|
Triazene Cleavage
Triazenes are organic compounds that contain the functional group −N(R)−N=N− (where R is H, alkyl, aryl). Some anti-cancer medications and dyes are triazenes. Formally, triazenes are related to the unstable triazene, H2N−N=NH. The relationship is more theoretical than practical. Production 200px, Dacarbazine is a triazene used in the treatment of melanoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma">melanoma.html" ;"title="Dacarbazine is a triazene used in the treatment of melanoma">Dacarbazine is a triazene used in the treatment of melanoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma. Triazenes are prepared from the ''N''-coupling reaction between diazonium salts and primary or secondary amines. Symmetrical triazenes, for example 1,3-diphenyltriazene (PhN=N−NHPh), are prepared by the partial diazotization of aromatic primary amines, aniline in this example, and the subsequent coupling reaction in the presence of sodium acetate. Asymmetrical triazenes, for example (phenyldiazenyl)pyrrolidine (PhN=N−NC4H8) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tröger's Base
Tröger's base is a white solid tetracyclic organic compound. structure and formula of (CH3C6H3NCH2)2CH2. Tröger's base and its analogs are soluble in various organic solvents and strong acidic aqueous solutions due to their protonation. History Tröger's original research in 1887 failed to elaborate the exact structure of his new product that lead Johannes Wislicenus, the departmental director of the time, to assign a mediocre grade for Tröger's thesis. Despite various possible structures had been drawn for Tröger's product, its correct structure remained as a mystery for 48 years, until the final elucidation in 1935 by Spielman. Structure and chirality The nitrogen inversion normally leads to a rapid equilibrium between the enantiomers of chiral amines, that prevents them showing any optical activity. The inversion can be stopped by conformational strain as Tröger's base has demonstrated that nitrogen is capable of forming a stereogenic center in organic molecules. In Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactam
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size: * α-Lactam (3-atom rings) * β-Lactam (4-atom rings) * γ-Lactam (5-atom rings) * δ-Lactam (6-atom rings) * ε-Lactam (7-atom rings) This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that a hydrolyzed α-Lactam leads to an α-amino acid and a β-Lactam to a β-amino acid, ''etc''. Synthesis General synthetic methods exist for the organic synthesis of lactams. Beckmann rearrangement Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement. Schmidt reaction Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclization of amino acids Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the same molecule. Lactamization is most efficient in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnoline
Cinnoline is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinoxaline, phthalazine and quinazoline. Properties The free base can be obtained as an oil by treatment of the hydrochloride with base. It co-crystallizes with one molecule of ether as white silky needles, (m.p. 24–25 °C) upon cooling ethereal solutions. The free base melts at 39 °C. It has a taste resembling that of chloral hydrate and leaves a sharp irritation for some time. Cinnoline derivatives are obtained from oxycinnoline carboxylic acid, which is formed by digesting orthophenyl propiolic acid diazo chloride with water. Oxycinnoline carboxylic acid on heating gives oxycinnoline, melting at 225 °C, which with phosphorus pentachloride gives chlorcinnoline. This substance is reduced by iron filings and sulfuric acid to dihydrocinnoline. Discovery and synthesis The compound was first obtained in impure form by cyclization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triazene 1
Triazene is an unsaturated compound, unsaturated inorganic compound having the chemical formula nitrogen, N3hydrogen, H3. It has one covalent bond, double bond and is the second-simplest member of the azene class of hydronitrogen compounds, after diimide. Triazenes are a class of organic compounds containing the functional group -N(H)-N=N-. Triazene, possibly along with its isomer triimide (HNNHNH), has been synthesized in electron-irradiated ices of ammonia and ammonia/dinitrogen and detected in the gas phase after Sublimation (phase transition), sublimation.Forstel, Tsegaw, Maksyutenko, Mebel, Sander, & Kaiser. "On the formation of N3H3 isomers in irradiated ammonia bearing ices: Triazene (H2NNNH) or Triimide (HNHNNH)", ''ChemPhysChem'', 2016, 17, 2726. References External links *IUPAC Gold Book]definition {{Hydrides by group Nitrogen hydrides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. Aromatic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
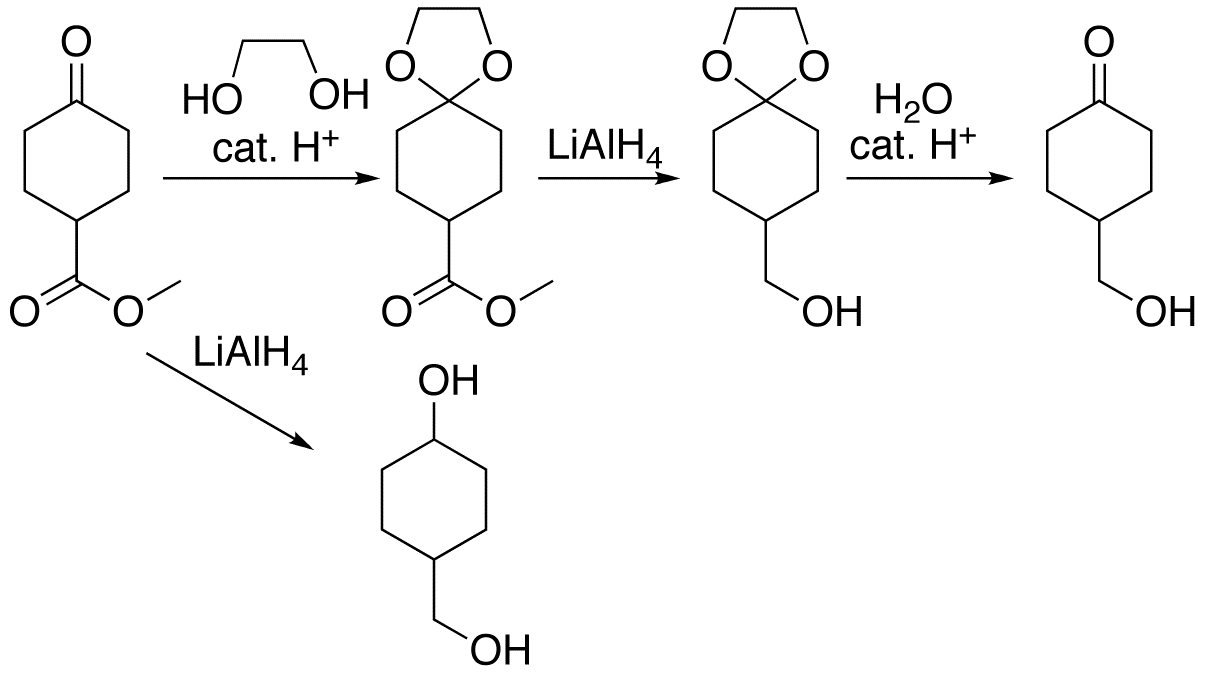
Protecting Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, some specific parts of their molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. Then, these parts, or groups, must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive but useful reagent capable of reducing esters to alcohols. It will always react with carbonyl groups, and this cannot be discouraged by any means. When a reduction of an ester is required in the presence of a carbonyl, the attack of the hydride on the carbonyl has to be prevented. For example, the carbonyl is converted into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the step involving the hydride is complete, the acet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiophenol
Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols except the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. Thiophenols also describes a class of compounds formally derived from thiophenol itself. All have a sulfhydryl group (-SH) covalently bonded to an aromatic ring. The organosulfur ligand in the medicine thiomersal is a thiophenol. Synthesis There are several methods of synthesis for thiophenol and related compounds, although thiophenol itself is usually purchased for laboratory operations. Methods a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Sulfide
Sodium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2 S, or more commonly its hydrate Na2S·9 H2O. Both the anhydrous and the hydrated salts in pure crystalline form are colorless solids, although technical grades of sodium sulfide are generally yellow to brick red owing to the presence of polysulfides and commonly supplied as a crystalline mass, in flake form, or as a fused solid. They are water-soluble, giving strongly alkaline solutions. When exposed to moist air, Na2S and its hydrates emit hydrogen sulfide, an extremely toxic, flammable and corrosive gas which smells like rotten eggs. Some commercial samples are specified as Na2S·''x''H2O, where a weight percentage of Na2S is specified. Commonly available grades have around 60% Na2S by weight, which means that ''x'' is around 3. These grades of sodium sulfide are often marketed as 'sodium sulfide flakes'. Structure Na2S adopts the antifluorite structure, which means that the Na+ centers occupy sites of the fluoride in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazonium
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. General properties and reactivity Arenediazonium cations and related species According to X-ray crystallography the linkage is linear in typical diazonium salts. The bond distance in benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is 1.083(3) Å, which is almost identical to that for dinitrogen molecule (N≡N). The linear free energy constants σm and σp indicate that the diazonium group is strongly electron-withdrawing. Thus, the diazonio-substituted phenols and benzoic acids have greatly reduced p''K''a values compared to their unsubstituted counterparts. The p''K''a of phenolic proton of 4-hydroxybenzenediazonium is 3.4, versus 9.9 for phenol itself. In other words, the diazonium group lowers the p''K''a (enhances the acidity) by a million-fold. The stabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Amine
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds (called quaternary amines in oilfield parlance) are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule. Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners. As an antimicrobial, they are able to inactivate enveloped viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2). Quats tend to be gentler on surfaces than bleach-based disinfectants, and are generally fabric-safe. Synthesis Quaternary ammonium compoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazonium Salts
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. General properties and reactivity Arenediazonium cations and related species According to X-ray crystallography the linkage is linear in typical diazonium salts. The bond distance in benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is 1.083(3) Å, which is almost identical to that for dinitrogen molecule (N≡N). The linear free energy constants σm and σp indicate that the diazonium group is strongly electron-withdrawing. Thus, the diazonio-substituted phenols and benzoic acids have greatly reduced p''K''a values compared to their unsubstituted counterparts. The p''K''a of phenolic proton of 4-hydroxybenzenediazonium is 3.4, versus 9.9 for phenol itself. In other words, the diazonium group lowers the p''K''a (enhances the acidity) by a million-fold. The stabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |