|
Trinity Catholic College, Middlesbrough
Trinity Catholic College is a large, co-educational secondary school and sixth form in the town of Middlesbrough, North Yorkshire, England. It is part of Nicholas Postgate Catholic Academy Trust. Founded in 2009 following the amalgamation of St David's Roman Catholic Technology College, Newlands Catholic School FCJ, and St Mary's Catholic Sixth Form College, it is one of the largest Catholic secondary schools in the north east and the biggest in Teesside, with over 1,300 students on-roll. The College is based on a multi-million pound campus between Ladgate Lane and Saltersgill Avenue, which includes a state-of-the-art main building and a brand-new sixth form centre. The campus opened in 2011 after over £24 million in investment through the Building Schools for the Future programme. In 2020, the school announced it would be further extending its facilities. The school has been a member of the Nicholas Postgate Catholic Academy Trust since 2018, a multi academy trust which s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy (English School)
An academy school in England is a state-funded school which is directly funded by the Department for Education and independent of local authority control. The terms of the arrangements are set out in individual Academy Funding Agreements. Most academies are secondary schools, though slightly more than 25% of primary schools (4,363 as of December 2017) are academies. Academies are self-governing non-profit charitable trusts and may receive additional support from personal or corporate sponsors, either financially or in kind. Academies are inspected and follow the same rules on admissions, special educational needs and exclusions as other state schools and students sit the same national exams. They have more autonomy with the National Curriculum, but do have to ensure that their curriculum is broad and balanced, and that it includes the core subjects of English, maths and science. They must also teach relationships and sex education, and religious education. They are free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
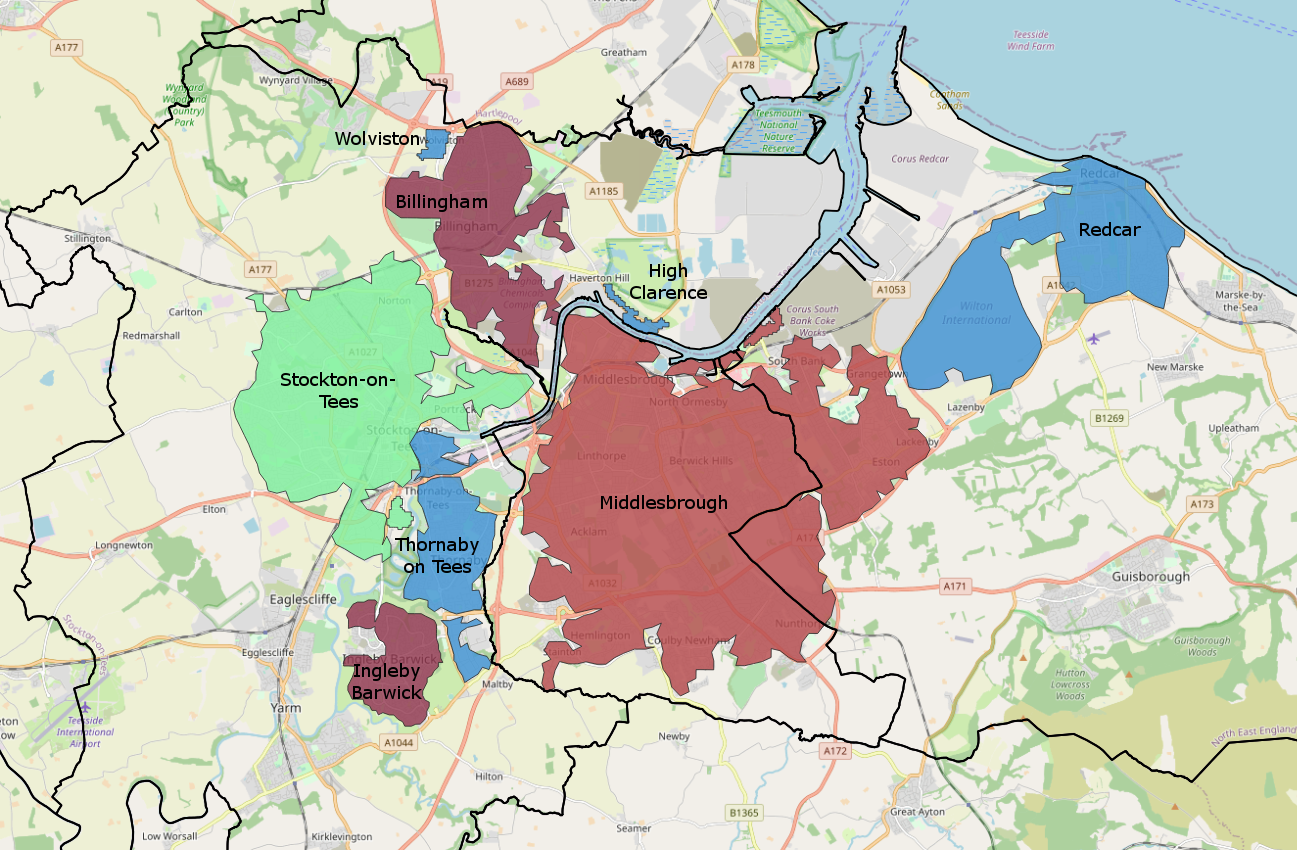
Teesside
Teesside () is a built-up area around the River Tees in the north of England, split between County Durham and North Yorkshire. The name was initially used as a county borough in the North Riding of Yorkshire. Historically a hub for heavy manufacturing, the number of people employed in this type of work declined from the 1960s onwards, with steel-making and chemical manufacturing (particularly through Imperial Chemical Industries) replaced to some extent by new science businesses and service sector roles. History 1968–1974: County borough Before the county of Cleveland was created, the area (including Stockton-on-Tees) existed as a part of the North Riding of Yorkshire, due to most land being south of the Tees. Teesside was created due to Stockton-on-Tees being linked heavily with Thornaby (which had amalgamated with South Stockton/Mandale to form the Borough of Thornaby), Middlesbrough and Redcar by industry. Compared to the modern Teesside conurbation, the area was sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Group
Educational stages are subdivisions of formal learning, typically covering early childhood education, primary education, secondary education and tertiary education. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) recognizes nine levels of education in its International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED) system (from Level 0 (pre-primary education) through Level 8 (doctoral)). UNESCO's International Bureau of Education maintains a database of country-specific education systems and their stages. Organization Education during childhood and early adulthood is typically provided through either a two- or three-stage system of childhood school, followed by additional stages of higher education or vocational education for those who continue their formal education: *Early childhood education at preschool, nursery school, or kindergarten (outside the U.S. and Canada) *Primary education at primary school or elementary school, and sometimes in the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School-houses
One-room schools, or schoolhouses, were commonplace throughout rural portions of various countries, including Prussia, Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Spain. In most rural and small town schools, all of the students met in a single room. There, a single teacher taught academic basics to several grade levels of elementary-age children. While in many areas one-room schools are no longer used, some remain in developing nations and rural or remote areas. In the United States, the concept of a "little red schoolhouse" is a stirring one, and historic one-room schoolhouses have widely been preserved and are celebrated as symbols of frontier values and of local and national development. When necessary, the schools were enlarged or replaced with two-room schools. More than 200 are listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. In Norway, by contrast, one-room schools were viewed more as impositions upon conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
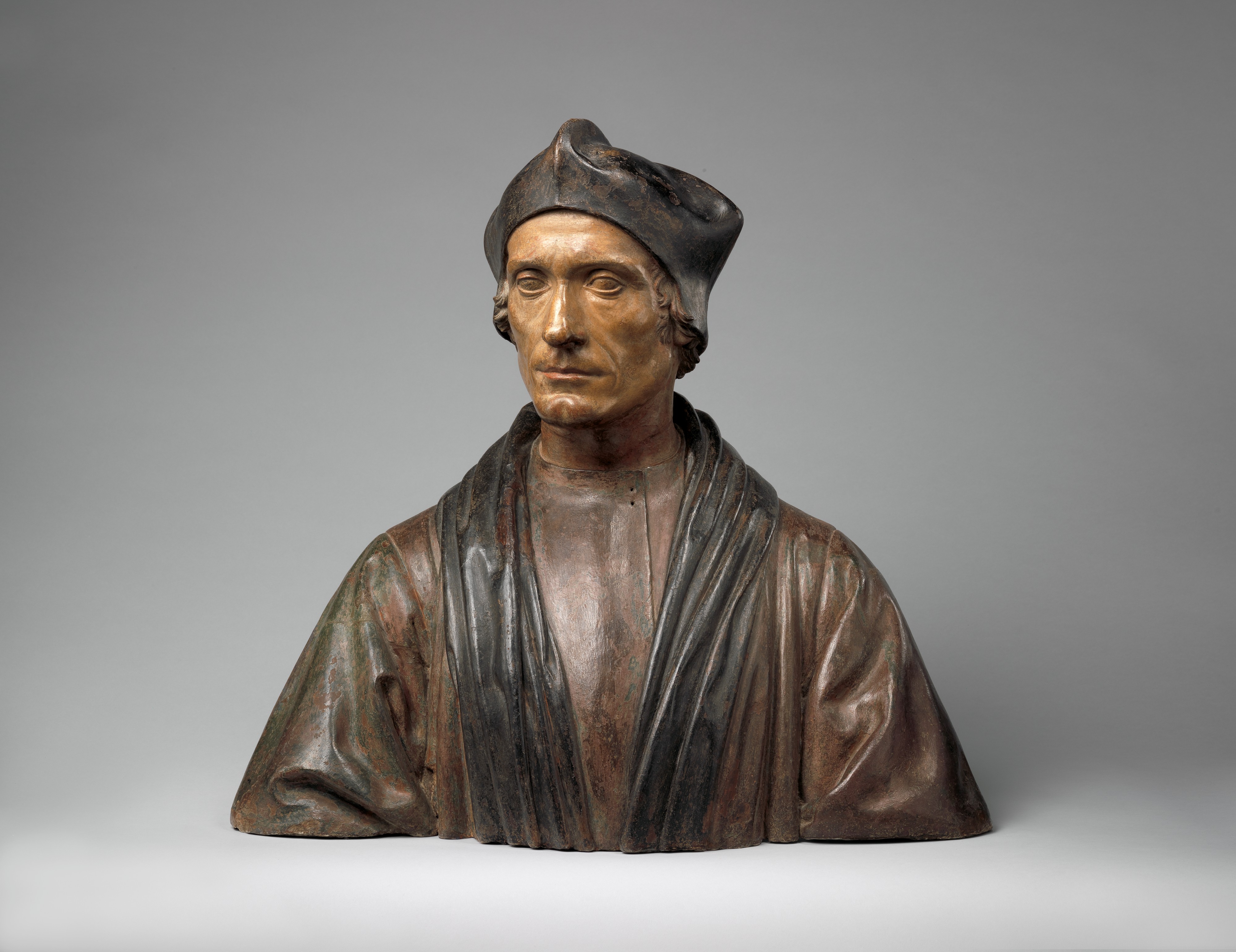
St John Fisher
John Fisher (c. 19 October 1469 – 22 June 1535) was an English Catholic bishop, cardinal, and theologian. Fisher was also an academic and Chancellor of the University of Cambridge. He was canonized by Pope Pius XI. Fisher was executed by order of Henry VIII during the English Reformation for refusing to accept him as the supreme head of the Church of England and for upholding the Catholic Church's doctrine of papal supremacy. He was named a cardinal shortly before his death. He is honoured as a martyr and saint by the Catholic Church. He shares his feast day with Thomas More on 22 June in the Catholic calendar of saints and on 6 July in that of the Church of England. Early life John Fisher was born in Beverley, Yorkshire, in 1469, the eldest son of Robert Fisher, a modestly prosperous merchant of Beverley, and Agnes, his wife. He was one of four children. His father died when John was eight. His mother remarried and had five more children by her second husband, Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Margaret Clitherow
Margaret Clitherow (1556 – 25 March 1586) was an English saint and martyr of the Roman Catholic Church, known as "the Pearl of York". She was pressed to death for refusing to enter a plea to the charge of harbouring Catholic priests. She was canonised in 1970 by Pope Paul VI. Life Margaret Clitherow was born in 1556, one of five children of Thomas and Jane Middleton. Her father was a respected businessman, a wax-chandler and Sheriff of York in 1564,Camm, Bede. "St. Margaret Clitherow." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 4. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1908. 27 March 2016 who died when Margaret was fourteen. In 1571, she married John Clitherow, a wealthy butcher and a chamberlain of the city, and bore him three children; the family lived at today's [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilda Of Whitby
Hilda (or Hild) of Whitby (c. 614 – 680) was a Christian saint and the founding abbess of the monastery at Whitby, which was chosen as the venue for the Synod of Whitby in 664. An important figure in the Christianisation of Anglo-Saxon England, she was abbess at several monasteries and recognised for the wisdom that drew kings to her for advice. The source of information about Hilda is the ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' by Bede in 731, who was born approximately eight years before her death. He documented much of the Christian conversion of the Anglo-Saxons. Early life According to Bede, Hilda was born in 614 into the Deiran royal household. She was the second daughter of Hereric, nephew of Edwin, King of Deira and his wife, Breguswīþ. When Hilda was still an infant, her father was poisoned while in exile at the court of the Brittonic king of Elmet in what is now West Yorkshire. In 616, Edwin killed Æthelfrith, the son of Æthelric of Bernicia, in bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom of Northumbria of the Angles (contemporarily Monkwearmouth–Jarrow Abbey in Tyne and Wear, England). Born on lands belonging to the twin monastery of Monkwearmouth–Jarrow in present-day Tyne and Wear, Bede was sent to Monkwearmouth at the age of seven and later joined Abbot Ceolfrith at Jarrow. Both of them survived a plague that struck in 686 and killed a majority of the population there. While Bede spent most of his life in the monastery, he travelled to several abbeys and monasteries across the British Isles, even visiting the archbishop of York and King Ceolwulf of Northumbria. He was an author, teacher (Alcuin was a student of one of his pupils), and scholar, and his most famous work, ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Postgate
Nicholas Postgate (1596 or 1597 – 7 August 1679) was an English Catholic priest who was executed for treason on the Knavesmire in York on 6 August 1679 as part of the anti-Catholic persecution that was sweeping England at that time. He is one of the 85 English Catholic Martyrs of England and Wales beatified by Pope John Paul II in November 1987. Early life and priesthood Postgate was born at Kirkdale House, Egton, Yorkshire, England. He entered Douay College, in France, 11 July 1621. He took the college oath on 12 March 1623, received minor orders, 23 December 1624, the subdiaconate, 18 December 1627, the diaconate, 18 March 1628, and the priesthood two days later. He was sent to the mission on 29 June 1630, and worked in England for the Catholic religion, finally settling back to Ugthorpe, not far from his birthplace, in the 1660s. His parish, which was known by the extinct name of Blackamoor, extended between Guisborough, Pickering and Scarborough. Thomas Ward, who late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Of The Church
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or Sikh gur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Catholic Martyrs Of The English Reformation
The Catholic martyrs of the English Reformation are men and women executed under treason legislation in the English Reformation, between 1534 and 1680, and recognised as martyrs by the Catholic Church. Though consequences of the English Reformation were felt in Ireland and Scotland as well, this article only covers those who died in the Kingdom of England. On 25 February 1570, Pope Pius V's "Regnans in Excelsis" bull excommunicated the English Queen Elizabeth I, and any who obeyed her. This papal bull also required all Catholics to rebel against the English Crown as a matter of faith. In response, in 1571 legislation was enacted making it treasonable to be under the authority of the Pope, including being a Jesuit, being Catholic or harbouring a Catholic priest. The standard penalty for all those convicted of treason at the time was execution by being hanged, drawn and quartered. In the reign of Pope Gregory XIII (1572–85), authorisation was given for 63 recognised marty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)