|
Tree Alignment
In computational phylogenetics, tree alignment is a computational problem concerned with producing multiple sequence alignments, or alignments of three or more sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein. Sequences are arranged into a phylogenetic tree, modeling the evolutionary relationships between species or taxa. The edit distances between sequences are calculated for each of the tree's internal vertices, such that the sum of all edit distances within the tree is minimized. Tree alignment can be accomplished using one of several algorithms with various trade-offs between manageable tree size and computational effort. Definition Input: A set S of sequences, a phylogenetic tree T leaf-labeled by S and an edit distance function d between sequences. Output: A labeling of the internal vertices of T such that \Sigma_ d(e) is minimized, where d(e) is the edit distance between the endpoints of e. The task is NP-hard. Background Sequence alignment In bioinformatics, the basic method of inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computational Phylogenetics
Computational phylogenetics, phylogeny inference, or phylogenetic inference focuses on computational and optimization algorithms, Heuristic (computer science), heuristics, and approaches involved in Phylogenetics, phylogenetic analyses. The goal is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of genes, species, or taxa. Maximum likelihood estimation, Maximum likelihood, Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics), parsimony, Bayesian inference in phylogeny, Bayesian, and minimum evolution are typical optimality criteria used to assess how well a phylogenetic tree topology describes the sequence data. Nearest Neighbour Interchange (NNI), Subtree Prune and Regraft (SPR), and Tree Bisection and Reconnection (TBR), known as tree rearrangements, are deterministic algorithms to search for optimal or the best phylogenetic tree. The space and the landscape of searching for the optimal phylogenetic tree is known as phylogeny search space. Maximum Likelihood (al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
NP-complete
In computational complexity theory, NP-complete problems are the hardest of the problems to which ''solutions'' can be verified ''quickly''. Somewhat more precisely, a problem is NP-complete when: # It is a decision problem, meaning that for any input to the problem, the output is either "yes" or "no". # When the answer is "yes", this can be demonstrated through the existence of a short (polynomial length) ''solution''. # The correctness of each solution can be verified quickly (namely, in polynomial time) and a brute-force search algorithm can find a solution by trying all possible solutions. # The problem can be used to simulate every other problem for which we can verify quickly that a solution is correct. Hence, if we could find solutions of some NP-complete problem quickly, we could quickly find the solutions of every other problem to which a given solution can be easily verified. The name "NP-complete" is short for "nondeterministic polynomial-time complete". In this name, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
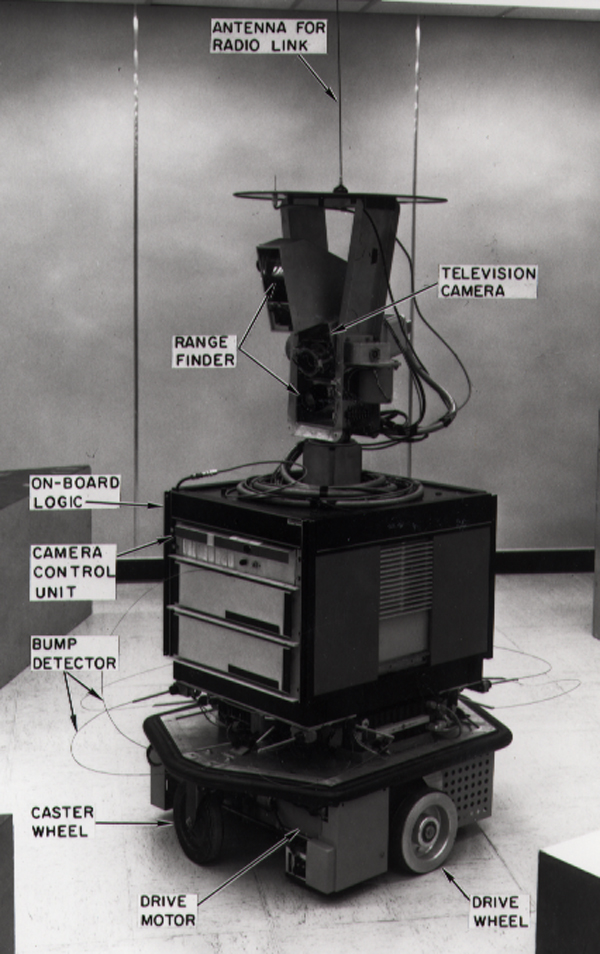
A* Search Algorithm
A* (pronounced "A-star") is a graph traversal and pathfinding algorithm that is used in many fields of computer science due to its completeness, optimality, and optimal efficiency. Given a weighted graph, a source node and a goal node, the algorithm finds the shortest path (with respect to the given weights) from source to goal. One major practical drawback is its O(b^d) space complexity where is the depth of the shallowest solution (the length of the shortest path from the source node to any given goal node) and is the branching factor (the maximum number of successors for any given state), as it stores all generated nodes in memory. Thus, in practical travel-routing systems, it is generally outperformed by algorithms that can pre-process the graph to attain better performance, as well as by memory-bounded approaches; however, A* is still the best solution in many cases. Peter Hart, Nils Nilsson and Bertram Raphael of Stanford Research Institute (now SRI International) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Particle Swarm Optimization
In computational science, particle swarm optimization (PSO) is a computational method that Mathematical optimization, optimizes a problem by iterative method, iteratively trying to improve a candidate solution with regard to a given measure of quality. It solves a problem by having a population of candidate solutions, here dubbed Point particle, particles, and moving these particles around in the Optimization (mathematics)#Concepts and notation, search-space according to simple formula, mathematical formulae over the particle's Position (vector), position and velocity. Each particle's movement is influenced by its local best known position, but is also guided toward the best known positions in the search-space, which are updated as better positions are found by other particles. This is expected to move the swarm toward the best solutions. PSO is originally attributed to James Kennedy (social psychologist), Kennedy, Russell C. Eberhart, Eberhart and Yuhui Shi, Shi and was first int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iterative
Iteration is the repetition of a process in order to generate a (possibly unbounded) sequence of outcomes. Each repetition of the process is a single iteration, and the outcome of each iteration is then the starting point of the next iteration. In mathematics and computer science, iteration (along with the related technique of recursion) is a standard element of algorithms. Mathematics In mathematics, iteration may refer to the process of iterating a function, i.e. applying a function repeatedly, using the output from one iteration as the input to the next. Iteration of apparently simple functions can produce complex behaviors and difficult problems – for examples, see the Collatz conjecture and juggler sequences. Another use of iteration in mathematics is in iterative methods which are used to produce approximate numerical solutions to certain mathematical problems. Newton's method is an example of an iterative method. Manual calculation of a number's square root is a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heuristic Algorithm
A heuristic or heuristic technique (''problem solving'', '' mental shortcut'', ''rule of thumb'') is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless "good enough" as an approximation or attribute substitution. Where finding an optimal solution is impossible or impractical, heuristic methods can be used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution. Heuristics can be mental shortcuts that ease the cognitive load of making a decision. Context Gigerenzer & Gaissmaier (2011) state that sub-sets of ''strategy'' include heuristics, regression analysis, and Bayesian inference. Heuristics are strategies based on rules to generate optimal decisions, like the anchoring effect and utility maximization problem. These strategies depend on using readily accessible, though loosely applicable, information to control problem solving in human beings, machines and abstract issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Combinatorial Game Theory
Combinatorial game theory is a branch of mathematics and theoretical computer science that typically studies sequential games with perfect information. Research in this field has primarily focused on two-player games in which a ''position'' evolves through alternating ''moves'', each governed by well-defined rules, with the aim of achieving a specific winning condition. Unlike game theory, economic game theory, combinatorial game theory generally avoids the study of games of chance or games involving imperfect information, preferring instead games in which the current state and the full set of available moves are always known to both players. However, as mathematical techniques develop, the scope of analyzable games expands, and the boundaries of the field continue to evolve. Authors typically define the term "game" at the outset of academic papers, with definitions tailored to the specific game under analysis rather than reflecting the field’s full scope. Combinatorics, Comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Evolutionary Tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In other words, it is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. In evolutionary biology, all life on Earth is theoretically part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. Phylogenetics is the study of phylogenetic trees. The main challenge is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of species or taxa. Computational phylogenetics (also phylogeny inference) focuses on the algorithms involved in finding optimal phylogenetic tree in the phylogenetic landscape. Phylogenetic trees may be rooted or unrooted. In a ''rooted'' phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Combinatorial Optimization
Combinatorial optimization is a subfield of mathematical optimization that consists of finding an optimal object from a finite set of objects, where the set of feasible solutions is discrete or can be reduced to a discrete set. Typical combinatorial optimization problems are the travelling salesman problem ("TSP"), the minimum spanning tree problem ("MST"), and the knapsack problem. In many such problems, such as the ones previously mentioned, exhaustive search is not tractable, and so specialized algorithms that quickly rule out large parts of the search space or approximation algorithms must be resorted to instead. Combinatorial optimization is related to operations research, algorithm theory, and computational complexity theory. It has important applications in several fields, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, auction theory, software engineering, VLSI, applied mathematics and theoretical computer science. Applications Basic applications of combina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exponential
Exponential may refer to any of several mathematical topics related to exponentiation, including: * Exponential function, also: **Matrix exponential, the matrix analogue to the above *Exponential decay, decrease at a rate proportional to value * Exponential discounting, a specific form of the discount function, used in the analysis of choice over time *Exponential growth, where the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value * Exponential map (Riemannian geometry), in Riemannian geometry *Exponential map (Lie theory), in Lie theory * Exponential notation, also known as scientific notation, or standard form *Exponential object, in category theory * Exponential time, in complexity theory *in probability and statistics: **Exponential distribution, a family of continuous probability distributions ** Exponentially modified Gaussian distribution, describes the sum of independent normal and exponential random variables **Exponential family, a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computational Biology
Computational biology refers to the use of techniques in computer science, data analysis, mathematical modeling and Computer simulation, computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and data science, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, molecular biology, cell biology, chemistry, and genetics. History Bioinformatics, the analysis of informatics processes in biological systems, began in the early 1970s. At this time, research in artificial intelligence was using network models of the human brain in order to generate new algorithms. This use of biological data pushed biological researchers to use computers to evaluate and compare large data sets in their own field. By 1982, researchers shared information via Punched card, punch cards. The amount of data grew exponentially by the end of the 1980s, requiring new computational methods for quickly interpreting relevant information. Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
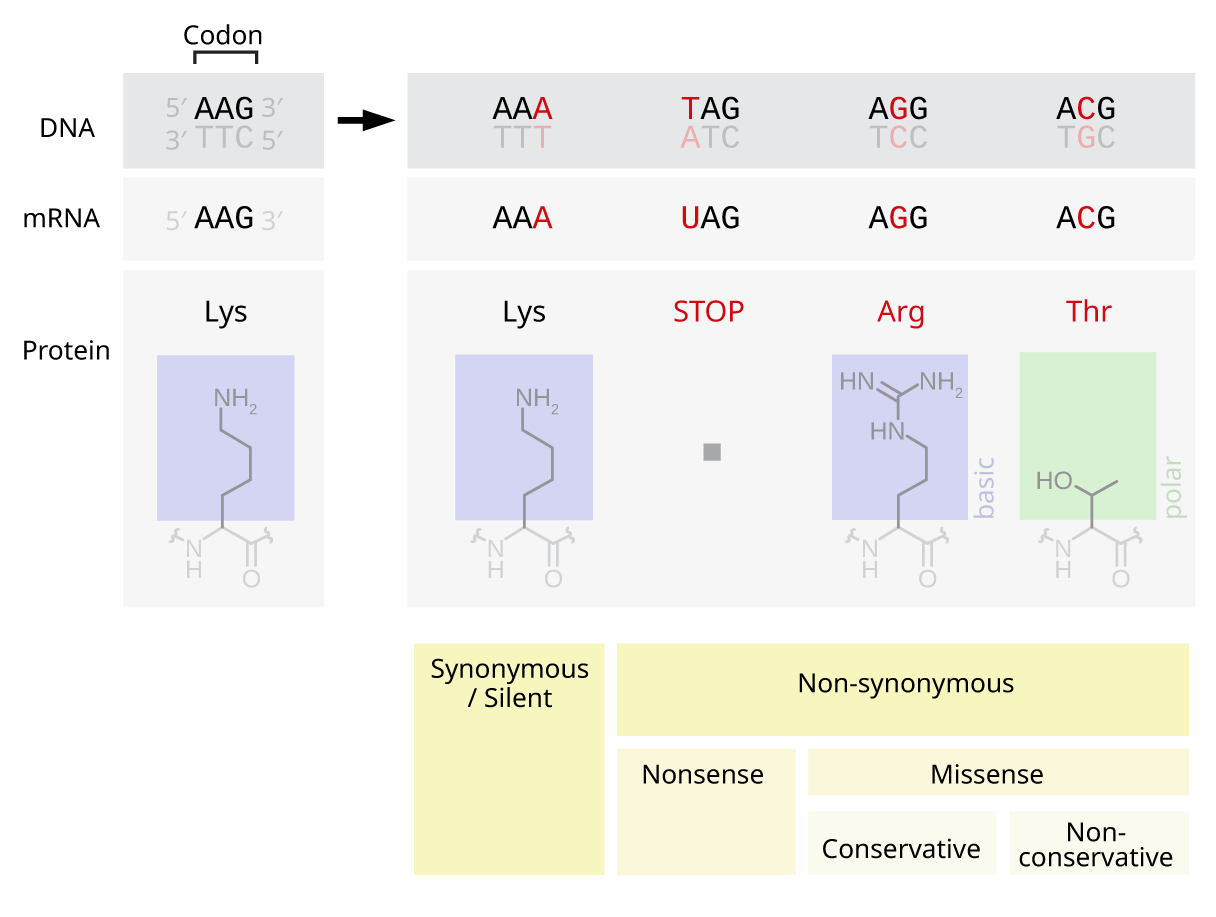
Base-pair Substitution
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA replication. The rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |