|
Tropical Storm Nuri (2020)
The 2020 Pacific typhoon season was the first with below-average tropical cyclone activity since 2001, with 23 named storms, 10 of which became typhoons and only 2 became super typhoons. This low activity was a consequence of La Niña that persisted from the summer of the year. It had the fifth-latest start in the basin on record, slightly behind 1973, and was the first to start that late since 2016. The first half of the season was unusually inactive, with only four systems, two named storms and one typhoon at the end of July. Additionally, the JTWC recorded no tropical cyclone development in the month of July, the first such occurrence since reliable records began. The season's first named tropical cyclone, Vongfong, developed on May 8, while the season's last named tropical cyclone, Krovanh, dissipated on December 24. However, the season's last system was an unnamed tropical depression which dissipated on December 29. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Goni
Typhoon Goni, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Rolly, was an extremely powerful tropical cyclone that made landfall as a Category 5 equivalent super typhoon on Catanduanes in the Philippines, and in Vietnam as a tropical storm. It was the strongest landfalling tropical typhoon on record by 1-minute maximum sustained winds. The nineteenth named storm, ninth typhoon, and second super typhoon of the 2020 Pacific typhoon season, Goni originated as a tropical depression south portion of Guam on October 26. It was then named as Tropical Storm Goni on October 27. On the next day, Goni explosively intensified over the Philippine Sea, becoming a Category 5–equivalent super typhoon on October 30. Goni maintained Category 5 strength for over a day, before making landfall on Catanduanes at peak intensity, with 10-minute sustained winds of 220 km/h (140 mph), and 1-minute sustained winds of 315 km/h (195 mph), with a minimum central pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Area Of Responsibility
The Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR) is an area in the Northwestern Pacific where PAGASA, the Philippines' national meteorological agency, monitors weather occurrences. Significant weather disturbances, specifically tropical cyclones that enter or develop in the PAR, are given Philippine-specific names. Boundary The area is bounded by six points namely: * * * * * * This area encompasses almost all of the land territory of the Philippines, except for the southernmost portions of the province of Tawi-Tawi, and some of the country's claimed islands in the Spratly Islands, Spratlys. The area also includes the main island of Palau, most of Taiwan, as well as portions of the Malaysian state of Sabah and the Japanese prefecture of Okinawa. Function The establishing decree of PAGASA Pagasa may refer to: * ''Pagasa'' (genus), an insect genus in the family Nabidae * PAGASA, an acronym for the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Haishen (2020)
Typhoon Haishen, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Kristine, was a powerful tropical cyclone that became the first super typhoon of the 2020 Pacific typhoon season. Being also the tenth named storm and this season's fifth typhoon, Haishen's origins can be tracked back to a disorganised low pressure area situated near Guam. While the disturbance tracked south-westward and quickly organised, the JTWC issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (TCFA) on the system, and a day later, on September 1, the system became a tropical depression. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Haishen according to the Japan Meteorological Agency as it moved southwestward. At about 12:00 UTC on September 2, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geological and Astronomical Services Administration indicated that Haishen had entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility and was subsequently named Kristine. Later that day, Haishen became a typhoon. Intensification on September 3 was significant. Drifting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Maysak (2020)
Typhoon Maysak, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Julian, was a deadly, damaging and powerful tropical cyclone that struck the Ryukyu Islands and the Korean Peninsula in September 2020. The third typhoon of the 2020 Pacific typhoon season, Maysak formed from a tropical disturbance. The disturbance gradually organized, receiving the name ''Julian'' from PAGASA as it became a tropical depression. As the depression strengthened, the JMA subsequently named the system ''Maysak''. Maysak rapidly intensified into a strong typhoon before weakening and making landfall in South Korea. Maysak was the second of three typhoons to affect the Korean Peninsula within two weeks, the others being Bavi and Haishen. It was also responsible for the loss of a livestock carrier Gulf Livestock 1, that sank 100 nautical miles West off from Amami Ōshima, Japan on September 2, 2020, taking 41 out of the 43 crew members on board. Meteorological history Following the impacts of Typhoon Bavi on the K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
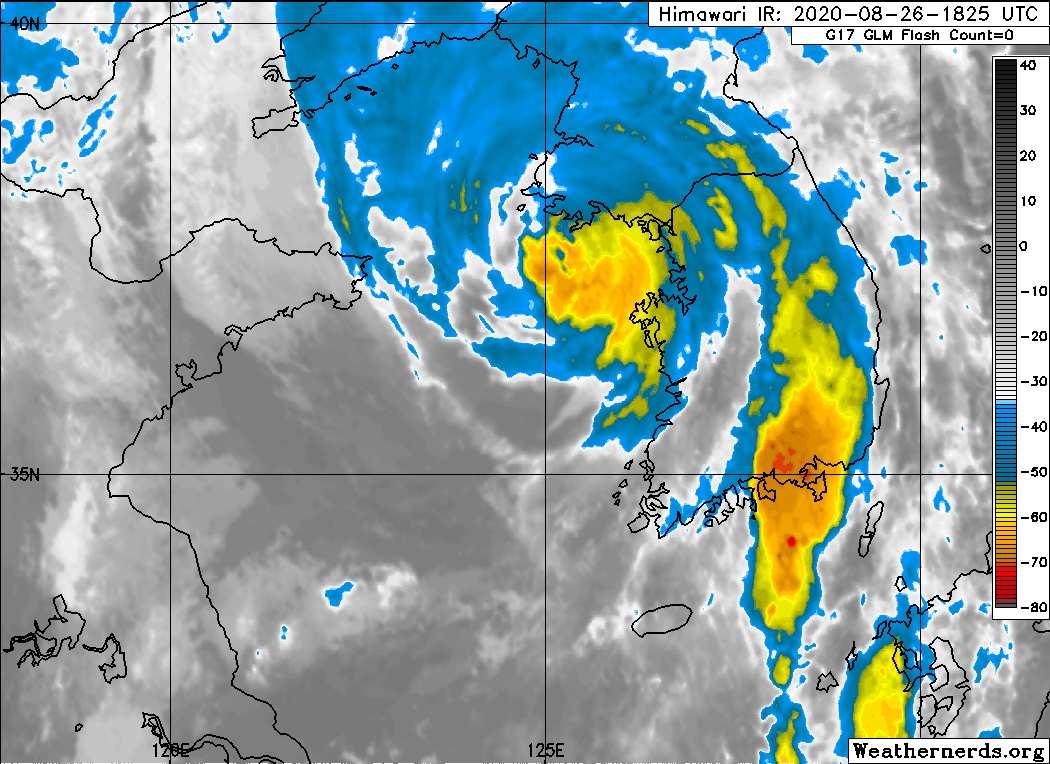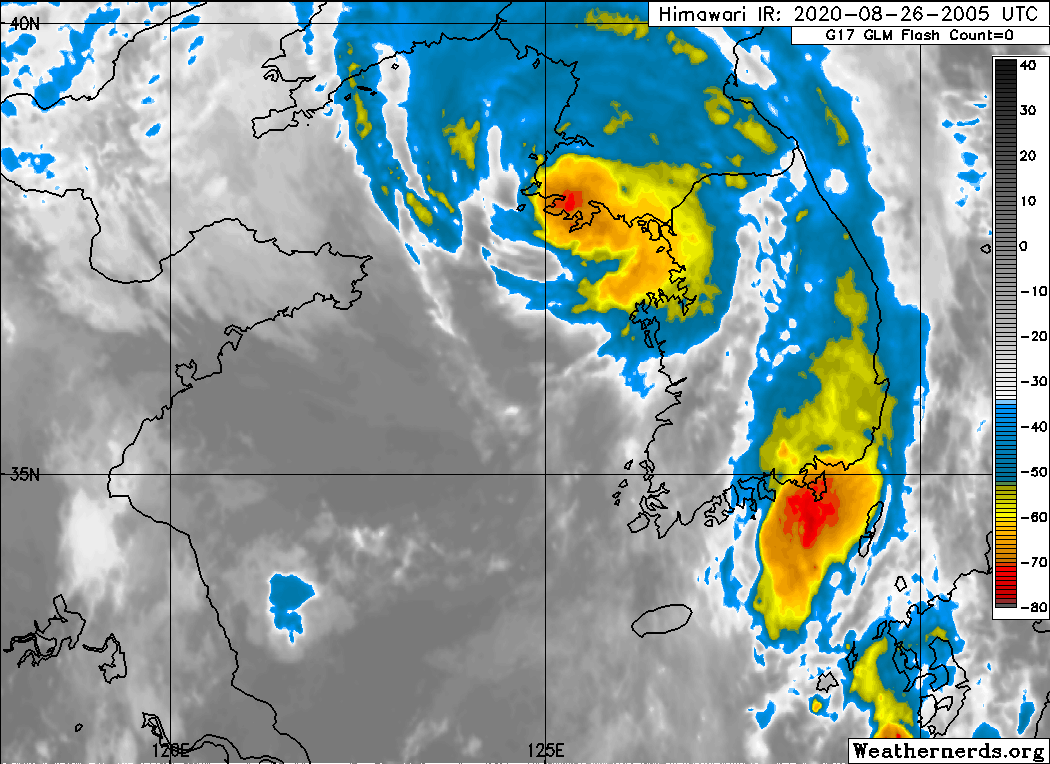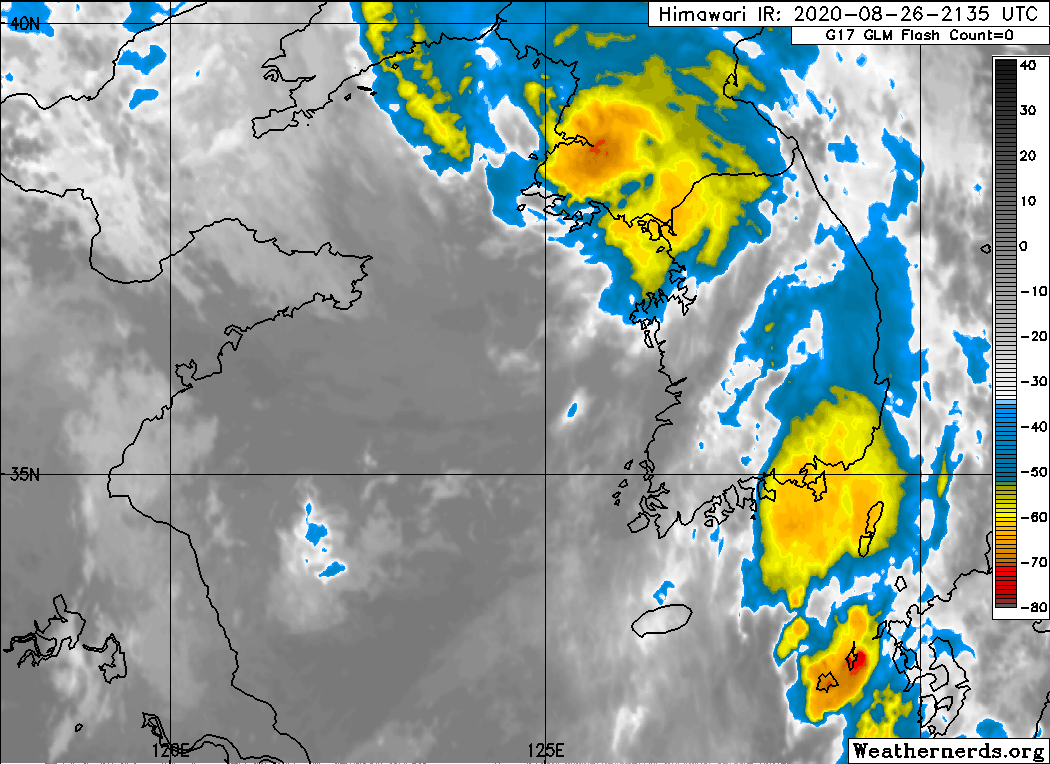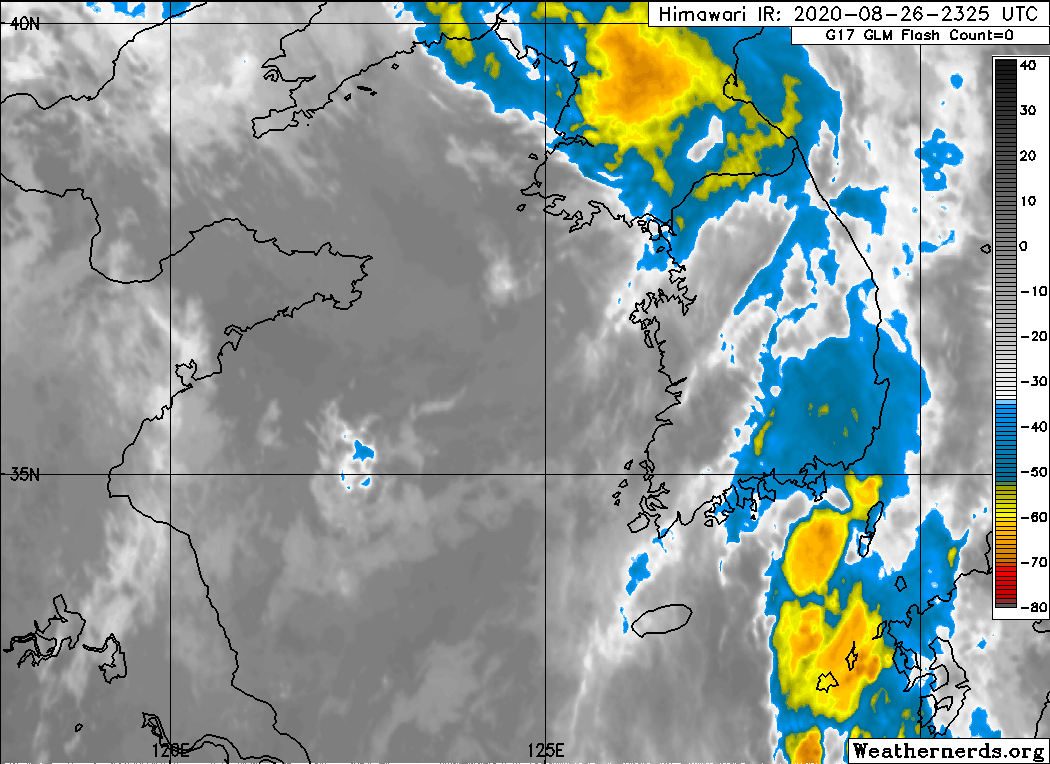
Typhoon Bavi (2020)
Typhoon Bavi, known in the Philippines as Severe Tropical Storm Igme, was a powerful tropical cyclone that made landfall in North Korea in August 2020. The eighth named storm and third typhoon of the 2020 Pacific typhoon season, Bavi formed from a low pressure area depression on August 21 to the north of the Philippines and strengthened into a tropical storm on August 22. Bavi gradually strengthened as it skirted Taiwan and Okinawa, and became a typhoon on August 24. Passing over warm waters, Bavi turned to northwest and reached its peak intensity near Jeju Island on August 26. Thereafter, increasing wind shear and cooler waters caused Bavi to quickly weaken. Bavi made landfall in North Korea on August 27, and became an extratropical cyclone shortly thereafter. Bavi caused minimal damage in portions of South Korea and Japan, but caused widespread structural damage and flooding in North Korea. It was the first storm in two weeks span to affect Korea. Others were Maysak and Hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Higos (2020)
Severe Tropical Storm Higos, known in the Philippines as Tropical Depression Helen, was a tropical storm that affected China and Vietnam around the same area as Nuri two months prior. Higos formed from a tropical disturbance north of Luzon, the Philippines, on August 16. The storm tracked northeast and quickly intensified, becoming a tropical storm on August 17. The storm made landfall in Zhuhai, Guangdong at peak intensity on August 19, and quickly weakened soon after. Higos killed 7 people and caused 45 billion đồng (US$2 million) in damages in Vietnam. Higos also caused more than US$140 million in damages, but no fatalities in China. Meteorological history A new tropical depression formed from the Intertropical Convergence Zone east of Luzon on August 16. At 15:00 UTC, the PAGASA named the system ''Helen'' and began issuing severe weather bulletins for the tropical depression, but dropped the alerts as Helen left the Philippine area of responsibility after 4 hours. Around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Mekkhala (2020)
Severe Tropical Storm Mekkhala, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Ferdie, was a severe tropical storm that affected China in August 2020 causing 1.1 billion yuan (US$159 million) in damage. However, no fatalities had been reported. Meteorological history An area of persistent convection formed within the proximity of a through that would spawn Tropical Storm Jangmi on August 7, west of Luzon. As Jangmi became the dominant system in the area, this low-pressure area remained disorganized. However, on the next day, as Jangmi moved away from the area, the system began to organize, and on August 9, the JTWC upgraded the storm to a Tropical Depression. Soon after, at 8:00 p.m. PST, the PAGASA followed and upgraded the storm and gave it the name Ferdie. By the next day, the JTWC upgraded Ferdie into a tropical storm. PAGASA then issued its last warning as Ferdie exited the Philippine Area of Responsibility. Then soon, the JMA followed suit and upgraded Ferdie to a tropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Sinlaku (2020)
Tropical Storm Sinlaku was a weak but deadly tropical cyclone that impacted Vietnam, Thailand and Laos in August 2020. Beginning as a tropical depression on July 31 in the South China Sea, Sinlaku was the fifth storm of the 2020 Pacific typhoon season. It gradually organized as it took a slow west-northwest course, strengthening into a tropical storm the following day despite its monsoonal structure. The storm subsequently made landfall in Vietnam as a broad but weak tropical storm. Persistent land interaction weakened Sinlaku, leading to its dissipation on August 3. Sinlaku brought heavy monsoonal rains to much of Southeast Asia, especially to Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand. Two people were killed in Vietnam, and two people were killed in Thailand. Meteorological history In late July 2020, an area of atmospheric convection began to persist approximately 410 km (255 mi) east of Virac, Catanduanes. Afterwards, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) designated the syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoon Hagupit (2020)
Typhoon Hagupit, known in the Philippines as Severe Tropical Storm Dindo, was a Category 1 typhoon that heavily impacted Eastern China and South Korea in August 2020. It was the fourth named storm and the second typhoon of the annual typhoon season. The JMA began monitoring a tropical depression that developed in the Philippine Sea on July 30, with PAGASA assigning the name “Dindo” to the storm, later that day it strengthened into a tropical storm, according to the JMA. PAGASA issued its final advisory on Dindo early on August 3, as it moved out of their area of responsibility. Hagupit intensified into a typhoon on August 3, before making landfall in Wenzhou, China at 19:30 UTC that day at peak intensity. Hagupit subsequently weakened over China, before degenerating into an extratropical low on August 5. Hagupit's remnants persisted for another several days, as the storm moved eastward, before dissipating south of Alaska on August 14. Hagupit caused over a foot of rainfall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean Dipole
The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also known as the Indian Niño, is an irregular oscillation of sea surface temperatures in which the western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer (positive phase) and then colder (negative phase) than the eastern part of the ocean. Phenomenon The IOD involves an aperiodic oscillation of sea-surface temperatures (SST), between "positive", "neutral" and "negative" phases. A positive phase sees greater-than-average sea-surface temperatures and greater precipitation in the western Indian Ocean region, with a corresponding cooling of waters in the eastern Indian Ocean—which tends to cause droughts in adjacent land areas of Indonesia and Australia. The negative phase of the IOD brings about the opposite conditions, with warmer water and greater precipitation in the eastern Indian Ocean, and cooler and drier conditions in the west. The IOD also affects the strength of monsoons over the Indian subcontinent. A significant positive IOD occurred in 1997� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is an irregular periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics. The warming phase of the sea temperature is known as ''El Niño'' and the cooling phase as ''La Niña''. The ''Southern Oscillation'' is the accompanying atmospheric component, coupled with the sea temperature change: ''El Niño'' is accompanied by high air surface pressure in the tropical western Pacific and ''La Niña'' with low air surface pressure there. The two periods last several months each and typically occur every few years with varying intensity per period. The two phases relate to the Walker circulation, which was discovered by Gilbert Walker during the early twentieth century. The Walker circulation is caused by the pressure gradient force that results from a high-pressure area over the eastern Pacific Ocean, and a low-pressure system over Indonesia. Weak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Weather Bureau
The Central Weather Bureau (CWB; ) is the government meteorological research and forecasting institution of the Republic of China (Taiwan). In addition to meteorology, the Central Weather Bureau also makes astronomical observations, reports on sea conditions, and conducts research into seismology and provides earthquake reports. The Central Weather Bureau is headquartered in Taipei City and is administered under the Ministry of Transportation and Communications. History While Taiwan was under Japanese rule, the government set up five weather monitoring stations on the island, located in Taipei, Taichung, Tainan, Hengchun, and Penghu. On 19 December 1897, the Governor-General moved the headquarters to the present location occupied by the eventual successor agency of the Japanese "Taipei Observatory": the Central Weather Bureau. In 1945 when the Kuomintang took control of Taiwan the various stations set up by the Japanese were incorporated into the new Taiwan Provincial Weather In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |