|
Tsakonia
Tsakonia ( ell, Τσακωνιά) or the Tsakonian region () refers to the small area in the eastern Peloponnese where the Tsakonian language is spoken, in the area surrounding 13 towns, villages and hamlets located around Pera Melana in Arcadia. It is not a formally defined political entity of the modern Greek state. Extent In his ''Brief Grammar of the Tsakonian Dialect'' published in 1951, Prof. Thanasis Costakis defines Tsakonia as the area from the town of Agios Andreas in Kynouria south to Leonidio and Tyros and inland as far as Kastanitsa and Sitaina, but asserts that in former times the Tsakonian-speaking area extended as far as Cape Malea in eastern Laconia. The principal town in Tsakonia at this time was Prastos, which benefited from a special trading privilege granted by the authorities in Constantinople. Prastos was burned by Ibrahim Pasha in the Greek War of Independence and was abandoned, with many of its residents fleeing to the area around Leonidio and Tyros or ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsakonian Language
Tsakonian or Tsaconian (also Tzakonian or Tsakonic, Greek and Tsakonian: , ) is a highly divergent modern variety of Greek, spoken in the Tsakonian region of the Peloponnese, Greece. Tsakonian derives from Doric Greek, being its only extant variant. Although it is conventionally treated as a dialect of Greek, some compendia treat it as a separate language. Tsakonian is critically endangered, with only a few hundred/thousand, mostly elderly, fluent speakers left. Although Tsakonian and standard Modern Greek are related, they are not mutually intelligible. Etymology The term Tsakonas or Tzakonas first emerges in the writings of Byzantine chroniclers who derive the ethnonym from a corruption of Lakonas, a Laconian/Lacedaemonian (Spartan)—a reference to the Doric roots of the Tsakonian language. Geographic distribution Tsakonian is found today in a group of mountain towns and villages slightly inland from the Argolic Gulf, although it was once spoken farther to the south and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonidio
Leonidio ( el, Λεωνίδιο, Katharevousa: Λεωνίδιον, Tsakonian: Αγιελήδι) is a town and a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality South Kynouria, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 418.65 km2, the community 102.67 km2. It is considered a traditional settlement. Name In the local Tsakonian language, the only surviving descendant of Doric Greek, the town is called ''Agie Lidi''.*. Page 19. Landscape The town of Leonidio, with a population of 3,826, emerges from a spectacular landscape, bound by two abrupt mountainsides enclosing the town from the north and south. The River Dafnon passes through the town, and its banks are linked with three bridges. The town is capital of the Tsakonia region, notable for its cultural and linguistic particularities, and the settlement itself offers striking and picturesque architecture; now a protected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanasis Costakis
Thanasis Costakis ( el, Θανάσης Κωστάκης, 1907–2009) was a Greek linguist and lexicographer best known for his work on the now-moribund Tsakonian language spoken in the eastern Peloponnese. Costakis was born in Pera Melana in Arcadia, a Tsakonian-speaking village. Costakis taught at several gymnasia and lycea in Athens before affiliating with the Academy of Athens (modern), where he contributed to the composition of the Historical Lexicon of Modern Greek. In addition to his linguistic works, he also published a volume on the traditional architecture of Tsakonia. Costakis also developed a writing system for the Tsakonian language, which included orthography using dots, ''spiritus asper'', and caron A caron (), háček or haček (, or ; plural ''háčeks'' or ''háčky'') also known as a hachek, wedge, check, kvačica, strešica, mäkčeň, varnelė, inverted circumflex, inverted hat, flying bird, inverted chevron, is a diacritic mark (� ... for use in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
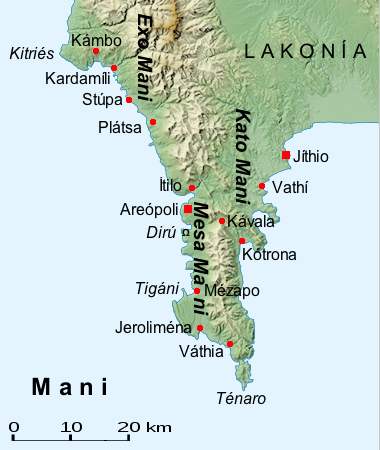
Maniot Dialect
The Maniots or Maniates ( el, Μανιάτες) are the inhabitants of Mani Peninsula, located in western Laconia and eastern Messenia, in the southern Peloponnese, Greece. They were also formerly known as Mainotes and the peninsula as ''Maina''. The Maniots claim to be the descendants of the ancient Spartans and they have often been described as such. The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible (until recently many Mani villages could be accessed only by sea), and the regional name "Mani" is thought to have meant originally "dry" or "barren". The name "Maniot" is a derivative meaning "of Mani". In the early modern period, Maniots had a reputation as fierce and proudly independent warriors, who practiced piracy and fierce blood feuds. For the most part, the Maniots lived in fortified villages (and "house-towers") where they defended their lands against the armies of William II Villehardouin and later against those of the Ottoman Empire. Names The surnames of the Maniots unifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maniots
The Maniots or Maniates ( el, Μανιάτες) are the inhabitants of Mani Peninsula, located in western Laconia and eastern Messenia, in the southern Peloponnese, Greece. They were also formerly known as Mainotes and the peninsula as ''Maina''. The Maniots claim to be the descendants of the ancient Spartans and they have often been described as such. The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible (until recently many Mani villages could be accessed only by sea), and the regional name "Mani" is thought to have meant originally "dry" or "barren". The name "Maniot" is a derivative meaning "of Mani". In the early modern period, Maniots had a reputation as fierce and proudly independent warriors, who practiced piracy and fierce blood feuds. For the most part, the Maniots lived in fortified villages (and "house-towers") where they defended their lands against the armies of William II Villehardouin and later against those of the Ottoman Empire. Names The surnames of the Maniots unif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, , or , ''Kiní Neoellinikí Glóssa''), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the languages sometimes referred to as Standard Modern Greek. The end of the Medieval Greek period and the beginning of Modern Greek is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic features of the modern language arose centuries earlier, beginning around the fourth century AD. During most of the Modern Greek period, the language existed in a situation of diglossia, with regional spoken dialects existing side by side with learned, more archaic written forms, as with the vernacular and learned varieties (''Dimotiki'' and ''Katharevousa'') that co-existed in Greece throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Varieties Varieties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastanitsa
Kastanitsa ( el, Καστάνιτσα, Tsakonian: Γαστένιτσα) is a village in Arcadia in Greece, on the southern slope of Mount Parnon. It is considered a traditional settlement. It is noted for its production of chestnuts, from which it takes its name, and for formerly being a majority Tsakonian-speaking settlement. History Kastanitsa is first mentioned in writing in 1293, but the settlement is thought to be nearly two centuries older, founded by Tsakones fleeing the rule of Slavic tribes that had invaded the Peloponnese. According to Kastaniot tradition, the village was founded by two families called Pentalonas and Bezenikos. A Byzantine fort called ''Koutoupou'' was placed on the nearby hill of ''Pyrgos'' while the restored Byzantine monarchy warred with the Frankish lords of the Peloponnese to recover territory lost in the wake of the Fourth Crusade. Further documentary evidence is scant until the eighteenth century. In 1788, a French traveller named Villehouso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
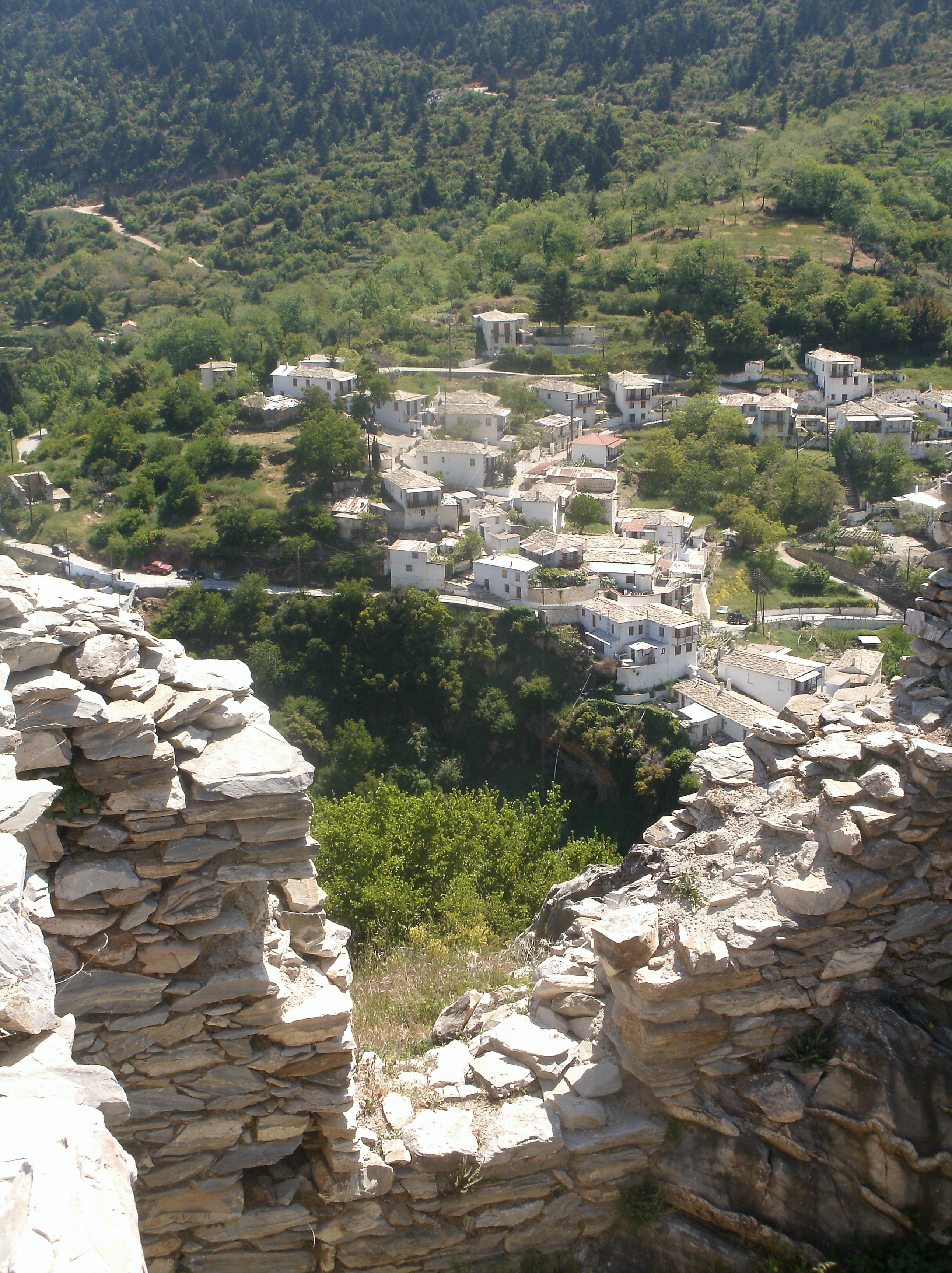
Prastos
Prastos ( el, Πραστός, Tsakonian: Πραστέ) is a settlement in Arcadia, Greece. Formerly, Prastos was the premier town of the Tsakonian region, but declined in importance after its devastation by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt during the Greek War of Independence and a general economic migration to urban areas that occurred in the following decades. It is considered a traditional settlement. History During the Ottoman period, Prastos was the leading city of Tsakonia, and one of the richest in the Peloponnese. The inhabitants had special trading rights granted by the Sublime Porte, which contributed to the town's economic success. It was the seat of a bishopric, that of "Rheoi and Prastos." During the Greek War of Independence, the town was sacked by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt and its olive groves burned, making the settlement unsuitable for habitation for decades hence. Much of the surviving population fled to Leonidio and the Argolid and could not be persuaded to return to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsakonikos
The Tsakonikos or Tsakonikos horos ( el, Τσακώνικος χορός "Tsakonian dance") is a dance performed in the Peloponnese in Greece. It comes from the region, chiefly in Arcadia, known as Tsakonia. It is danced in many towns and villages there with little variation to the steps. In Ayios Andreas, it is performed as a mixed dance in an open circle, with the hands held up (αγκαζέ ''angaze'', in Greek). The most popular songs for the ''tsakonikos'' are "''Sou ipa mana kale mana''" and "''Kinisan ta tsamopoula''". The dance is performed to a (3+2) rhythm in an open circle which slowly winds in upon itself, forming a snail-shaped design. This labyrinthine formation is, according to legend, linked to the Crane dance of Theseus in Greek mythology, who slew the Minotaur in the Labyrinth of King Minos. It has also been linked to the slaying by Apollo of the Python at Delphi. Song words to the Tsakonikos Dance ΚΙΝΗΣΑΝΤΑ Κινῆσαν τὰ - κι ἀμὰν ἀ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. They also form a significant diaspora (), with Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire of the late 11th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyros, Greece
Tyros ( el, Τυρός, Tsakonian: Τερέ) is a tourist and old naval town in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. It is located 19 km north of Leonidio, 26 km southeast of Astros and 71 km southeast of Tripoli, lying in the heart of Kynouria, between the Parnon mountains and the Myrtoan Sea. It is considered a traditional settlement. Since the 2011 Greek government reform it is part of the municipality South Kynouria, of which it forms the municipal unit of Tyros. The municipal unit has an area of 88.567 km2. At the 2011 census, the population of the municipal unit was 2,063. The municipal unit consists of the communities Tyros, Sapounakaiika and Pera Melana. In the region, the Tsakonian language used to be spoken. It originates from the ancient Doric dialect and is nowadays in danger of becoming extinct. In Tyros, every Easter one of the most famous Greek traditions takes place. On Good Friday a procession of the Epitaph is held on the coastal road of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kynouria
Cynuria ( – ''Kynouria'' or – ''Kynouriake'') is an ancient district on the eastern coast of the Peloponnese, between the Argolis and Laconia, so called from the Cynurians, one of the most ancient tribes in the peninsula. It was believed to have taken its name from the mythical Cynurus. Location and history Herodotus regarded the Cynurians as autochthones, but at the same time called them Ionians. There can be little doubt, however, that they were Pelasgians; but in consequence of their maritime position, they were regarded as a different race from the Arcadian Pelasgians, and came to be looked upon as Ionians, which was the case with the Pelasgians dwelling upon the coast of the Gulf of Corinth, in the district afterwards called Achaia. They were a semi-barbarous and predatory tribe, dwelling chiefly in the eastern slopes of Mount Parnon; but their exact boundaries cannot be defined, as they were only a tribe, and never formed a political body. At a later time they were alm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
