|
True-range Multilateration
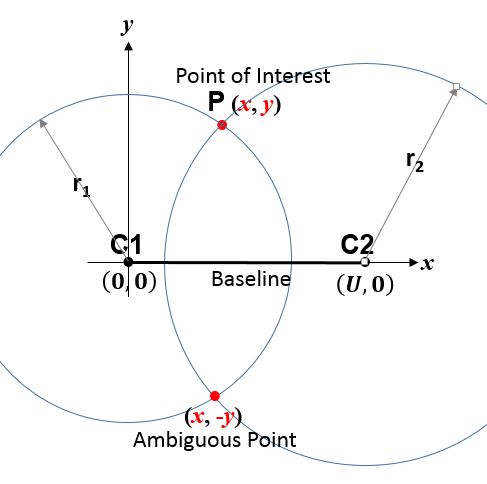
True-range multilateration (also termed range-range multilateration and spherical multilateration) is a method to determine the location of a movable vehicle or stationary point in space using multiple ranges (distances) between the vehicle/point and multiple spatially-separated known locations (often termed "stations"). ''Accuracy limitations of range-range (spherical) multilateration systems'' Harry B. Lee, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Lincoln Laboratory, Report Number: DOT/TSC-RA-3-8-(1) (Technical note 1973-43), Oct. 11, 1973 Energy waves may be involved in determining range, but are not required. True-range multilateration is both a mathematical topic and an applied technique used in several fields. A practical application involving a fixed locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging
Length measurement, distance measurement, or range measurement (ranging) refers to the many ways in which length, distance, or range can be measured. The most commonly used approaches are the rulers, followed by transit-time methods and the interferometer methods based upon the speed of light. For objects such as crystals and diffraction gratings, diffraction is used with X-rays and electron beams. Measurement techniques for three-dimensional structures very small in every dimension use specialized instruments such as ion microscopy coupled with intensive computer modeling. Standard rulers The ruler the simplest kind of length measurement tool: lengths are defined by printed marks or engravings on a stick. The metre was initially defined using a ruler before more accurate methods became available. Gauge blocks are a common method for precise measurement or calibration of measurement tools. For small or microscopic objects, microphotography where the length is calibrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Clocks
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions between such states they interact with a very specific frequency of electromagnetic radiation. This phenomenon serves as the basis for the International System of Units' (SI) definition of a second:The second, symbol s, is the SI unit of time. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, \Delta \nu_\mathsf, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This definition is the basis for the system of International Atomic Time (TAI), which is maintained by an ensemble of atomic clocks around the world. The system of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) that is the basis of civil time implements leap seconds to allow c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercept Method
In astronomical navigation, the intercept method, also known as Marcq St. Hilaire method, is a method of calculating an observer's position on earth (geopositioning). It was originally called the ''azimuth intercept'' method because the process involves drawing a line which intercepts the azimuth line. This name was shortened to ''intercept'' method and the ''intercept distance'' was shortened to 'intercept'. The method yields a line of position (LOP) on which the observer is situated. The intersection of two or more such lines will define the observer's position, called a "fix". Sights may be taken at short intervals, usually during hours of twilight, or they may be taken at an interval of an hour or more (as in observing the Sun during the day). In either case, the lines of position, if taken at different times, must be advanced or retired to correct for the movement of the ship during the interval between observations. If observations are taken at short intervals, a few minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of celestial navigation. The estimation of this angle, the altitude, is known as ''sighting'' or ''shooting'' the object, or ''taking a sight''. The angle, and the time when it was measured, can be used to calculate a position line on a nautical or aeronautical chart—for example, sighting the Sun at noon or Polaris at night (in the Northern Hemisphere) to estimate latitude (with sight reduction). Sighting the height of a landmark can give a measure of ''distance off'' and, held horizontally, a sextant can measure angles between objects for a position on a chart. A sextant can also be used to measure the lunar distance between the moon and another celestial object (such as a star or planet) in order to determine Greenwich Mean Time and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Trigonometry
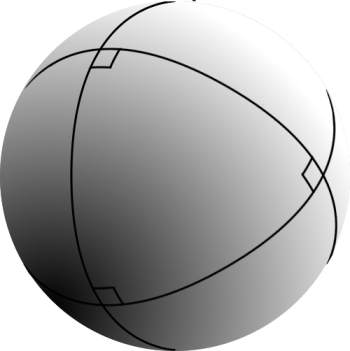
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion methods, and the use of numerical methods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Chronometer
A marine chronometer is a precision timepiece that is carried on a ship and employed in the determination of the ship's position by celestial navigation. It is used to determine longitude by comparing Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), or in the modern world its successor Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), and the time at the current location found from observations of celestial bodies. When first developed in the 18th century, it was a major technical achievement, as accurate knowledge of the time over a long sea voyage was vital for effective navigation, lacking electronic or communications aids. The first true chronometer was the life work of one man, John Harrison, spanning 31 years of persistent experimentation and testing that revolutionized naval (and later aerial) navigation and enabling the Age of Discovery and Colonialism to accelerate. The term '' chronometer'' was coined from the Greek words '' χρόνος (chronos)'' (meaning time) and '' meter'' (meaning measure) in 171 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Moon (annotated) in Arabic and Maltese
{{disambiguation ...
Sun Moon may refer to: *Abbreviation of Korean names with the surname Moon (문) and the generation name Sun (선, Seon): **Sun Myung Moon (1920–2012), founder of the Unification Church **Sun-hee Moon, South Korean voice actress * Sun Moon Lake, Yuchi, Nantou, Taiwan, Republic of China *Sun Moon University, Cheonan, South Korea * Pokémon Sun and Moon See also * Sun and moon *Sun and moon letters In Arabic and Maltese, the consonants are divided into two groups, called the sun letters or solar letters ( ar, حروف شمسية ', mt, konsonanti xemxin) and moon letters or lunar letters (Arabic: ', mt, konsonanti qamrin), based on whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ERAM
The En Route Automation Modernization (ERAM) system architecture replaces the En Route Host computer system and its backup. ERAM provides all of today's functionality and: * Adds new capabilities needed to support the evolution of US National Airspace System * Improves information security and streamlines traffic flow at US international borders * Processes flight radar data * Provides communications support * Generates display data to air traffic controllers * The display system provides real-time electronic aeronautical information and efficient data management. * Provides a fully functional backup system, precluding the need to restrict operations in the event of a primary failure * The backup system provides the National Transportation Safety Board-recommended safety alerts, altitude warnings and conflict alerts. * Improves surveillance by using a greater number and variety of surveillance sources * Detects and alerts air traffic controllers when aircraft are flying too close to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Trilateration
3-D, 3D, or 3d may refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Relating to three-dimensionality * Three-dimensional space ** 3D computer graphics, computer graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data ** 3D film, a motion picture that gives the illusion of three-dimensional perception ** 3D modeling, developing a representation of any three-dimensional surface or object ** 3D printing, making a three-dimensional solid object of a shape from a digital model ** 3D display, a type of information display that conveys depth to the viewer ** 3D television, television that conveys depth perception to the viewer ** Stereoscopy, any technique capable of recording three-dimensional visual information or creating the illusion of depth in an image Other uses in science and technology or commercial products * 3D projection * 3D rendering * 3D scanning, making a digital representation of three-dimensional objects * 3D video game (other) * 3-D Secure, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Transverse Mercator Coordinate System
The Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) is a map projection system for assigning coordinates to locations on the surface of the Earth. Like the traditional method of latitude and longitude, it is a horizontal position representation, which means it ignores altitude and treats the earth as a perfect ellipsoid. However, it differs from global latitude/longitude in that it divides earth into 60 zones and projects each to the plane as a basis for its coordinates. Specifying a location means specifying the zone and the ''x'', ''y'' coordinate in that plane. The projection from spheroid to a UTM zone is some parameterization of the transverse Mercator projection. The parameters vary by nation or region or mapping system. Most zones in UTM span 6 degrees of longitude, and each has a designated central meridian. The scale factor at the central meridian is specified to be 0.9996 of true scale for most UTM systems in use. History The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Cosines
In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula, cosine rule, or al-Kashi's theorem) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Using notation as in Fig. 1, the law of cosines states :c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab\cos\gamma, where denotes the angle contained between sides of lengths and and opposite the side of length . For the same figure, the other two relations are analogous: :a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos\alpha, :b^2=a^2+c^2-2ac\cos\beta. The law of cosines generalizes the Pythagorean theorem, which holds only for right triangles: if the angle is a right angle (of measure 90 degrees, or radians), then , and thus the law of cosines reduces to the Pythagorean theorem: :c^2 = a^2 + b^2. The law of cosines is useful for computing the third side of a triangle when two sides and their enclosed angle are known. History Though the notion of the cosine was not yet developed in his time, Euclid's ''Elements'', dating back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |