Membrane protein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Membrane proteins are common
Membrane proteins are common

Membrane Protein Structural Dynamics ConsortiumExperts for Membrane Protein Research and Purification
TCDB
- Transporter Classification database, a comprehensive classification of transmembrane transporter proteins
Orientations of Proteins in Membranes (OPM) database
- 3D structures of
Protein Data Bank of Transmembrane Proteins
- 3D models of
TransportDB
- Genomics-oriented database of transporters from TIGR
Membrane PDB
- Database of 3D structures of integral membrane proteins and hydrophobic peptides with an emphasis on crystallization conditions
Mpstruc database
- A curated list of selected transmembrane proteins from the
MemProtMD
- a database of membrane protein structures simulated by coarse-grained
 Membrane proteins are common
Membrane proteins are common protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the ...
and can either penetrate the membrane ( transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane.
Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structure
Protein structure is the molecular geometry, three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single ami ...
s remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment.
Function
Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the survival of organisms: *Membrane receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integra ...
proteins relay signals between the cell's internal and external environments.
* Transport proteins move molecules and ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
across the membrane. They can be categorized according to the Transporter Classification database.
* Membrane enzymes may have many activities, such as oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually ...
, transferase
A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved in hundreds of ...
or hydrolase
Hydrolase is a class of enzyme that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are es ...
.
* Cell adhesion molecule
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell surface proteins that are involved in the binding of cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM), in a process called cell adhesion. In essence, CAMs help cells stick to each ...
s allow cells to identify each other and interact. For example, proteins involved in immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could ...
The localization of proteins in membranes can be predicted reliably using hydrophobicity analyses of protein sequences, i.e. the localization of hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, ...
amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
sequences.
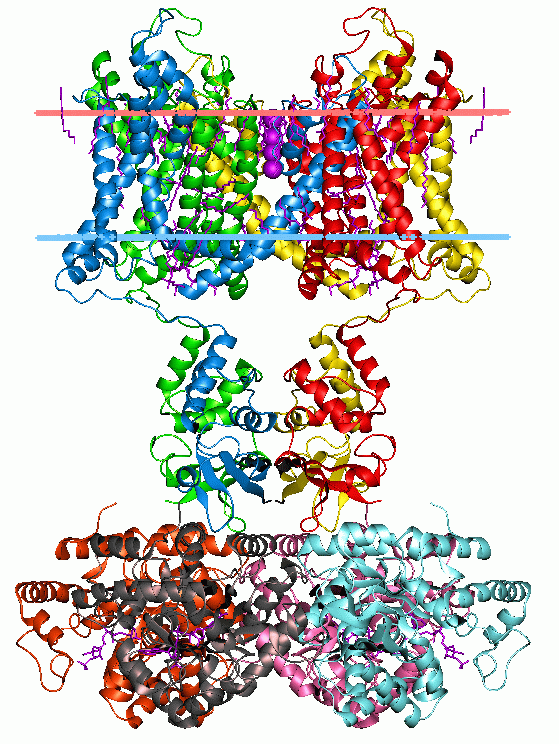
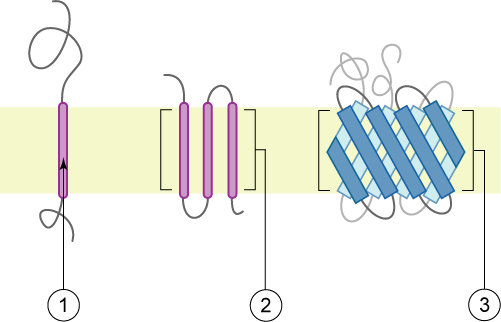
Integral membrane proteins

Integral membrane protein
An integral, or intrinsic, membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All ''transmembrane proteins'' are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a sign ...
s are permanently attached to the membrane. Such proteins can be separated from the biological membranes only using detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are m ...
s, nonpolar solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for p ...
s, or sometimes denaturing agents. They can be classified according to their relationship with the bilayer
A bilayer is a double layer of closely packed atoms or molecules.
The properties of bilayers are often studied in condensed matter physics, particularly in the context of semiconductor devices, where two distinct materials are united to form junc ...
:
* Integral polytopic proteins are transmembrane proteins that span across the membrane more than once. These proteins may have different transmembrane topology. These proteins have one of two structural architectures:
**Helix bundle A helix bundle is a small protein fold composed of several alpha helices that are usually nearly parallel or antiparallel to each other.
Three-helix bundles
Three-helix bundles are among the smallest and fastest known cooperatively folding struct ...
proteins, which are present in all types of biological membranes;
** Beta barrel proteins, which are found only in outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wa ...
, and outer membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it i ...
.
* Bitopic proteins are transmembrane proteins that span across the membrane only once. Transmembrane helices from these proteins have significantly different amino acid distributions to transmembrane helices from polytopic proteins.
* Integral monotopic protein
Integral monotopic proteins are permanently attached to the cell membrane from one side, and are a type of integral membrane protein (IMP).
Three-dimensional structures of the following integral monotopic proteins have been determined:
*prostagl ...
s are integral membrane proteins that are attached to only one side of the membrane and do not span the whole way across.
Peripheral membrane proteins
Peripheral membrane protein
Peripheral membrane proteins, or extrinsic membrane proteins, are membrane proteins that adhere only temporarily to the biological membrane with which they are associated. These proteins attach to integral membrane proteins, or penetrate the per ...
s are temporarily attached either to the lipid bilayer or to integral proteins by a combination of hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, ...
, electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for am ...
, and other non-covalent interactions. Peripheral proteins dissociate following treatment with a polar reagent, such as a solution with an elevated pH or high salt concentrations.
Integral and peripheral proteins may be post-translationally modified, with added fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
, diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as sur ...
or prenyl chains, or GPI (glycosylphosphatidylinositol), which may be anchored in the lipid bilayer.
Polypeptide toxins
Polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides ...
toxins and many antibacterial peptides, such as colicins or hemolysins, and certain proteins involved in apoptosis, are sometimes considered a separate category. These proteins are water-soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance
Substance may refer to:
* Matter, anything that has mass and takes up space
Chemistry
* Chemical substance, a material with a definite chemical composition
* Drug substance
** Substan ...
but can aggregate and associate irreversibly with the lipid bilayer and become reversibly or irreversibly membrane-associated.
In genomes
Membrane proteins, like solubleglobular protein
In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types (the others being fibrous, disordered and membrane proteins). Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble (fo ...
s, fibrous proteins, and disordered proteins, are common. It is estimated that 20–30% of all gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s in most genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
s encode for membrane proteins. For instance, about 1000 of the ~4200 proteins of '' E. coli'' are thought to be membrane proteins, 600 of which have been experimentally verified to be membrane resident. In humans, current thinking suggests that fully 30% of the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
encodes membrane proteins.
In disease
Membrane proteins are the targets of over 50% of all modern medicinal drugs. Among the human diseases in which membrane proteins have been implicated areheart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
, Alzheimer's and cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
.
Purification of membrane proteins
Although membrane proteins play an important role in all organisms, their purification has historically, and continues to be, a huge challenge for protein scientists. In 2008, 150 unique structures of membrane proteins were available, and by 2019 only 50 human membrane proteins had had their structures elucidated. In contrast, approximately 25% of all proteins are membrane proteins. Theirhydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, ...
surfaces make structural and especially functional characterization difficult. Detergents can be used to render membrane proteins water-soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance
Substance may refer to:
* Matter, anything that has mass and takes up space
Chemistry
* Chemical substance, a material with a definite chemical composition
* Drug substance
** Substan ...
, but these can also alter protein structure and function. Making membrane proteins water-soluble can also be achieved through engineering the protein sequence, replacing selected hydrophobic amino acids with hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are ...
ones, taking great care to maintain secondary structure while revising overall charge.
Affinity chromatography is one of the best solutions for purification of membrane proteins. The activity of membrane proteins decreases very fast in contrast to other proteins. So, affinity chromatography provides a fast and specific purification of membrane proteins. The polyhistidine-tag is a commonly used tag for membrane protein purification, and the alternative rho1D4 tag has also been successfully used.
Further reading
* *See also
References
External links
Organizations
Membrane Protein Structural Dynamics Consortium
Membrane protein databases
TCDB
- Transporter Classification database, a comprehensive classification of transmembrane transporter proteins
Orientations of Proteins in Membranes (OPM) database
- 3D structures of
integral
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with ...
and peripheral membrane protein
Peripheral membrane proteins, or extrinsic membrane proteins, are membrane proteins that adhere only temporarily to the biological membrane with which they are associated. These proteins attach to integral membrane proteins, or penetrate the per ...
s arranged in the lipid bilayer
Protein Data Bank of Transmembrane Proteins
- 3D models of
transmembrane protein
A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequentl ...
s approximately arranged in the lipid bilayer.
TransportDB
- Genomics-oriented database of transporters from TIGR
Membrane PDB
- Database of 3D structures of integral membrane proteins and hydrophobic peptides with an emphasis on crystallization conditions
Mpstruc database
- A curated list of selected transmembrane proteins from the
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, c ...
MemProtMD
- a database of membrane protein structures simulated by coarse-grained
molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamic "evolution" of th ...
* Membranome database
Membranome database provides structural and functional information about more than 6000 single-pass (bitopic) transmembrane proteins from ''Homo sapiens'', ''Arabidopsis thaliana'', ''Dictyostelium discoideum'', ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', '' ...
provides information about bitopic proteins from several model organisms
{{DEFAULTSORT:Membrane Protein