|
Turbomeca Palouste
The Turbomeca Palouste is a French gas turbine engine, first run in 1952. Designed purely as a compressed air generator, the Palouste was mainly used as a ground-based aircraft engine starter unit. Other uses included rotor tip propulsion for helicopters. Design and development Designed and built by Turbomeca, the Palouste was also built under license in Britain by Blackburn and Rolls-Royce. Originally conceived as an aircraft ground support equipment starter gas generator, it was used also as propulsion for the Sud-Ouest Djinn and other tip-jet powered helicopters. The Palouste was a very simple unit, its primary purpose being to supply a high flow rate of compressed air to start larger jet engines such as the Rolls-Royce Spey as installed in the Blackburn Buccaneer (this aircraft having no onboard starting system). Air from the centrifugal compressor was divided between external supply (known as bleed air) and its own combustion chamber. Several British naval aircraft were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
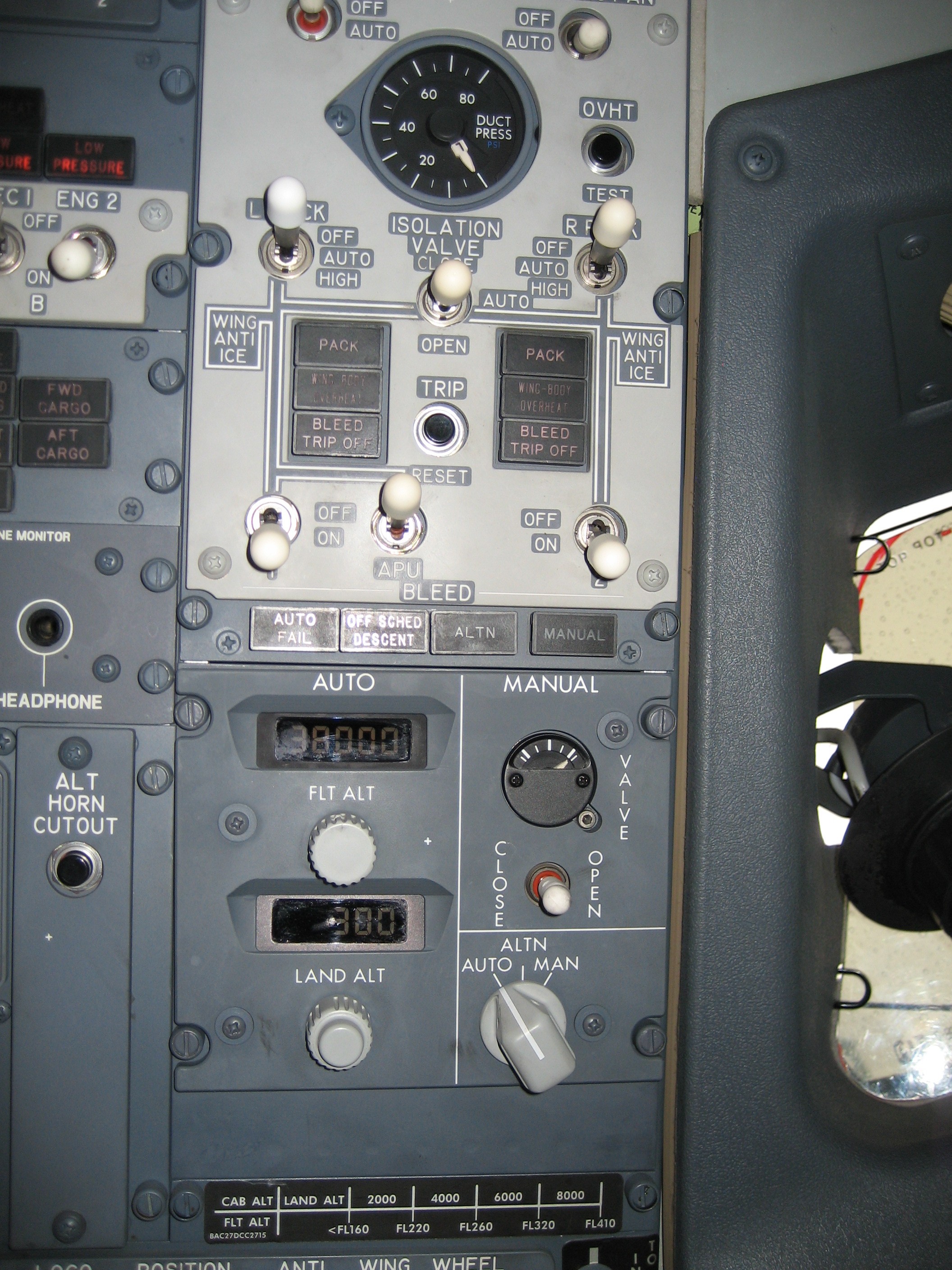
Bleed Air
Bleed air is compressed air taken from the compressor stage of a gas turbine upstream of its fuel-burning sections. Automatic air supply and cabin pressure controller (ASCPCs) valves bleed air from high or low stage engine compressor sections. Low stage air is used during high power setting operation, and high during descent and other low power setting operations. Bleed air from that system can be utilized for internal cooling of the engine, cross-starting another engine, engine and airframe anti-icing, cabin pressurization, pneumatic actuators, air-driven motors, pressurizing the hydraulic reservoir, and waste and water storage tanks. Some engine maintenance manuals refer to such systems as "customer bleed air". Bleed air is valuable in an aircraft for two properties: high temperature and high pressure (typical values are 200–250 °C and 275 kPa (40 PSI), for regulated bleed air exiting the engine pylon for use throughout the aircraft). Uses In civil aircraft, bleed air' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Aircraft Engines
This is an alphabetical list of aircraft engines by manufacturer. 0–9 2si *2si 215 *2si 230 * 2si 430 * 2si 460 *2si 500 * 2si 540 * 2si 690 3W ''Source: RMV'' *3W 106iB2 *3W-110 *3W-112 *3W-170 *3W-210 *3W-220 A Abadal (Francisco Serramalera Abadal) *Abadal Y-12 350/400 hp ABC ''Source: Lumsden.'' * ABC 8 hp * ABC 30hp V-4 * ABC 45hp V-6 * ABC 60hp V-8 * ABC 85hp V-6 * ABC 100hp V-8 * ABC 115 hp * ABC 170hp V-12 * ABC 225hp V-16 *ABC Dragonfly *ABC Gadfly *ABC Gnat *ABC Hornet * ABC Mosquito *ABC Scorpion *ABC Wasp *ABC type 10 APU *ABC type 11 APU ABECO ''Source: RMV'' *ABECO GEM Aberg ''Source: RMV'' *Type Sklenar ABLE ''Source: RMV'', Able Experimental Aircraft Engine Co. (Able Experimental Aircraft Engine Co., Altimizer, Hoverhawk (US)) *ABLE 2275 *ABLE 2500 *ABLE VW x 2 Geared Drive Accurate Automation Corp *Accurate Automation AT-1500 *Accurate Automation AT-1700 Ace (Ace American Engr Corp, Horace Keane Aeroplane Co, North Beac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Oryx
The Napier Oryx was a British gas-turbine engine designed and built by Napier in the early 1950s for the Percival P.74 tip jet-powered helicopter project. The P.74 was unsuccessful and it and the Oryx were cancelled. Design and development The engine was developed by the Aero Gas Turbine Division of Napier in conjunction with Percival, later Hunting Percival. Funding came from the Ministry of Supply. The Percival P.74 was a design for a tipjet-powered helicopter. The jet power was to be supplied from engines within the helicopter and piped to the rotor tips. Napier developed the Oryx specifically to power the P.74. The output gas temperature from the engines had to be below 400 °C for the helicopter's stainless steel rotor ducts, so a bypass design was used. This also blew "cold" air from the compressor, rather than purely hot turbine exhaust gas. In order to give a compact installation, rather than using an oversized compressor with a bypass around the turbine (as comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbomeca Artouste
The Turbomeca Artouste is an early French turboshaft engine, first run in 1947. Originally conceived as an auxiliary power unit (APU), it was soon adapted to aircraft propulsion, and found a niche as a powerplant for turboshaft-driven helicopters in the 1950s. Artoustes were licence-built by Bristol Siddeley (formerly Blackburn) in the UK, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited in India, and developed by Continental CAE in the US as the Continental T51. Two major versions of the Artouste were produced. The Artouste II family, mainly used in the Aérospatiale Alouette II helicopter, had a one-stage centrifugal compressor and a two-stage turbine, with gearbox-limited power of . The Artouste III family, mainly used in Aérospatiale's Alouette III and Lama helicopters, had a two-stage axial-centrifugal compressor and a three-stage turbine, with gearbox-limited power of . Variants ;Artouste I: ;Artouste II: ;Artouste IIB, IIB1: for takeoff, continuous ;Artouste IIC, IIC1, IIC2, IIC5, IIC6: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairey Ultra-light Helicopter
The Fairey Ultra-light Helicopter was a small British military helicopter intended to be used for reconnaissance and casualty evacuation, designed by the Fairey Aviation Company. The Ultra-light had been conceived of as a straightforward, low cost and easily transportable helicopter. It lacked any tail rotor due to the decision to propel the rotorcraft using unconventional tip jets positioned at the ends of the rotor blades. It had been selected amongst various competing projects to meet a Ministry of Supply requirement for a lightweight helicopter to be used by the British Army for aerial observation purposes. Early trials with prototypes proved promising, however political factors ultimately undermined the project. The Ultra-light found itself a casualty of the British defence economies of the later 1950s, as well as of intense competition from rival firms who had their own light rotorcraft projects, in particular the Saunders-Roe Skeeter. While Fairey attempted to proceed wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Model 65
The Bell Model 65 Air Test Vehicle (ATV) was an experimental tiltjet VTOL aircraft built by Bell using parts from a number of general aviation aircraft. the Aviation History Online Museum Design and development Bell used the fuselage of a glider with the wing of a and the landing gear of a helicopter. Two thrust |
Sud-Ouest S
Sud-Ouest (French for southwest) may refer to: Places * Sud-Ouest Region (Burkina Faso), the Burkina Faso region * Sud-Ouest Region (Cameroon), the Cameroon region * Ile du Sud-Ouest, an isle in the Cosmoledo atoll * Le Sud-Ouest, a borough in Montreal, Quebec * Province du Sud-Ouest, the Southwest Province in Cameroon * Rivière du Sud-Ouest, a river in Quebec Companies * ''Sud Ouest'' (newspaper), a newspaper * CIT du Sud-Ouest (CITSO), a bus company * SNCASO (''Société nationale des constructions aéronautiques du sud-ouest''), a French former aircraft manufacturer See also * Southwest (other) Southwest is a compass point. Southwest, south-west, south west, southwestern or south-western or south western may also refer to: * Southwest (direction), an intercardinal direction Geography *South West (Western Australia), one of the nine reg ... * South West France (other) * {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
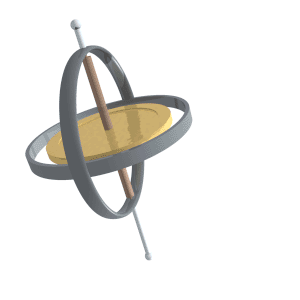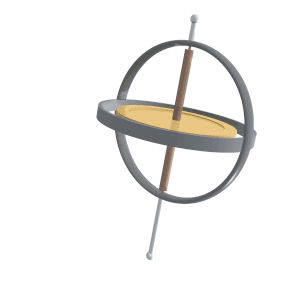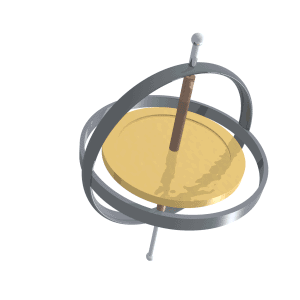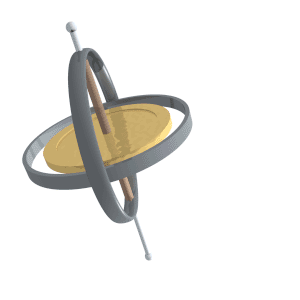
Gyroscopic Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called ''nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, but the angular velocity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
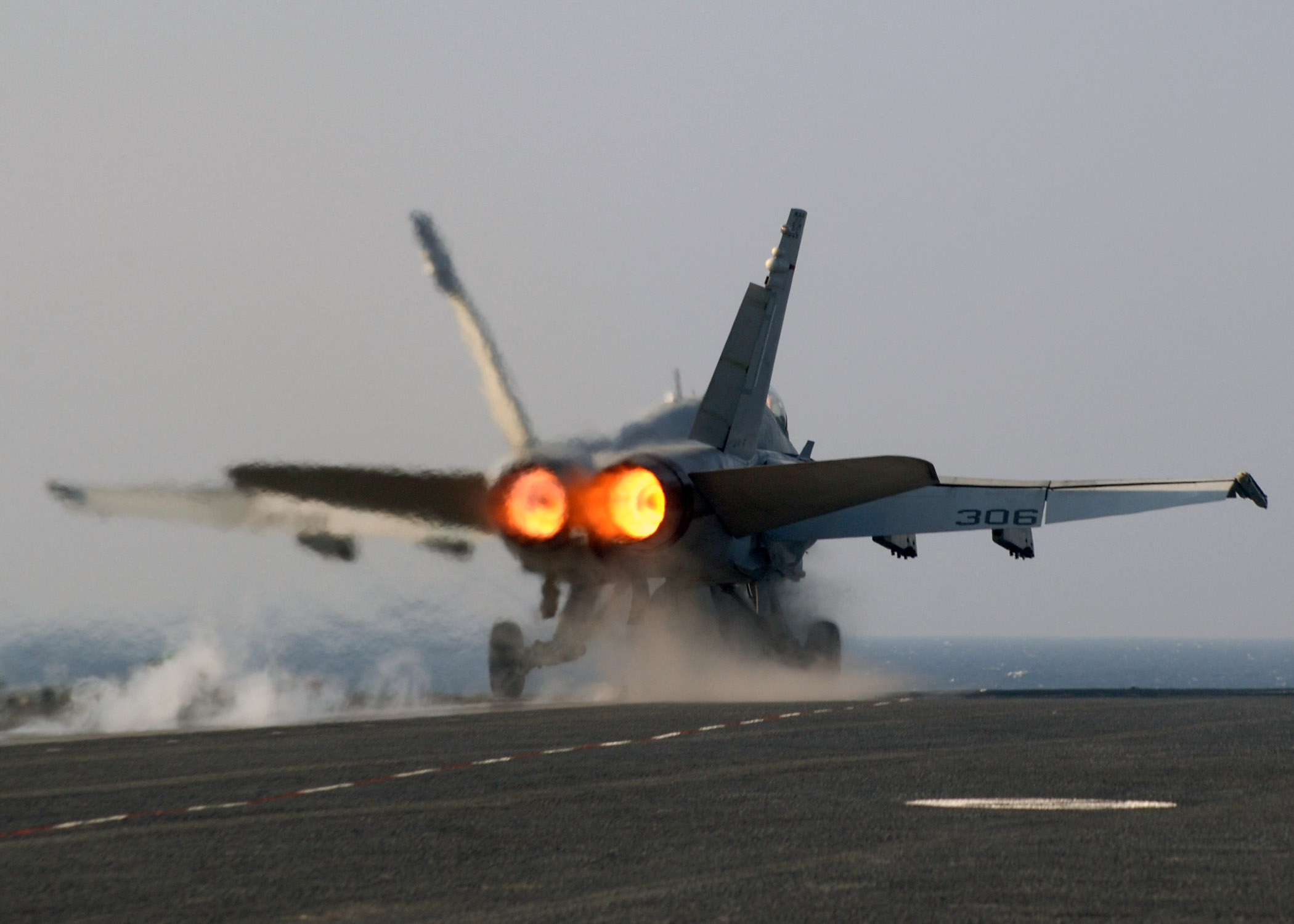
Afterburner
An afterburner (or reheat in British English) is an additional combustion component used on some jet engines, mostly those on military supersonic aircraft. Its purpose is to increase thrust, usually for supersonic flight, takeoff, and combat. The afterburning process injects additional fuel into a combustor in the jet pipe behind (''i.e.'', "after") the turbine, "reheating" the exhaust gas. Afterburning significantly increases thrust as an alternative to using a bigger engine with its attendant weight penalty, but at the cost of increased fuel consumption (decreased fuel efficiency) which limits its use to short periods. This aircraft application of "reheat" contrasts with the meaning and implementation of "reheat" applicable to gas turbines driving electrical generators and which reduces fuel consumption. Jet engines are referred to as operating ''wet'' when afterburning and ''dry'' when not. An engine producing maximum thrust wet is at ''maximum power,'' while an engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auto-Cycle Union
The Auto-Cycle Union (ACU) is the governing body of motorcycle sport in Great Britain, including the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man, but excluding Northern Ireland.About the ACU (official website) Retrieved 14 September 2015 History The ACU was founded in 1903 with the name of the Auto-Cycle Club, as a branch of the Automobile Club of Great Britain (later to become the ). Its aim was to develop motor sport through clubs and arrange touring facilities for members. The ACU acquired its current name in 1907,[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_c1962.jpg)




.jpg)