|
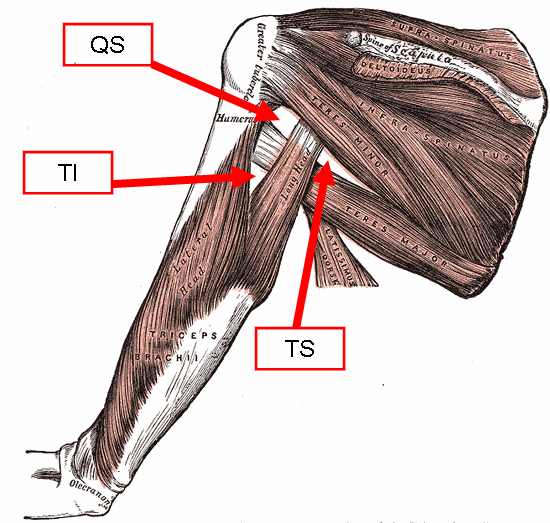
Triangular Space
The triangular space (also known as the medial triangular space, upper triangular space, medial axillary space or foramen omotricipitale) is one of the three spaces found at the axillary space. The other two spaces are the quadrangular space and the triangular interval. Boundaries It has the following boundaries: * Inferior: the superior border of the teres major; * Lateral: the long head of the triceps; * Superior: Teres minor or Subscapularis For the superior border, some sources list the teres minor, while others list the subscapularis. Contents It contains the scapular circumflex vessels. Unlike the quadrangular space or the triangular interval, no major nerve passes through the triangular space. See also * Quadrangular space * Triangular interval The triangular interval (also known as the lateral triangular space, lower triangular space, and triceps hiatus) is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axillary Space
The axillary spaces are anatomic spaces. through which axillary contents leave the axilla. They consist of the quadrangular space, triangular space, and triangular interval. It is bounded by teres major, teres minor, medial border of the humerus, and long head of triceps brachii. They should not be confused with the true "axillary space" within the borders of the axilla. Structure Axilla The true axilla is a conical space with its apex at the Cervico-axillary Canal, Base at the axillary fascia and skin of the armpit. When viewed in an axillary plane (axillary cut), it is more triangle with: Medial Wall: Serratus Anterior, Anterior Wall: pectoral muscles, Posterior Wall: subscapularis muscle, where the "apex" of the triangle is the humerus Quadrangular space This space is in the posterior wall of the axilla. It is a quadrangular space bounded laterally by surgical neck of the humerus, medially by long head of triceps brachii and inferiorly by teres major. It is bounded su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrangular Space
The quadrangular space, also known as the quadrilateral space f Velpeau'' and the foramen humerotricipitale, is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval. Structure The quadrangular space is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. Boundaries The quadrangular space is defined by: - "Scapular Region: Quadrangular Space of Scapular Region" * ''above/superior:'' teres minor muscle. * ''below/inferior:'' teres major muscle. * ''medially:'' long head of the triceps brachii muscle (lateral margin). * ''laterally:'' surgical neck of the humerus. * ''anteriorly:'' subscapularis muscle. Contents The quadrangular space transmits the axillary nerve, and the posterior humeral circumflex artery. Clinical significance The quadrangular space is a clinically important anatomic space in the arm as it provides the anterior regions of the axilla a passageway to the posterior regions. In the quadrangular space, the ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Interval
The triangular interval (also known as the lateral triangular space, lower triangular space, and triceps hiatus) is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: quadrangular space and triangular space. Borders Two of its borders are as follows: * teres major - superior * long head of the triceps brachii - medial Some sources state the lateral border is the humerus, while others define it as the lateral head of the triceps. (The effective difference is relatively minor, though.) Contents The radial nerve is visible through the triangular interval, on its way to the posterior compartment of the arm. Profunda Brachii The deep artery of arm (also known as arteria profunda brachii and the deep brachial artery) is a large vessel which arises from the lateral and posterior part of the brachial artery, just below the lower border of the teres major. Structure It ... also passes through the triangu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teres Major
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle. The teres major muscle (from Latin ''teres'', meaning "rounded") is positioned above the latissimus dorsi muscle and assists in the extension and medial rotation of the humerus. This muscle is commonly confused as a rotator cuff muscle, but it is not because it does not attach to the capsule of the shoulder joint, unlike the teres minor muscle for example. Structure The teres major muscle originates on the dorsal surface of the inferior angle and the lower part of the lateral border of the scapula. The fibers of teres major insert into the medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus. Relations The tendon, at its insertion, lies behind that of the latissimus dorsi, from which it is separated by a bursa, the two tendons being, however, united along their lower borders for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceps
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of 3 parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the arm). Structure The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. It extends distally anterior to the teres minor and posterior to the teres major. The medial head arises proximally in the humerus, just inferior to the groove of the radial nerve; from the dorsal (back) surface of the humerus; from the medial intermuscular septum; and its distal part also arises from the lateral intermuscular septum. The medial head is mostly covered by the lateral and long heads, and is only visible distally on the humerus. The lateral head arises from the dorsal surface of the humerus, lateral and proximal to the groove of the radial nerve, from the greater tubercle d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
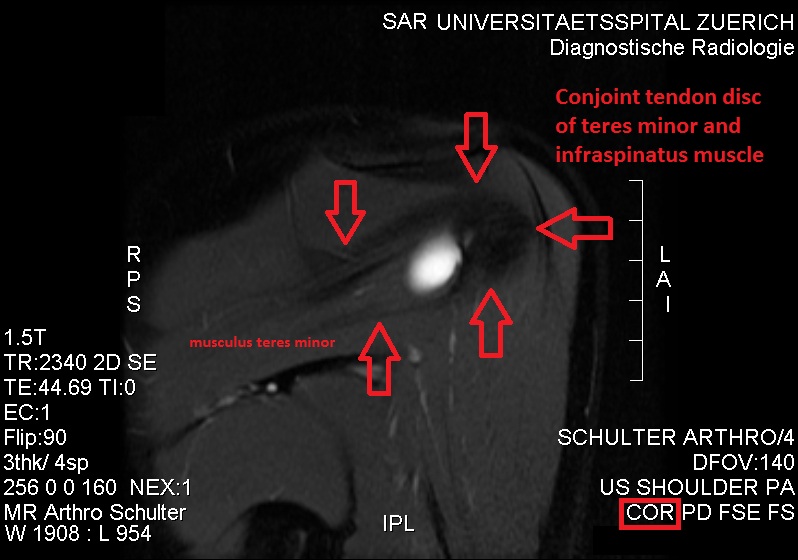
Teres Minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule. The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve. Structure It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminae, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the teres major muscle. Its fibers run obliquely upwards and laterally; the upper ones end in a tendon which is inserted into the lowest of the three impressions on the greater tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subscapularis
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the shoulder-joint. Structure It arises from its medial two-thirds and Some fibers arise from tendinous laminae, which intersect the muscle and are attached to ridges on the bone; others from an aponeurosis, which separates the muscle from the teres major and the long head of the triceps brachii. The fibers pass laterally and coalesce into a tendon that is inserted into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the anterior part of the shoulder-joint capsule. Tendinous fibers extend to the greater tubercle with insertions into the bicipital groove. Relations The tendon of the muscle is separated from the neck of the scapula by a large bursa, which communicates with the cavity of the shoulder-joint through an aperture in the capsule. The subscapularis is separated from the serratus anterior books.google.com/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapular Circumflex
The circumflex scapular artery (scapular circumflex artery, dorsalis scapulae artery) is a branch of the subscapular artery and part of the scapular anastomoses. It curves around the axillary border of the scapula, traveling through the anatomical "Triangular space" made up of the Teres minor superiorly, the Teres major inferiorly, and the long head of the Triceps laterally. It enters the infraspinatous fossa under cover of the Teres minor, and anastomoses with the transverse scapular artery (suprascapular) and the descending branch of the transverse cervical (a.k.a. dorsal scapular artery). Branches In its course it gives off two branches: * one (infrascapular) enters the subscapular fossa beneath the Subscapularis, which it supplies, anastomosing with the transverse scapular artery and the descending branch of the transverse cervical. * the other is continued along the axillary border of the scapula, between the Teres major and minor, and at the dorsal surface of the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrangular Space
The quadrangular space, also known as the quadrilateral space f Velpeau'' and the foramen humerotricipitale, is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval. Structure The quadrangular space is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. Boundaries The quadrangular space is defined by: - "Scapular Region: Quadrangular Space of Scapular Region" * ''above/superior:'' teres minor muscle. * ''below/inferior:'' teres major muscle. * ''medially:'' long head of the triceps brachii muscle (lateral margin). * ''laterally:'' surgical neck of the humerus. * ''anteriorly:'' subscapularis muscle. Contents The quadrangular space transmits the axillary nerve, and the posterior humeral circumflex artery. Clinical significance The quadrangular space is a clinically important anatomic space in the arm as it provides the anterior regions of the axilla a passageway to the posterior regions. In the quadrangular space, the ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Interval
The triangular interval (also known as the lateral triangular space, lower triangular space, and triceps hiatus) is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: quadrangular space and triangular space. Borders Two of its borders are as follows: * teres major - superior * long head of the triceps brachii - medial Some sources state the lateral border is the humerus, while others define it as the lateral head of the triceps. (The effective difference is relatively minor, though.) Contents The radial nerve is visible through the triangular interval, on its way to the posterior compartment of the arm. Profunda Brachii The deep artery of arm (also known as arteria profunda brachii and the deep brachial artery) is a large vessel which arises from the lateral and posterior part of the brachial artery, just below the lower border of the teres major. Structure It ... also passes through the triangu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |