|
Tsunami Deposit
A tsunami deposit (the term tsunamiite is also sometimes used) is a sedimentary unit deposited as the result of a tsunami. Such deposits may be left onshore during the inundation phase or offshore during the 'backwash' phase. Such deposits are used to identify past tsunami events and thereby better constrain estimates of both earthquake and tsunami hazards. There remain considerable problems, however, in distinguishing between deposits caused by tsunamis and those caused by storms or other sedimentary processes. Tsunamiite The term "tsunamiite" or "tsunamite" was introduced in the 1980s to describe deposits interpreted to have been formed by traction processes associated with tsunamis and is particularly used for marine deposits formed during the "backwash" phase. The term's application has broadened to encompass all tsunami-related deposits, but its use has been challenged. The main criticism of the term is that it describes deposits that have formed by many different processes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsunami Deposit Environments
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
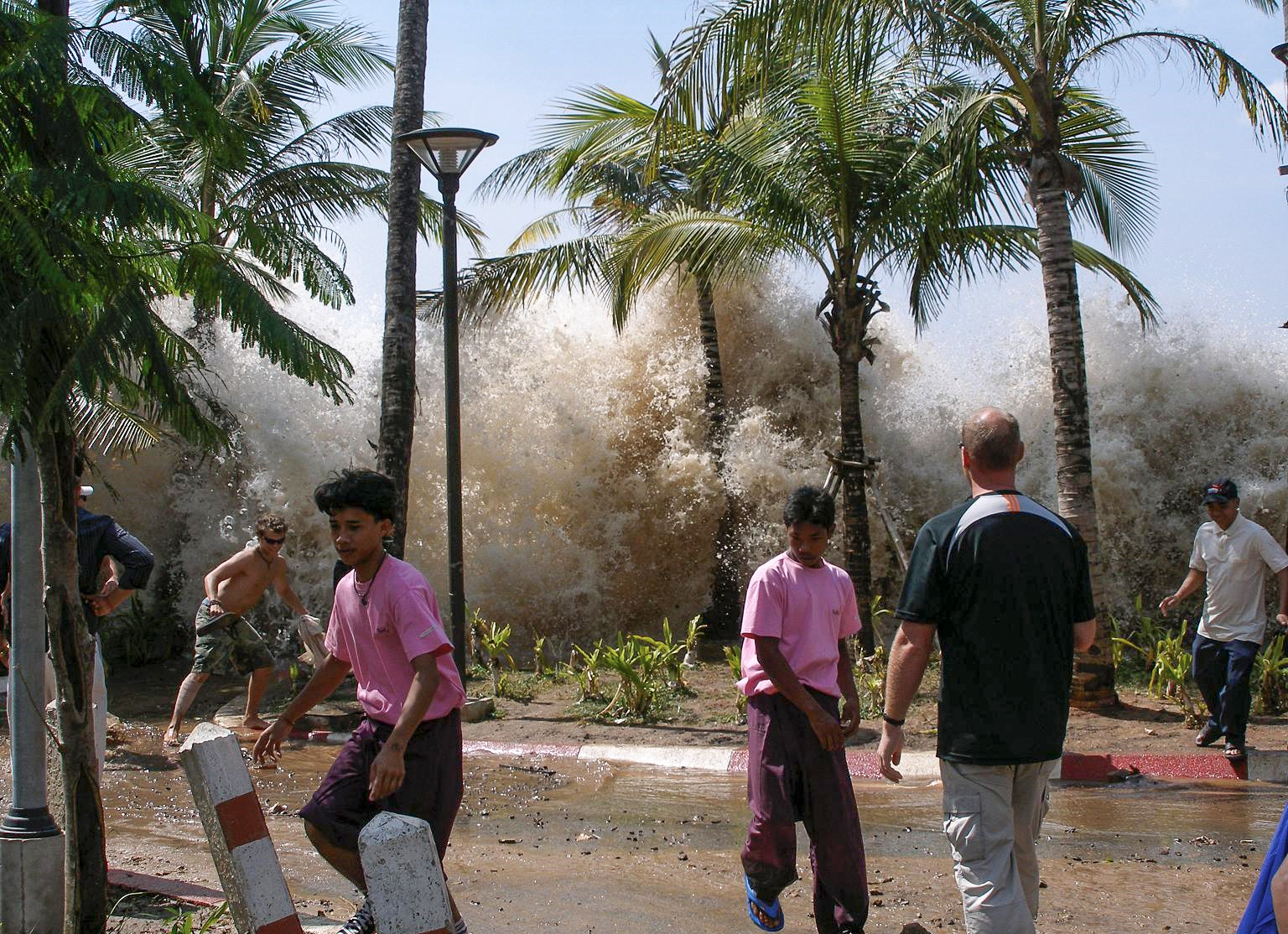
Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washover
Overwash is the flow of water and sediment over a coastal dune or beach crest during storm events (or other situations with high water). 'Overwash' may refer only to the landward flux of water due to overtopping of a dune system while 'washover' may refer to the sediment deposited by overwash. A common process on barrier islands, Overwash redistributes sediment and facilitates the migration of barrier islands in response to sea level rise. Overwash can occur as a result of runup (the maximum height of the swash), or inundation. Deposition from overwash (washover) can be deposited onto the beach berm, the dune, or as far as the back barrier bay, marsh, estuary, or lagoon. Sediment deposits created during overwash exhibit consistent scaling — for example, the distance inland that an overwash deposit extends is proportional to the area that the overwash deposit covers. The distance inland that an overwash deposit extends is also correlated with the volume of sand deposited. The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
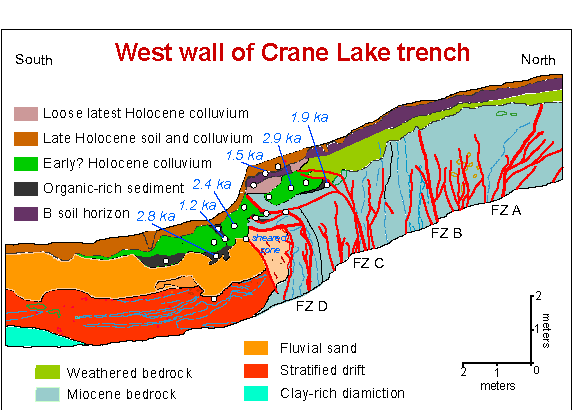
Paleoseismology
Paleoseismology looks at geologic sediments and rocks, for signs of ancient earthquakes. It is used to supplement seismic monitoring, for the calculation of seismic hazard. Paleoseismology is usually restricted to geologic regimes that have undergone continuous sediment creation for the last few thousand years, such as swamps, lakes, river beds and shorelines. In this typical example, a trench is dug in an active sedimentation regime. Evidence of thrust faulting can be seen in the walls of the trench. It becomes a matter of deducting the relative age of each fault, by cross-cutting patterns. The faults can be dated in absolute terms, if there is dateable carbon, or human artifacts. Many notable discoveries have been made using the techniques of paleoseismology. For example, there is a common misconception that having many smaller earthquakes can somehow 'relieve' a major fault such as the San Andreas Fault, and reduce the chance of a major earthquake. It is now known ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
869 Jogan Sanriku Earthquake
__NOTOC__ Year 869 ( DCCCLXIX) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Summer – Emperor Basil I allies with the Frankish emperor Louis II against the Saracens. He sends a Byzantine fleet of 400 ships (according to the ''Annales Bertiniani''), under the command of Admiral Niketas Ooryphas, to support Louis (who is besieging the city port of Bari) and to clear the Adriatic Sea of Muslim raiders. * The Hagia Sophia Basilica (church) in Constantinople suffers great damage during an earthquake, which makes the eastern half-dome collapse. Basil I orders it to be repaired. Europe * August 8 – Lothair II, King of Middle Francia ( Lotharingia), dies at Piacenza, on his way home from meeting Pope Adrian II at Rome, to get assent for a divorce. Lotharingia is subsequently divided between Lothair's uncles, Charles the Bald of France and Louis the German. Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Return Period
A return period, also known as a recurrence interval or repeat interval, is an average time or an estimated average time between events such as earthquakes, floods, landslides, or river discharge flows to occur. It is a statistical measurement typically based on historic data over an extended period, and is used usually for risk analysis. Examples include deciding whether a project should be allowed to go forward in a zone of a certain risk or designing structures to withstand events with a certain return period. The following analysis assumes that the probability of the event occurring does not vary over time and is independent of past events. Estimating a return period Recurrence interval = :''n'' number of years on record; :''m'' is the rank of observed occurrences when arranged in descending order For floods, the event may be measured in terms of m3/s or height; for storm surges, in terms of the height of the surge, and similarly for other events.This is the Weibull's For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEPCO
, also known as or TEPCO, is a Japanese electric utility holding company servicing Japan's Kantō region, Yamanashi Prefecture, and the eastern portion of Shizuoka Prefecture. This area includes Tokyo. Its headquarters are located in Uchisaiwaicho, Chiyoda, Tokyo, and international branch offices exist in Washington, D.C., and London. It is a founding member of strategic consortiums related to energy innovation and research; such as JINED, INCJ and MAI. In 2007, TEPCO was forced to shut the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant after the Niigata-Chuetsu-Oki earthquake. That year it posted its first loss in 28 years. Corporate losses continued until the plant reopened in 2009. Following the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, one of its power plants was the site of one of the world's most serious ongoing nuclear disaster, the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. TEPCO could face ¥ ($) in special losses in the current business year to March 2012, and the Japanese go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant
The is a disabled nuclear power plant located on a site in the towns of Ōkuma and Futaba in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The plant suffered major damage from the magnitude 9.0 earthquake and tsunami that hit Japan on March 11, 2011. The chain of events caused radiation leaks and permanently damaged several of its American-designed reactors, making them impossible to restart. By political decision, the remaining reactors were not restarted. First commissioned in 1971, the plant consists of six American-designed boiling water reactors. These light water reactors drove electrical generators with a combined power of 4.7 GWe, making Fukushima Daiichi one of the 15 largest nuclear power stations in the world. Fukushima was the first nuclear plant to be designed, constructed, and run in conjunction with General Electric and Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO). The March 2011 disaster disabled the reactor cooling systems, leading to releases of radioactivity and tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Tōhoku Earthquake And Tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the , among other names. The disaster is often referred to in both Japanese and English as simply 3.11 (read in Japanese). It was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan, and the fourth most powerful earthquake in the world since modern record-keeping began in 1900. The earthquake triggered powerful tsunami waves that may have reached heights of up to in Miyako in Tōhoku's Iwate Prefecture, Yomiuri Shimbun evening edition 2-11-04-15 page 15, nearby Aneyoshi fishery port (姉吉漁港)(Google map E39 31 57.8, N 142 3 7.6) 2011-04-15大震災の津波、宮古で38.9 m…明治三陸上回るby okayasu Akio (岡安 章夫) and which, in the Sendai area, traveled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |