|
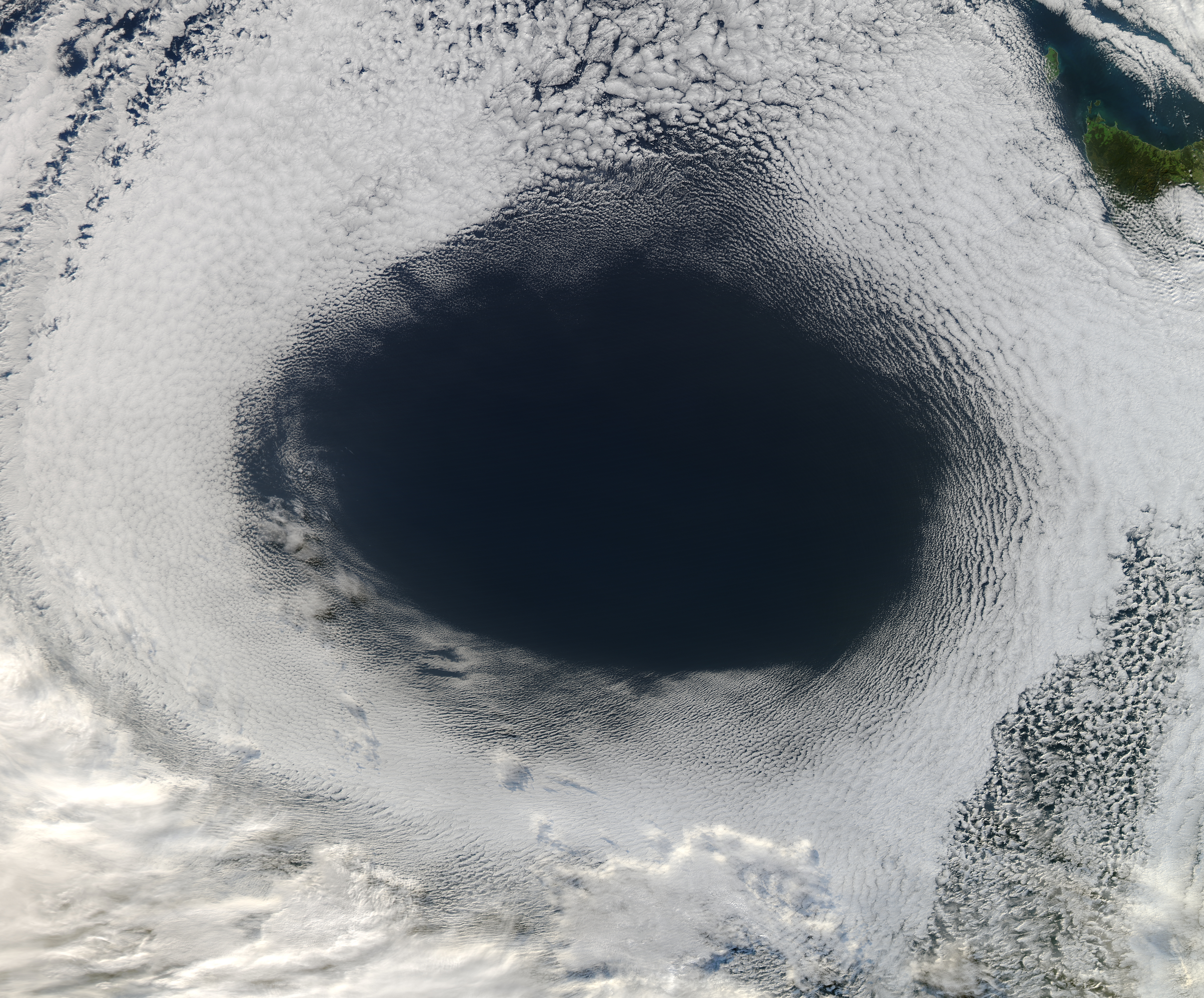
Tropical Storm Arlene (1981)
Tropical Storm Arlene was a rare off-season tropical cyclone that hit Cuba and the Bahamas in May 1981. Its formation was unusual, originating from a tropical disturbance that crossed from the eastern Pacific Ocean into the Caribbean Sea; few Atlantic hurricanes develop in this manner. On May 6, a tropical depression developed, and the next day it became Tropical Storm Arlene near the Cayman Islands, three weeks before the start of the hurricane season. This marked the first Atlantic tropical storm in May since 1970's Hurricane Alma. Arlene moved northeastward throughout its life, bringing rainfall and locally gusty winds as it crossed Cuba and the southeastern Bahamas. On May 9, the storm dissipated when a large non-tropical storm absorbed Arlene. There were no reports of deaths or significant damage. Meteorological history The origins of Arlene were from a cloud mass that developed in the eastern Pacific Ocean in early May 1981. The system crossed Central A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, and Atlantic Ocean meet. Cuba is located east of the Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico), south of both the American state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Hispaniola ( Haiti/Dominican Republic), and north of both Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. Havana is the largest city and capital; other major cities include Santiago de Cuba and Camagüey. The official area of the Republic of Cuba is (without the territorial waters) but a total of 350,730 km² (135,418 sq mi) including the exclusive economic zone. Cuba is the second-most populous country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with over 11 million inhabitants. The territory that is now Cuba was inhabited by the Ciboney people from the 4th millennium BC with the Gua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
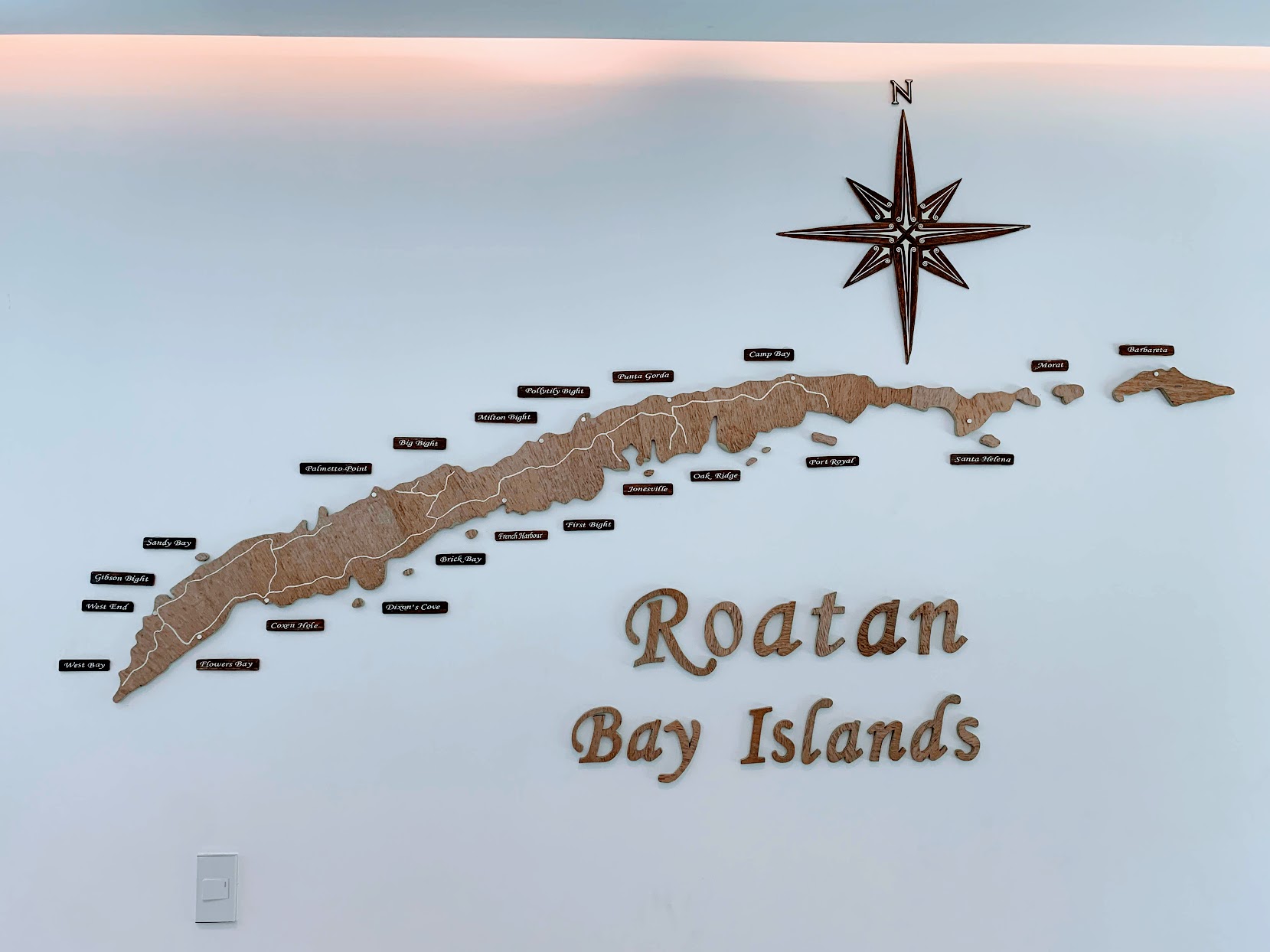
Roatán
Roatán () is an island in the Caribbean, about off the northern coast of Honduras. It is located between the islands of Utila and Guanaja, and is the largest of the Bay Islands of Honduras. The island was formerly known in English as Ruatan and Rattan. It is approximately long, and less than across at its widest point. The island consists of two municipalities: José Santos Guardiola in the east and Roatán, including the Cayos Cochinos, further south in the west. Geography The island rests on an exposed ancient coral reef, rising to about above sea level. Offshore reefs offer opportunities for diving. Most habitation is in the western half of the island. The most populous town of the island is Coxen Hole, capital of Roatán municipality, located in the southwest. West of Coxen Hole are the settlements of Gravel Bay, Flowers Bay and Pensacola on the south coast, and Sandy Bay, West End and West Bay on the north coast. To the east of Coxen Hole are the settlements of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricanes In Cuba
Cuba is an island country east of the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, south of both the U.S. state of Florida and the Bahamas, west of Haiti and north of both Jamaica and the Cayman Islands. The country has experienced the effects of at least 54 Atlantic hurricanes, or storms that were once tropical or subtropical cyclones, including 37 since 2000. The storms collectively killed 5,613 people, most of them related to a powerful hurricane in 1932. 1800s *October 10, 1846 - A powerful hurricane, possibly a Category 5, moved across Cuba. The high winds destroyed crops, houses, and nearly every boat in Havana harbor. Dozens to hundreds of people were killed across Cuba. 1900s *October 14, 1910 - Known locally as the "Cyclone of the Five Days", a hurricane struck western Cuba, executed a small loop, and passed again near the western end of the island five days later. The storm killed at least 100 people, possibly as high as 700, and left more than US$1 million in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Tropical Storms
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Storms Named Arlene
The name Arlene has been used for twelve tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean, making Arlene the most frequently used storm name in the basin. * Tropical Storm Arlene (1959), a tropical storm which brought flooding to Louisiana, killing one person * Hurricane Arlene (1963), a Category 3 major hurricane which passed over Bermuda, only causing light damage * Hurricane Arlene (1967), a Category 1 hurricane in the central Atlantic Ocean which did not affect land * Tropical Storm Arlene (1971), a tropical storm that moved parallel to the east coast of the United States without making landfall * Tropical Storm Arlene (1981), a tropical storm that crossed Cuba and the Bahamas, with only minimal effects * Hurricane Arlene (1987), a Category 1 hurricane that spent much of its life as a tropical storm far from land * Tropical Storm Arlene (1993), a tropical storm that brought heavy rain to Mexico and Texas; killed 29 people * Tropical Storm Arlene (1999), a tropical storm that drifted p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camagüey Province
Camagüey () is the largest of the provinces of Cuba. Its capital is Camagüey. Other towns include Florida and Nuevitas. Geography Camagüey is mostly low lying, with no major hills or mountain ranges passing through the province. Numerous large cays (including what used to be one of Fidel Castro's favourite fishing spots; the Archipiélago Jardines de la Reina) characterize the southern coasts, while the northern coast is lined by Jardines del Rey of the Sabana-Camagüey Archipelago. Sandy beaches are found on both coasts also, and despite a large potential for tourism, the province has seen little development in that area with the exception of Santa Lucía beach, on the province's North coast. Economy The economy of the Camagüey province is primarily cattle and sugar (in the north and south) farming, and the province is known for its cowboy culture, with rodeos frequently held. Chickens and rice are also farmed, and a small citrus fruit ''Citrus'' is a genus of flower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayman Brac
Cayman Brac is an island that is part of the Cayman Islands. It lies in the Caribbean Sea about north-east of Grand Cayman and east of Little Cayman. It is about long, with an average width of . Its terrain is the most prominent of the three Cayman Islands due to " The Bluff", a limestone outcrop that rises steadily along the length of the island up to above sea level at the eastern end. The island is named after this prominent feature, as "brac" is a Gaelic name for a bluff. History Christopher Columbus sighted Cayman Brac and its sister island, Little Cayman, on 10 May 1503 when his ship was blown off course during a trip between Hispaniola and Panama. He named them "Las Tortugas" because of the many turtles he spotted on the islands. The Cayman Islands were renamed by Sir Francis Drake, who came upon the islands during a voyage in 1586. He used the word "Caymanas", taken from the Carib name for crocodiles after seeing many of the large crocodilians. Many people believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm Warning
At sea, a storm warning is a warning issued by the National Weather Service of the United States when winds between 48 knots (89 km/h, 55 mph) and 63 knots (117 km/h, 73 mph) are occurring or predicted to occur soon. The winds must not be associated with a tropical cyclone. If the winds are associated with a tropical cyclone, a tropical storm warning will be substituted for the storm warning and less severe gale warning. In US maritime warning flag systems, a red square flag with a black square taking up the middle ninth of the flag is used to indicate a storm warning (the use of two such flags denotes a hurricane force wind warning or a hurricane warning). The same flag as a storm warning is used to indicate a tropical storm warning. On land, the National Weather Service issues a 'high wind warning' (Specific Area Message Encoding code: HWW) for storm-force winds, which also encompasses the lesser gale-force and greater hurricane force winds. In most cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical Storm
A subtropical cyclone is a weather system that has some characteristics of both tropical and an extratropical cyclone. As early as the 1950s, meteorologists were uncertain whether they should be characterized as tropical or extratropical cyclones. They were officially recognized and titled by the National Hurricane Center in 1972. Beginning in 2002, subtropical cyclones received names from the official tropical cyclone lists in the North Atlantic, South-west Indian Ocean, and South Atlantic basins. There are two definitions currently used for subtropical cyclones depending on their location. Across the north Atlantic and southwest Indian Ocean, they require some central convection fairly near the center surrounding a warming core existing in the mid-levels of the troposphere. Across the eastern half of the northern Pacific however, they require a mid-tropospheric cyclone to be cut off from the main belt of the westerlies and with only a weak surface circulation. Subtropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Pressure Area
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, toward the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, if the planet is rotating, the straight direction of the air flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 30th parallel north in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the 31st parallel north in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The agency, which is co-located with the Miami branch of the National Weather Service, is situated on the campus of Florida International University in Westchester, Florida. The NHC's Tropical Analysis and Forecast Branch (TAFB) routinely issues marine forecasts, in the form of graphics and high seas forecasts year round, with the Ocean Prediction Center having backup responsibility for this unit. The Technology and Science Branch (TSB) provides technical support for the center, which includes new infusions of technology from abroad. The Chief, Aerial Reconnaissance Coordination, All Hurricanes (CARCAH) unit tasks planes, for r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |