|
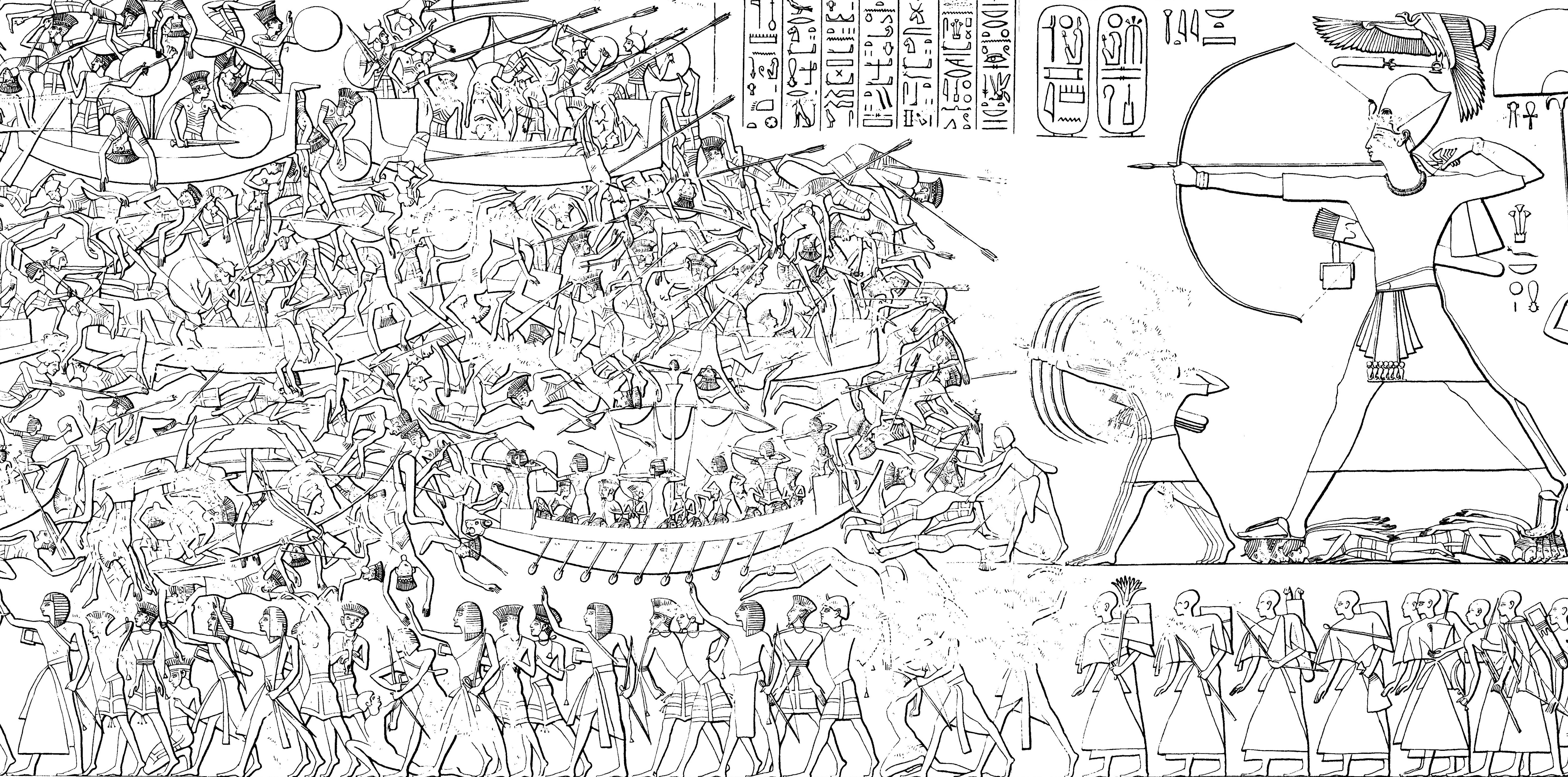
Tudḫaliya IV
Tudhaliya IV was a king of the Hittite Empire (New kingdom), and the younger son of Hattusili III. He reigned c. 1245–1215 BC (middle chronology) or c. 1237–1209 BC (short chronology). His mother was the great queen, Puduhepa. Biography Tudhaliya was likely born in his father's court in Hattusa, after his brother and crown prince Nerikkaili, but still while their father was governing on his brother Muwatalli II's behalf. He was a good friend of Muwatalli's son, Kurunta, and Hattusili ordered that they stay on good terms. After Hattusili as King wrote up a treaty with "Ulmi-Tessup" which confirmed Kurunta's rule over Tarhuntassa, Hattusili elevated Tudhaliya over his older brother to be his crown prince. Tudhaliya as king drew up a bronze tablet treaty confirming the links between him and Kurunta. During his reign, 13 dams were built after a severe drought, one of which still survives to this day at Alacahöyük] He suffered a severe defeat at the hands of Tukulti-Ninurta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hittite Kings
The dating and sequence of the Hittites, Hittite kings is compiled from fragmentary records, supplemented by the recent find in Hattusa of a cache of more than 3500 seal impressions giving names and titles and genealogy of Hittite kings. All dates given here are approximate, relying on synchronisms with known Chronology of the ancient Near East, chronologies for neighbouring countries and Egypt. All reign lengths are approximate. The list uses the middle chronology, the most generally accepted Chronology of the ancient Near East, chronology of the Ancient Near East and the chronology that accords best with Hittite evidence. Old Kingdom (c. 1650–1500 BC) Middle Kingdom (c. 1500–1420 BC) New Kingdom (c. 1420–1190 BC) See also *List of Neo-Hittite kings, for the rulers of the Neo-Hittite states, some of whom were direct descendants of the Hittite kings **The rulers of Carchemish in particular presented themselves as successors of the Hittite kings and ruled in northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurunta
Kurunta (Cuneiform: ) was younger son of the early 13th century BC Hittite king Muwatalli II and cousin of Tudhaliya IV. Kurunta was thereby a Hittite prince and king of Tarhuntassa country. It has been suggested that he may have captured the Hittite capital for a very short time during the reign of the Hittite king Tuthaliya IV and declared himself a great king. Name His Luwian name ''Kurunta'' was after one of the patron gods in the Hittite pantheon. As is customary for late Hittite princes, the Kurunta had also a Hurrian name ''Ulmi-Teššup'' (spelled also''Ulmi-Teshup"''). The names of the gods and the monarchs are derived from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*ker-'', meaning 'head', 'horn'. In the Anatolian branch, the root originated Hittite ''kara=war-'' and Cuneiform Luwian ''zarwaniya'' ('pertaining to horn'). Life Most of the information about Kurunta is known from two treaties concluded between Hittite state and kingdom of Tarhuntassa. His name is also mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittite King
The dating and sequence of the Hittite kings is compiled from fragmentary records, supplemented by the recent find in Hattusa of a cache of more than 3500 seal impressions giving names and titles and genealogy of Hittite kings. All dates given here are approximate, relying on synchronisms with known chronologies for neighbouring countries and Egypt. All reign lengths are approximate. The list uses the middle chronology, the most generally accepted chronology of the Ancient Near East and the chronology that accords best with Hittite evidence. Old Kingdom (c. 1650–1500 BC) Middle Kingdom (c. 1500–1420 BC) New Kingdom (c. 1420–1190 BC) See also *List of Neo-Hittite kings, for the rulers of the Neo-Hittite states, some of whom were direct descendants of the Hittite kings **The rulers of Carchemish in particular presented themselves as successors of the Hittite kings and ruled in northern Syria until defeated by the Assyrians in 717 BC. *History of the Hittites *Tawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kültepe , Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia (around 1650 BC). This empire reached its height during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed an area that included most of Anatolia as well as parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Empire of Hattusa—in modern times conventionally called the Hittite Empire—came into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empire and the empire of Mitanni for control of the Near East. The Middle Assyrian Empire eventually emerged as the dominant power and annexed much of the Hittite Empire, while the remainder was sacked by Phrygian newcomers to the region. After BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse, the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea People
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near East, in particular Egypt, eastern Libya, the Balkans, the Aegean, Anatolia, and the Caucasus. It was sudden, violent, and culturally disruptive for many Bronze Age civilizations, and it brought a sharp economic decline to regional powers, notably ushering in the Greek Dark Ages. The palace economy of Mycenaean Greece, the Aegean region, and Anatolia that characterized the Late Bronze Age disintegrated, transforming into the small isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages, which lasted from around 1100 to the beginning of the better-known Archaic age around 750 BC. The Hittite Empire of Anatolia and the Levant collapsed, while states such as the Middle Assyrian Empire in Mesopotamia and the New Kingdom of Egypt survived but wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maathorneferure
Maathorneferure was an ancient Egyptian queen, the Great Royal Wife of Ramesses II. Family Maathorneferure was a daughter of the Hittite king Hattusili III and his wife, Queen Puduhepa. She was the sister of the crown prince Nerikkaili of Hatti and the sister of the later Hittite king Tudhaliya IV. Maathorneferure was married to the Egyptian Pharaoh Ramesses II in the 34th year of his reign, becoming the King's Great Wife. Her original name is unknown, but her Egyptian name translates as "One who sees Horus, the invisible splendor of Ra". Life Egypt and the Hittite empire had been increasingly at odds since the demise of the kingdom of the Mitanni, and Maathorneferure's marriage to the Egyptian king was the conclusion of the peace process which had begun with the signing of a peace treaty thirteen years earlier. On the Marriage Stela it is claimed that "The daughter of the great chief of Kheta marched in rontof the army .. The Hittite princess le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nihriya
The Battle of Niḫriya was the culminating point of the hostilities between the Hittites and the Assyrians for control over the remnants of the former empire of Mitanni. When Hittite king Šuppiluliuma I (r. c. 1344–1322 BC) conquered Mitanni, he created two provinces (Aleppo and Carchemish), and distributed the large part of territories of this kingdom between his allies. The rest of what had been the empire of Mitanni retained its independence as a Hittite vassal state called Ḫanigalbat. During the reign of the Hittite king Mursili III (better known as Urḫi-Tešub), Ḫanigalbat was conquered by the Assyria Empire and the Assyrians controlled the East bank of the Euphrates. When Ḫattusili III ousted his nephew Urḫi-Tešub and seized the Hittite throne, he had to be content with the permanent loss of Ḫanigalbat to the Assyrians despite its former status as a Hittite vassal state. The Assyrian involvement in Syria continued under the command of king Sulmanu-ašared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tukulti-Ninurta I
Tukulti-Ninurta I (meaning: "my trust is in he warrior god Ninurta"; reigned 1243–1207 BC) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. He is known as the first king to use the title "King of Kings". Biography Tukulti-Ninurta I succeeded Shalmaneser I, his father, as king and won a major victory against the Hittite Empire at the Battle of Nihriya in the first half of his reign, appropriating Hittite territory in Asia Minor and the Levant. Tukulti-Ninurta I retained Assyrian control of Urartu, and later defeated Kashtiliash IV, the Kassite king of Babylonia, and captured the rival city of Babylon to ensure full Assyrian supremacy over Mesopotamia. He set himself up as king of Babylon, thus becoming the first native Mesopotamian to rule there, its previous kings having all been non-native Amorites or Kassites. He took on the ancient title "King of Sumer and Akkad" first used by Ur-Nammu. Tukulti-Ninurta had petitioned the god Shamash before beginning his counter off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muwatalli II
:''See also Muwatalli I'' Muwatalli II (also Muwatallis, or Muwatallish) was a king of the New Kingdom of the Hittite empire c. 1295–1282 (middle chronology) and 1295–1272 BC in the short chronology. Biography He was the eldest son of Mursili II and Queen Gassulawiya, and he had several siblings. He is best known for relocating the Hittite capital to Tarhuntassa, appointing his brother Hattusili as governor in Hattusa, and fighting Ramesses II in the Battle of Kadesh. A copy of a treaty has been recovered between him and Alaksandu, ruler of Wilusa (Troy), one of the Arzawa lands. Egyptologists suspect that some time prior to Ramesses II's accession to the Egyptian throne, Muwattalli had reached an informal peace treaty or understanding with Seti I over Kadesh to avoid a clash between the two powers over control of Syria. In it, Seti effectively ceded Kadesh to the Hittite king in order to focus on domestic issues in Egypt. Muwatalli had a wife named Tanu-Ḫepa and at le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |