|
Tremataspis
''Tremataspis'' is a genus of an extinct osteostracan agnathan from the Silurian period of what is now Estonia. ''Tremataspis'' was about in length, and had an armored shield covering its head. Compared with its relatives, the shield was unusually elongated, covering the whole front of the body, and was more rounded in shape. It is thought that ''Tremataspis'' used its rounder shield to burrow in the ocean floor, searching for food. Because the shield consisted of one solid piece, it probably did not grow during the animal's life; presumably, the larva A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The ...e lacked the shield, which only appeared later in life. References Osteostraci genera Fauna of Estonia Silurian fish of Europe {{silurian-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tremataspis NT Small
''Tremataspis'' is a genus of an extinct osteostracan agnathan from the Silurian period of what is now Estonia. ''Tremataspis'' was about in length, and had an armored shield covering its head. Compared with its relatives, the shield was unusually elongated, covering the whole front of the body, and was more rounded in shape. It is thought that ''Tremataspis'' used its rounder shield to burrow in the ocean floor, searching for food. Because the shield consisted of one solid piece, it probably did not grow during the animal's life; presumably, the larva A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The ...e lacked the shield, which only appeared later in life. References Osteostraci genera Fauna of Estonia Silurian fish of Europe {{silurian-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tremataspis
''Tremataspis'' is a genus of an extinct osteostracan agnathan from the Silurian period of what is now Estonia. ''Tremataspis'' was about in length, and had an armored shield covering its head. Compared with its relatives, the shield was unusually elongated, covering the whole front of the body, and was more rounded in shape. It is thought that ''Tremataspis'' used its rounder shield to burrow in the ocean floor, searching for food. Because the shield consisted of one solid piece, it probably did not grow during the animal's life; presumably, the larva A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The ...e lacked the shield, which only appeared later in life. References Osteostraci genera Fauna of Estonia Silurian fish of Europe {{silurian-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
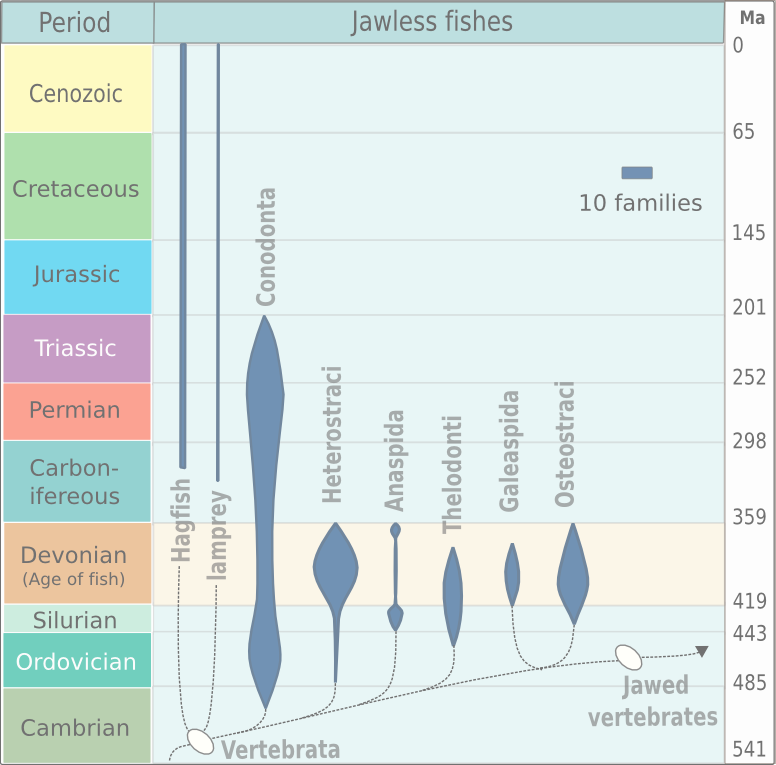
Osteostraci
The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, the osteostracans, especially the Devonian species, were among the most advanced of all known agnathans. This is due to the development of paired fins, and their complicated cranial anatomy. The osteostracans were more similar to lampreys than to jawed vertebrates in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear, as opposed to the three pairs found in the inner ears of jawed vertebrates. They are thought to be the sister-group to pituriaspids, and together, these two taxa of jawless vertebrates are the sister-group of gnathostomes. Several synapomorphies support this hypothesis, such as the presence of: sclerotic ossicles, paired pectoral fins, a dermal skeleton with three layers (a basal layer of isopedin, a middle layer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteostraci Genera
The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, the osteostracans, especially the Devonian species, were among the most advanced of all known agnathans. This is due to the development of paired fins, and their complicated cranial anatomy. The osteostracans were more similar to lampreys than to jawed vertebrates in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear, as opposed to the three pairs found in the inner ears of jawed vertebrates. They are thought to be the sister-group to pituriaspids, and together, these two taxa of jawless vertebrates are the sister-group of gnathostomes. Several synapomorphies support this hypothesis, such as the presence of: sclerotic ossicles, paired pectoral fins, a dermal skeleton with three layers (a basal layer of isopedin, a middle layer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatha
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (cyclostomes) and extinct ( conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While a few scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of . The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the autochthonous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language. The land of what is now modern Estonia has been inhabited by '' Homo sapiens'' since at least 9,000 BC. The medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last " pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immobil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of Estonia
Estonia is a small, heavily forested country situated on the Baltic Sea. It is a part of the Euro-Siberian region of terrestrial Palearctic realm, and the Temperate Northern Atlantic marine ecoregion. Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, Estonia is shared between the Central European and Eastern European provinces of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, WWF, the territory of Estonia belongs to the ecoregion of Sarmatic mixed forests. Estonia's sparse population and large areas of forest have allowed stocks of European lynx, wild boar, brown bears, and moose to survive, among other animals. Estonia is thought to have a wolf population of around 200, which is considered slightly above the optimum range of 100 to 200. Estonian birdlife is characterized by rare seabirds like the Steller's eider (''Polysticta stelleri''), lesser white-fronted goose (''Anser erythropus'') and black-tailed godwit (''Limosa limosa''), wetland bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)