|
Triton X-100
Triton X-100 (''n'') is a nonionic surfactant that has a hydrophilic polyethylene oxide chain (on average it has 9.5 ethylene oxide units) and an aromatic hydrocarbon lipophilic or hydrophobic group. The hydrocarbon group is a 4-( 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutyl)-phenyl group. Triton X-100 is closely related to IGEPAL CA-630, which might differ from it mainly in having slightly shorter ethylene oxide chains. As a result, Triton X-100 is slightly more hydrophilic than Igepal CA-630 thus these two detergents may not be considered to be functionally interchangeable for most applications. Triton X-100 was originally a registered trademark of Rohm & Haas Co. It was subsequently purchased by Union Carbide and then acquired by Dow Chemical Company upon the acquisition of Union Carbide. Soon afterward (in 2009), Dow also acquired Rohm & Haas Co. Physical properties Undiluted Triton X-100 is a clear viscous fluid (less viscous than undiluted glycerol). Undiluted Triton X-100 has a viscosity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonionic
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, dark urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Processing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transepithelial Potential Difference
Transepithelial potential difference (TEPD) is the voltage across an epithelium, and is the sum of the membrane potentials for the outer and inner cell membranes. TEPD in the nose The diagnosis of cystic fibrosis (CF) is usually based on high sweat chloride concentrations, characteristic clinical findings (including sinopulmonary infections), and/or family history. However, a small portion of patients with cystic fibrosis especially those with "mild" mutations of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) ion channel, have near-normal sweat tests. In these cases, a useful diagnostic, adjunct involves measuring the nasal transepithelial potential difference (ie, the charge on the respiratory epithelial surface as compared to interstitial fluid). Individuals with cystic fibrosis have a significantly more negative nasoepithelial surface than normal, due to increased luminal sodium absorption. In most exocrine glands, the CFTR protein normally secretes chloride ions into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunostaining
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods. Techniques Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry or IHC staining of tissue sections (or immunocytochemistry, which is the staining of cells), is perhaps the most commonly applied immunostaining technique. While the first cases of IHC staining used fluorescent dyes (see '' immunofluorescence''), other non-fluorescent methods using enzymes such as peroxidase (see '' immunoperoxidase staining'') and alkaline phosphatase are now used. These enzymes are capable of catalysing reactions that give a coloured product that is easily detectable by light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Extraction
The first isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was done in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher. Currently, it is a routine procedure in molecular biology or forensic analyses. For the chemical method, many different kits are used for extraction, and selecting the correct one will save time on kit optimization and extraction procedures. PCR sensitivity detection is considered to show the variation between the commercial kits. What does it deliver? DNA extraction is frequently a preliminary step in many diagnostic procedures used to identify environmental viruses and bacteria and diagnose illnesses and hereditary diseases. These methods consist of, but are not limited to: Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) technique was developed in the 1980s. The basic idea is to use a nucleic acid probe to hybridize nuclear DNA from either interphase cells or metaphase chromosomes attached to a microscopic slide. It is a molecular method used, among other things, to recognize and count partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysis Buffer
A lysis buffer is a buffer solution used for the purpose of breaking open cells for use in molecular biology experiments that analyze the labile macromolecules of the cells (e.g. western blot for protein, or for DNA extraction). Most lysis buffers contain buffering salts (e.g. Tris-HCl) and ionic salts (e.g. NaCl) to regulate the pH and osmolarity of the lysate. Sometimes detergents (such as Triton X-100 or SDS) are added to break up membrane structures. For lysis buffers targeted at protein extraction, protease inhibitors are often included, and in difficult cases may be almost required. Lysis buffers can be used on both animal and plant tissue cells. Choosing a buffer The primary purpose of lysis buffer is isolating the molecules of interest and keeping them in a stable environment. For proteins, for some experiments, the target proteins should be completely denatured, while in some other experiments the target protein should remain folded and functional. Different prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHAPS Detergent
CHAPS is a zwitterionic surfactant used in the laboratory to solubilize biological macromolecules such as proteins. It may be synthesized from cholic acid and is zwitterionic due to its quaternary ammonium and sulfonate groups; it is structurally similar to certain bile acids, such as taurodeoxycholic acid and taurochenodeoxycholic acid. It is used as a non- denaturing detergent in the process of protein purification and is especially useful in purifying membrane proteins, which are often sparingly soluble or insoluble in aqueous solution due to their native hydrophobicity. CHAPS is an abbreviation for 3- 3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio1-propanesulfonate. A related detergent, called CHAPSO, has the same basic chemical structure with an additional hydroxyl functional group; its full chemical name is 3- 3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio2-hydroxy-1-propanesulfonate. Both detergents have low light absorbance in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwitterion
In chemistry, a zwitterion ( ; ), also called an inner salt or dipolar ion, is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively- and negatively-charged functional groups. : With amino acids, for example, in solution a chemical equilibrium will be established between the "parent" molecule and the zwitterion. Betaines are zwitterions that cannot isomerize to an all-neutral form, such as when the positive charge is located on a quaternary ammonium group. Similarly, a molecule containing a phosphonium group and a carboxylate group cannot isomerize. Amino acids The equilibrium is established in two stages. In the first stage, a proton is transferred from the carboxyl group to a water molecule: :H2N(R)CO2H + H2O H2N(R)CO2- + H3O+ In the second stage, a proton is transferred from the hydronium ion to the amine group: :H2N(R)CO2- + H3O+ H3N+ (R)CO2- + H2O Overall, the reaction is an isomerization reaction :H2N(R)CO2H H3N+ (R)CO2- The ratio of the concentrations of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
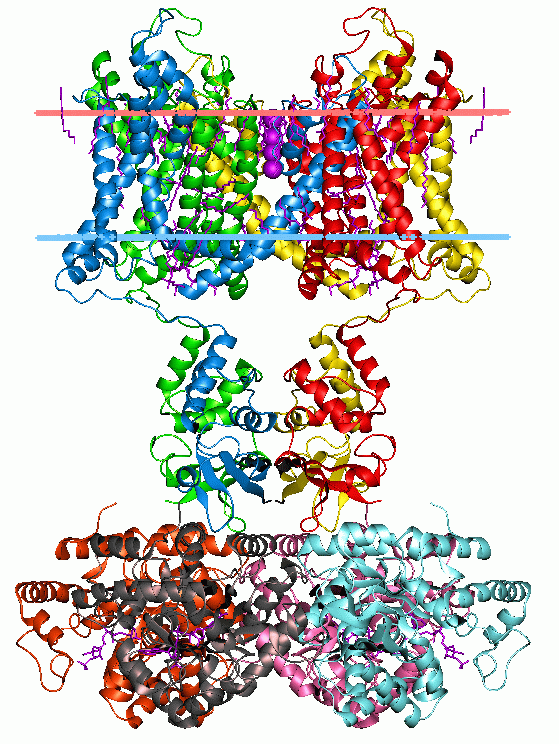
Membrane Protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane ( transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to '' Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 12.779. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the mass media, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluzone
Influenza vaccines, also known as flu shots, are vaccines that protect against infection by influenza viruses. New versions of the vaccines are developed twice a year, as the influenza virus rapidly changes. While their effectiveness varies from year to year, most provide modest to high protection against influenza. The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that vaccination against influenza reduces sickness, medical visits, hospitalizations, and deaths. Immunized workers who do catch the flu return to work half a day sooner on average. Vaccine effectiveness in those over 65 years old remains uncertain due to a lack of high-quality research. Vaccinating children may protect those around them. Vaccines are an effective means to control outbreaks of many diseases. However, vaccines for respiratory viral infections such as flu are still suboptimal and do not offer broad-spectrum protection. Vaccination against influenza began in the 1930s, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |