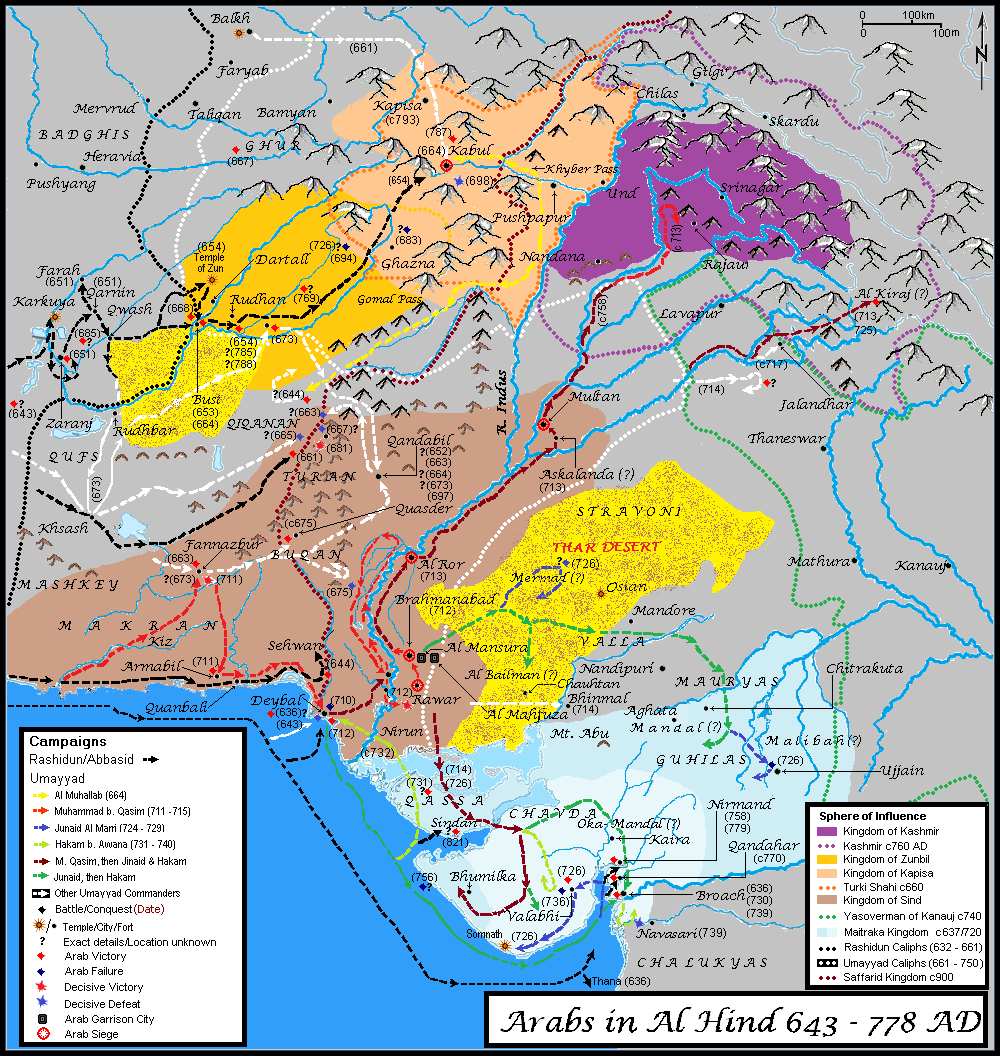
Turk Shahi
The Turk Shahis or Kabul Shahis were a dynasty of Western Turk, or mixed Western Turk, Turko-Hephthalite, origin, that ruled from Kabul and Kapisa (city), Kapisa to Gandhara in the 7th to 9th centuries AD. They may have been of Khalaj people, Khalaj ethnicity."The new rulers of Kabul, who according to me were Khalaj Turks, extended their rule over the former territory of the Kapisi kingdom [Kapisa to Gandhara], while a branch of them became independent in Zabulistan. A Korean monk Huichao (慧超) who visited these regions in the third decade of the 8th century, reported that both regions were ruled by the Turkish kings." The Gandhara territory may have been bordering the Kashmir kingdom and the Kanauj kingdom to the east. From the 560s, the Western Turks had gradually expanded southeasterward from Transoxonia, and occupied Bactria and the Hindu-Kush region, forming largely independent polities. The Turk Shahis may have been a political extension of the neighbouring Western Turk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zunbils
Zunbil, also written as Zhunbil, or Rutbils of Zabulistan, was a royal dynasty south of the Hindu Kush in present southern Afghanistan region. They ruled from circa 680 AD until the Saffarid conquest in 870 AD. The Zunbil dynasty was founded by Rutbil (Turkic: ''Iltäbär''), the elder brother of the Turk Shahi ruler (either Barha Tegin or Tegin Shah), who ruled over a Khalaj -Hephthalite kingdom from his capital in Kabul.Andre Wink, '' Al-Hind, the Making of the Indo-Islamic World'', Vol.1, (Brill, 1996), 115;"''"The Zunbils of the early Islamic period and the Kabulshahs were almost certainly epigoni of the southern-Hephthalite rulers of Zabul.''" The Zunbils are described as having Turkish troops in their service by Arabic sources like Tarikh al-Tabari and '' Tarikh-i Sistan''. The faith of this community has not been researched as much. According to the interpretation of Chinese sources by Marquarts and de Groots in 1915, the king of Ts'ao is said to have worn a crown with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. According to late 2022 estimates, the population of Kabul was 13.5 million people. In contemporary times, the city has served as Afghanistan's political, cultural, and economical centre, and rapid urbanisation has made Kabul the 75th-largest city in the world and the country's primate city. The modern-day city of Kabul is located high up in a narrow valley between the Hindu Kush, and is bounded by the Kabul River. At an elevation of , it is one of the highest capital cities in the world. Kabul is said to be over 3,500 years old, mentioned since at least the time of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. Located at a crossroads in Asia—roughly halfway between Istanbul, Turkey, in the west and Hanoi, Vietnam, in the east—it is situated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yabghus Of Tokharistan
The Tokhara Yabghus or Yabghus of Tokharistan () were a dynasty of Western Turk– Hephtalite sub-kings with the title "Yabghus", who ruled from 625 CE in the area of Tokharistan north and south of the Amu Darya, Oxus River, with some smaller remnants surviving in the area of Badakhshan until 758 CE. Their legacy extended to the southeast where it came into contact with the Turk Shahis and the Zunbils until the 9th century CE. Territorial expansion The Turks initially occupied the area of north of the Oxus ( Transoxonia, Sogdiana) following their destruction of the Hephthalites in 557–565 CE through an alliance with the Sasanian Empire. The Sasanians, on the other hand, took control of the area south of the Oxus, with Chaganiyan, Sind, Bust, Rukhkhaj, Zabulistan, Tokharistan, Turistan and Balistan being transformed into vassal kingdoms and principalities. After this time, a tense Turco-Persian border existed along the Oxus, which lasted several decades. The area south of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bukhar Khudahs
The Bukhar Khudahs or Bukhar Khudats ( Sogdian: ''βuxārak Xwaday'') were a local Sogdian dynasty, which ruled the city of Bukhara from an unknown date to the reign of the Samanid ruler Isma'il ibn Ahmad, who incorporated Bukhara into the Samanid state. Etymology The word “Bukhar” means Bukhara, while “khuda” means “lord”. Thus the word means “the lord of Bukhara”. History The founding date of the Bukhar Khudahs remains unknown; the 10th-century Iranian historian Narshakhi is known to have mentioned several names of rulers of Bukhara, but it is not known if they were all from the same dynasty. The first ruler mentioned by Narshakhi is Abru'i (also spelled Abarzi). According to Narshakhi, he was a cruel ruler, who was overthrown by a certain Turkic king named Qara Jurjin. The next ruler is named Kana, who is said to have introduced the minting of coins in Bukhara, which is, however, doubted by modern scholars. The next ruler is given as Makh, who was cred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patola Shahis
The Patola Shahis, or Patola Shahis, also Gilgit Shahis, were a dynasty of Buddhist kings of the Kingdom of Gilgit ("Lesser Bolü"), located in the northern tip of the Indian subcontinent in the 6th-8th century CE. The Kingdom was located on a strategic trans-Himalyan trade route, now known as the Karakoram Highway, which branched off the Grand Trunk Road. It followed the important stops of Shatial and Chilas. Early records Between 399 and 414, the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim Faxian visited Gilgit-Baltistan. Between 627 and 645, the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim Xuanzang travelled through this region on his pilgrimage to India. According to Chinese records from the Tang dynasty, between the 600s and the 700s, the region was governed by a Buddhist dynasty referred to as ''Bolü'' (), also transliterated as ''Palola'', ''Patola'', ''Balur''. They are believed to be the Patola Sāhi dynasty mentioned in a Brahmi inscription, and are devout adherents of Vajrayana Buddhism. At the time, Little ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karkota Empire
The Karkota Dynasty (c. 625 − 855 CE) ruled over the Kashmir valley and some northern parts of the Indian subcontinent during 7th and 8th centuries. Their rule saw a period of political expansion, economic prosperity and emergence of Kashmir as a centre of culture and scholarship. The Karkota rulers constructed several Vishnu shrines in their dominions. They however also allowed Buddhism to flourish under them. Stupa, Chaitya and Vihara can be found in the ruins of their capital. Martand Sun Temple in the Anantnag district were built by Lalitaditya. It is the oldest known Sun temple in India and was also one of the biggest temple complexes at the time. Avanti Varman ascended the throne of Kashmir in 855, establishing the Utpala dynasty and ending the rule of Karkota dynasty. Sources Literature The Nilamata Purana, believed to have been commissioned by Durlabhavardhana, the first ruler of the dynasty, provides information on contemporary affairs. However, not only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurjara-Pratihara Dynasty
The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj. The Gurjara-Pratiharas were instrumental in containing Arab armies moving east of the Indus River. Nagabhata I defeated the Arab army under Junaid and Tamin in the Caliphate campaigns in India. Under Nagabhata II, the Gurjara-Pratiharas became the most powerful dynasty in northern India. He was succeeded by his son Ramabhadra, who ruled briefly before being succeeded by his son, Mihira Bhoja. Under Bhoja and his successor Mahendrapala I, the Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty reached its peak of prosperity and power. By the time of Mahendrapala, the extent of its territory rivalled that of the Gupta Empire stretching from the border of Sindh in the west to Bengal in the east and from the Himalayas in the north to areas past the Narmada in the south. The expansion triggered a tripartite power struggle with the Rashtrakuta an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliphal Province Of Sind
Sind () was an administrative division of the Umayyad Caliphate and later of the Abbasid Caliphate in post-classical India, from around 711 CE with the conquest of Sind by the Arab military commander Muhammad ibn Qasim, to around 854 CE with the emergence of the independent dynasties of the Habbarid Emirate and the Multan Emirate. The "Governor of Sind" () was an official who administered the caliphates' province over what is now Sindh, Pakistan. The governor was the chief Muslim official in the province and was responsible for maintaining security in the region. As the leader of the provincial military, he was also in charge of carrying out campaigns against the non-Muslim kingdoms of India. Governors appointed to the region were selected either directly by the caliph or by an authorized subordinate, and remained in office until they either died or were dismissed. Geography Sind was a frontier province of the Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates from its conquest in c. 711 un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalukya Dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi (modern Badami) from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani (modern Basavakalyan) until the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maitrakas
The Maitraka dynasty ruled western India (now Gujarat) from approximately 475 to approximately 776 CE from their capital at Vallabhi. With the sole exception of Dharapaṭṭa (the fifth king in the dynasty), who followed the Mithraic mysteries, they were followers of Shaivism. Their origin is uncertain but they were probably Chandravanshi Kshatriyas. Following the decline of the Gupta Empire, Maitraka dynasty was founded by ''Senapati'' (general) Bhaṭārka, who was a military governor of Saurashtra under Gupta Empire, who had established himself as the independent around 475 CE. The first two Maitraka rulers Bhaṭārka and Dharasena I used only the title of ''Senapati'' (general). The third ruler Droṇasiṁha declared himself as the ''Maharaja''. During the reign Dhruvasena I, Jain council at Vallabhi was probably held. The next ruler Dharapaṭṭa is the only ruler considered as a sun-worshipper. King Guhasena stopped using the term ''Paramabhattaraka Padanudhyata'' alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after the split of the Turkic Khaganate (founded in the 6th century on the Mongolian Plateau by the Ashina clan) into a western and an eastern Khaganate. The whole confederation was called ''Onoq'', meaning "ten arrows". According to a Chinese source, the Western Turks were organized into ten divisions. The khaganate's capitals were Navekat (summer capital) and Suyab (principal capital), both situated in the Chui River valley of Kyrgyzstan, to the east of Bishkek. Tong Yabgu's summer capital was near Tashkent and his winter capital Suyab. The Western Turkic Khaganate was subjugated by the Tang dynasty in 657 and continued as its vassal until their collapse. History The first Turkic Khaganate was founded by Bumin in 552 on the Mongolian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |