|
Tritec Engine
The Tritec engine (also known as Pentagon) is a four-cylinder petrol engine that was manufactured between 1999 and 2007 by Tritec Motors in Brazil and was used in various cars including Chrysler and Mini models. Tritec Motors Ltda In 1997, Chrysler Corporation and Rover Group (then a subsidiary of BMW) formed a joint venture called Tritec Motors to design a new small straight-4 engine. The new company built a factory in Campo Largo of Curitiba, Brazil specifically to manufacture the new engine. The Tritec name stands for the union of the three countries involved: Germany, the United Kingdom, and Brazil. When BMW broke up the remains of Rover Group in 2000, BMW kept the stake in Tritec Motors as the engine was in use in the Mini range which BMW had retained. In 2007 BMW sold its 50% stake to DaimlerChrysler and cancelled its contract for the Tritec engine. BMW entered into a new joint venture with PSA Peugeot Citroen to develop the Prince engine which is used in the second gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mini Hatch
The Mini Hatch, stylised as MINI Hatch (or MINI Hardtop in the U.S.), also sold as Mini Cooper, Mini One, or simply called the (BMW) Mini, are a family of retro-styled two-door supermini hatchback and convertible; and (from 2014) a longer, subcompact 4/5-door hatchback. They were introduced in early 2000 by German automaker BMW under the 'Mini' brand. The second generation was launched in 2006 and the third, adding a longer 4/5-door hatchback, in 2014. A two-door convertible version was added in 2004, followed by its second generation in 2008. BMW unveiled their Mini hatch concept at the 1997 Frankfurt International Motor Show, when the Mini marque was still part of the Rover Group, owned by BMW. The styling of the concept-car, intended to replace the original Mini, was well received by the public and further developed. The new Mini (Hatch) was launched by BMW in 2001, one year after their sale of the Rover Group in March 2000, and the classic Mini's discontinuatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mini
The Mini is a small, two-door, four-seat car, developed as ADO15, and produced by the British Motor Corporation (BMC) and its successors, from 1959 through 2000. Minus a brief hiatus, original Minis were built for four decades and sold during six, from the last year of the 1950s into the last year of the 20th century, over a single generation, as fastbacks, estates, and convertibles. The original Mini is considered an icon of 1960s British popular culture. Its space-saving transverse engine and front-wheel drive layout – allowing 80% of the area of the car's floorpan to be used for passengers and luggage – influenced a generation of car makers. In 1999, the Mini was voted the second-most influential car of the 20th century, behind the Ford Model T, and ahead of the Citroën DS and Volkswagen Beetle. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bore (engine)
In a piston engine, the bore (or cylinder bore) is the diameter of each cylinder. Engine displacement is calculated based on bore, stroke length and the number of cylinders: displacement = The stroke ratio, determined by dividing the bore by the stroke, traditionally indicated whether an engine was designed for power at high engine speeds ( rpm) or torque at lower engine speeds. The term "bore" can also be applied to the bore of a locomotive cylinder or steam engine pistons. Steam locomotive The term bore also applies to the cylinder of a steam locomotive or steam engine. See also * Bore pitch * Compression ratio * Engine displacement Engine displacement is the measure of the cylinder volume swept by all of the pistons of a piston engine, excluding the combustion chambers. It is commonly used as an expression of an engine's size, and by extension as a loose indicator of t ... References {{Steam engine configurations Engine technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rover K-Series Engine
The Rover K-series engine is a series of internal combustion engines built by Powertrain Ltd, a sister company of MG Rover. The engine was a straight-four cylinder built in two forms, SOHC and DOHC, ranging from . Design history The K series was introduced in 1988 by Rover Group as a powerplant for the Rover 200 car. It was the second volume-production implementation of the low-pressure sand-casting (or LPS) technique in a new plant sited between East Works and Cofton Hackett. (The first volume application of the LPS process had been for the M-16 cylinder head, produced in South Works, adjacent to the former forge). The LPS process pumped liquid aluminium into a chemically-bonded sand mould from below. This reduced oxide inclusions and gave a casting yield of around 90%, compared with 60% for more conventional gravity casting processes. The process avoided many of the inherent problems of casting aluminium components and consequently permitted lower casting wall thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, which in turn may vary per application, and this spectrum of variance is often illustrated as a continuous energy profile. Non-transportation applications, such as industry, benefit from increased fuel efficiency, especially fossil fuel power plants or industries dealing with combustion, such as ammonia production during the Haber process. In the context of transport, fuel economy is the energy efficiency of a particular vehicle, given as a ratio of distance traveled per unit of fuel consumed. It is dependent on several factors including engine efficiency, transmission design, and tire design. In most countries, using the metric system, fuel economy is stated as "fuel consumption" in liters per 100 kilometers (L/100 km) or k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharged
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and/or increase power outputs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
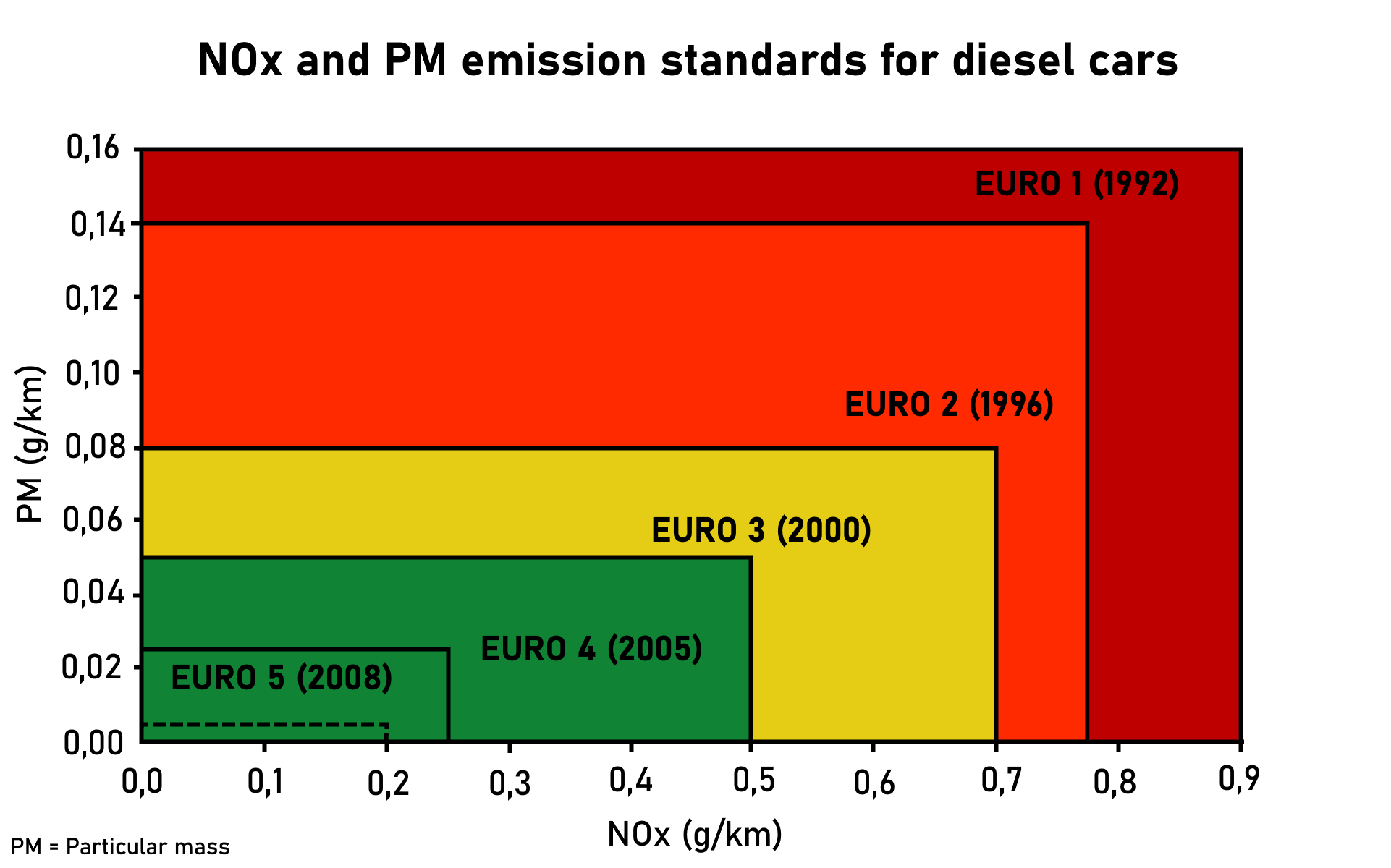
Euro IV
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a series of European Union directives staging the progressive introduction of increasingly stringent standards. , the standards do not include non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Details of Euro 7 have been postponed to 12 October 2022. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), locomotives, tractors and similar machinery, barges, but excluding seagoing ships and aeroplanes. For each vehicle type, different standards apply. Compliance is determined by running the engine at a standardised test cycle. Non-comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Throttle Control
Electronic throttle control (ETC) is an automobile technology which electronically "connects" the accelerator pedal to the throttle, replacing a mechanical linkage. A typical ETC system consists of three major components: (i) an accelerator pedal module (ideally with two or more independent sensors), (ii) a throttle valve that can be opened and closed by an electric motor (sometimes referred to as an electric or electronic throttle body (ETB)), and (iii) a powertrain or engine control module (PCM or ECM). The ECM is a type of electronic control unit (ECU), which is an embedded system that employs software to determine the required throttle position by calculations from data measured by other sensors, including the accelerator pedal position sensors, engine speed sensor, vehicle speed sensor, and cruise control switches. The electric motor is then used to open the throttle valve to the desired angle via a closed-loop control algorithm within the ECM. The benefits of electronic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiat Powertrain Technologies
FPT Industrial is an Italian multinational designer and manufacturer of transmissions, axles, diesel and petrol engines that was established in March 2005 as a Fiat Group division which included all the activities related to powertrains and transmissions. The company was formed following the dissolution of the alliance between Fiat and General Motors. Between 2005 and 2011, the company also included industrial and commercial powertrain activities that were subsequently spun off as a separate entity named FPT Industrial, which is currently an Iveco Group brand. The company has activities in nine different countries, it has 10 plants and around 20,000 employees. With output of around 2.9 million engines and 2.4 million transmissions and axles annually, FPT Industrial is one of the largest companies in the powertrain sector. FPT innovations * Variable Valve Timing (1960). First patent of automotive variable valve timing * Common Rail Common rail direct fuel injection is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSA Peugeot Citroen
The PSA Group (), legally known as Peugeot S.A. (Peugeot Société Anonyme, trading as Groupe PSA; formerly known as PSA Peugeot Citroën from 1991 to 2016) was a French multinational automotive manufacturing company which produced automobiles and motorcycles under the Peugeot, Citroën, DS, Opel and Vauxhall brands. On 18 December 2019, PSA and Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA) announced that they had agreed to the terms of a binding $50 billion merger. On 16 July 2020, both companies announced the new name for their merged operations, Stellantis. The deal closed on 16 January 2021. Stellantis is now the third largest automotive manufacturing company, behind only Volkswagen and Toyota. Peugeot was the largest PSA brand. PSA was listed on the Euronext Paris stock exchange and was a constituent of the CAC 40 index. Beginning in 2016, PSA began to outline a strategy which entailed the rapid expansion of the company, through both geographic expansion and acquisitions of other car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DaimlerChrysler
The Mercedes-Benz Group AG (previously named Daimler-Benz, DaimlerChrysler and Daimler) is a German multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is one of the world's leading car manufacturers. Daimler-Benz was formed with the merger of Benz & Cie. and Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft in 1926. The company was renamed DaimlerChrysler upon acquiring the American automobile manufacturer Chrysler Corporation in 1998, and was again renamed Daimler AG upon divestment of Chrysler in 2007. In 2021, Daimler AG was the second-largest German automaker and the sixth-largest worldwide by production. In February 2022, Daimler was renamed Mercedes-Benz Group. The Mercedes-Benz Group's marques are Mercedes-Benz for cars and vans (including Mercedes-AMG and Mercedes-Maybach) and Smart. It has shares in other vehicle manufactures such as Daimler Truck, Denza, BAIC Motor and Aston Martin. By unit sales, the Mercedes-Benz Group is the thirt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curitiba, Brazil
Curitiba () is the capital and largest city in the state of Paraná in Brazil. The city's population was 1,948,626 , making it the eighth most populous city in Brazil and the largest in Brazil's South Region. The Curitiba Metropolitan area comprises 26 municipalities with a total population of over 3.2 million (IBGE estimate in 2010), making it the seventh most populous metropolitan area in the country. The city sits on a plateau at above sea level. It is located west of the seaport of Paranaguá and is served by the Afonso Pena International and Bacacheri airports. Curitiba is an important cultural, political, and economic center in Latin America and hosts the Federal University of Paraná, established in 1912. In the 1700s, Curitiba's favorable location between cattle-breeding countryside and marketplaces led to a successful cattle trade and the city's first major expansion. Later, between 1850 and 1950, it grew due to logging and agricultural expansion in Paran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |