|
Truncation Selection
Truncation selection is a selection method in selective breeding and in evolutionary algorithms from computer science, which selects a certain share of fittest individuals from a population for reproduction in the next generation. Animal and plant breeding In animal and plant breeding, truncation selection is a standard method. Animals are ranked by their phenotypic value on some trait such as milk production, and the top percentage is reproduced. The effects of truncation selection for a continuous trait can be modeled by the standard breeder's equation by using heritability and truncated normal distributions. On a binary trait, it can be modeled easily using the liability threshold model. It is considered an easy and efficient method of breeding. Computer science In computer science, truncation selection is a selection method used in evolutionary algorithm Evolutionary algorithms (EA) reproduce essential elements of the biological evolution in a computer algorithm in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Selective Breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. Domesticated animals are known as breeds, normally bred by a professional breeder, while domesticated plants are known as varieties, cultigens, cultivars, or breeds. Two purebred animals of different breeds produce a crossbreed, and crossbred plants are called hybrids. Flowers, vegetables and fruit-trees may be bred by amateurs and commercial or non-commercial professionals: major crops are usually the provenance of the professionals. In animal breeding artificial selection is often combined with techniques such as inbreeding, linebreeding, and outcrossing. In plant breeding, similar methods are used. Charles Darwin discussed how selective breeding had been succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Evolutionary Algorithm
Evolutionary algorithms (EA) reproduce essential elements of the biological evolution in a computer algorithm in order to solve "difficult" problems, at least Approximation, approximately, for which no exact or satisfactory solution methods are known. They belong to the class of Metaheuristic, metaheuristics and are a subset of Population Based Bio-Inspired Algorithms, population based bio-inspired algorithms and evolutionary computation, which itself are part of the field of computational intelligence. The mechanisms of biological evolution that an EA mainly imitates are reproduction, mutation, genetic recombination, recombination and natural selection, selection. Candidate solutions to the optimization problem play the role of individuals in a population, and the fitness function determines the quality of the solutions (see also loss function). Evolution of the population then takes place after the repeated application of the above operators. Evolutionary algorithms often perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Animal Breeding
Animal breeding is a branch of animal science that addresses the evaluation (using best linear unbiased prediction and other methods) of the genetic value (estimated breeding value, EBV) of livestock. Selecting for breeding animals with superior EBV in growth rate, egg, meat, milk, or wool production, or with other desirable traits has revolutionized livestock production throughout the entire world. The scientific theory of animal breeding incorporates population genetics, quantitative genetics, statistics, and recently molecular genetics and is based on the pioneering work of Sewall Wright, Jay Lush, and Charles Henderson. Breeding stock Breeding stock is a group of animals used for the purpose of planned breeding. When individuals are looking to breed animals, they look for certain valuable traits in purebred animals, or may intend to use some type of crossbreeding to produce a new type of stock with different, and presumably superior abilities in a given area of endea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plant Breeding
Plant breeding is the science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. It is used to improve the quality of plant products for use by humans and animals. The goals of plant breeding are to produce crop varieties that boast unique and superior traits for a variety of applications. The most frequently addressed agricultural traits are those related to biotic and abiotic stress tolerance, grain or biomass yield, end-use quality characteristics such as taste or the concentrations of specific biological molecules (proteins, sugars, lipids, vitamins, fibers) and ease of processing (harvesting, milling, baking, malting, blending, etc.). Plant breeding can be performed using many different techniques, ranging from the selection of the most desirable plants for propagation, to methods that make use of knowledge of genetics and chromosomes, to more complex molecular techniques. Genes in a plant are what determine what type of qualitative or quantitativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
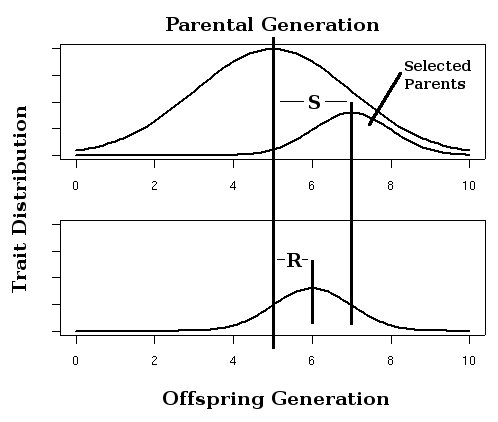
Breeder's Equation
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. The concept of heritability can be expressed in the form of the following question: "What is the proportion of the variation in a given trait within a population that is ''not'' explained by the environment or random chance?" Other causes of measured variation in a trait are characterized as environmental factors, including observational error. In human studies of heritability these are often apportioned into factors from "shared environment" and "non-shared environment" based on whether they tend to result in persons brought up in the same household being more or less similar to persons who were not. Heritability is estimated by comparing individual phenotypic variation among related individuals in a population, by examining the association between individ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heritability
Heritability is a statistic used in the fields of Animal husbandry, breeding and genetics that estimates the degree of ''variation'' in a phenotypic trait in a population that is due to genetic variation between individuals in that population. The concept of heritability can be expressed in the form of the following question: "What is the proportion of the variation in a given trait within a population that is ''not'' explained by the environment or random chance?" Other causes of measured variation in a trait are characterized as environment (biophysical), environmental factors, including observational error. In human studies of heritability these are often apportioned into factors from "shared environment" and "non-shared environment" based on whether they tend to result in persons brought up in the same household being more or less similar to persons who were not. Heritability is estimated by comparing individual phenotypic variation among related individuals in a population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truncated Normal Distribution
In probability and statistics, the truncated normal distribution is the probability distribution derived from that of a normally distributed random variable by bounding the random variable from either below or above (or both). The truncated normal distribution has wide applications in statistics and econometrics. Definitions Suppose X has a normal distribution with mean \mu and variance \sigma^2 and lies within the interval (a,b), \text \; -\infty \leq a < b \leq \infty . Then conditional on has a truncated normal distribution. Its , , for , is given by and by otherwise. Here, |
Liability Threshold Model
In mathematical or statistical modeling a threshold model is any model where a threshold value, or set of threshold values, is used to distinguish ranges of values where the behaviour predicted by the model varies in some important way. A particularly important instance arises in toxicology, where the model for the effect of a drug may be that there is zero effect for a dose below a critical or threshold value, while an effect of some significance exists above that value.Dodge, Y. (2003) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', OUP. Certain types of regression model may include threshold effects. Collective behavior Threshold models are often used to model the behavior of groups, ranging from social insects to animal herds to human society. Classic threshold models were introduced by Sakoda, in his 1949 dissertation and the Journal of Mathematical Sociology (JMS vol 1 #1, 1971). They were subsequently developed by Schelling, Axelrod, and Granovetter to model collectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Selection (genetic Algorithm)
Selection is a genetic operator in an evolutionary algorithm (EA). An EA is a metaheuristic inspired by Evolution, biological evolution and aims to solve challenging problems at least Approximation, approximately. Selection has a dual purpose: on the one hand, it can choose individual genomes from a population for subsequent breeding (e.g., using the Crossover (genetic algorithm), crossover operator). In addition, selection mechanisms are also used to choose candidate solutions (individuals) for the next generation. The biological model is natural selection. Retaining the best individual(s) of one generation unchanged in the next generation is called ''elitism'' or ''elitist selection''. It is a successful (slight) variant of the general process of constructing a new population. The basis for selection is the quality of an individual, which is determined by the fitness function. In Memetic algorithm, memetic algorithms, an extension of EA, selection also takes place in the select ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Breeding
Breeding is sexual reproduction that produces offspring, usually animals or plants. It can only occur between a male and a female animal or plant. Breeding may refer to: * Animal husbandry, through selected specimens such as dogs, horses, and rabbits * Breeding in the wild, the natural process of reproduction in the animal kingdom * Sexual reproduction of plants * Plant breeding, through specimens selected by humans for desirable traits Science * Breeding refers to nuclear transmutations that produce fuel for further reactions, in a breeder reactor to become fissile material or in a fusion reactor to produce tritium, see Biology * Breeding (sex act) * Breeding back, a breeding effort to re-assemble extinct breed genes * Breeding pair, bonded animals who cooperate to produce offspring * Breeding program, a planned breeding of animals or plants * Breeding season, the period during each year when a species reproduces * Captive breeding, raising plants or animals in zoos o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |