|
Transom (nautical)
A transom is the vertical reinforcement which strengthens the stern of a boat. This flat termination of the stern is typically above the waterline. The term was used as far back as Middle English in the 1300s, having come from Latin ''transversus'' (transverse) via Old French ''traversain'' (set crosswise). The stern of a boat is typically vertical. It can be raked such that there is an overhang above the water, as at the bow. A reverse transom is angled from the waterline forwards. Transoms can be used to support a rudder, outboard motor, or as a swimming and access platform. Gallery File:The Bermuda cedar (Juniperus bermudiana) transom of Spirit of Bermuda, 2016.jpg, The Bermuda cedar transom of the Spirit of Bermuda File:Sea Scooter transom.jpg, Flat transom on a dinghy with mount points for a rudder. File:Coble on shore at Boulmer (2) - geograph.org.uk - 1381157.jpg, Raked transom with rudder mount points. File:CS 30 Sailboat Kelsea 0297.jpg, Reverse transom with rudde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
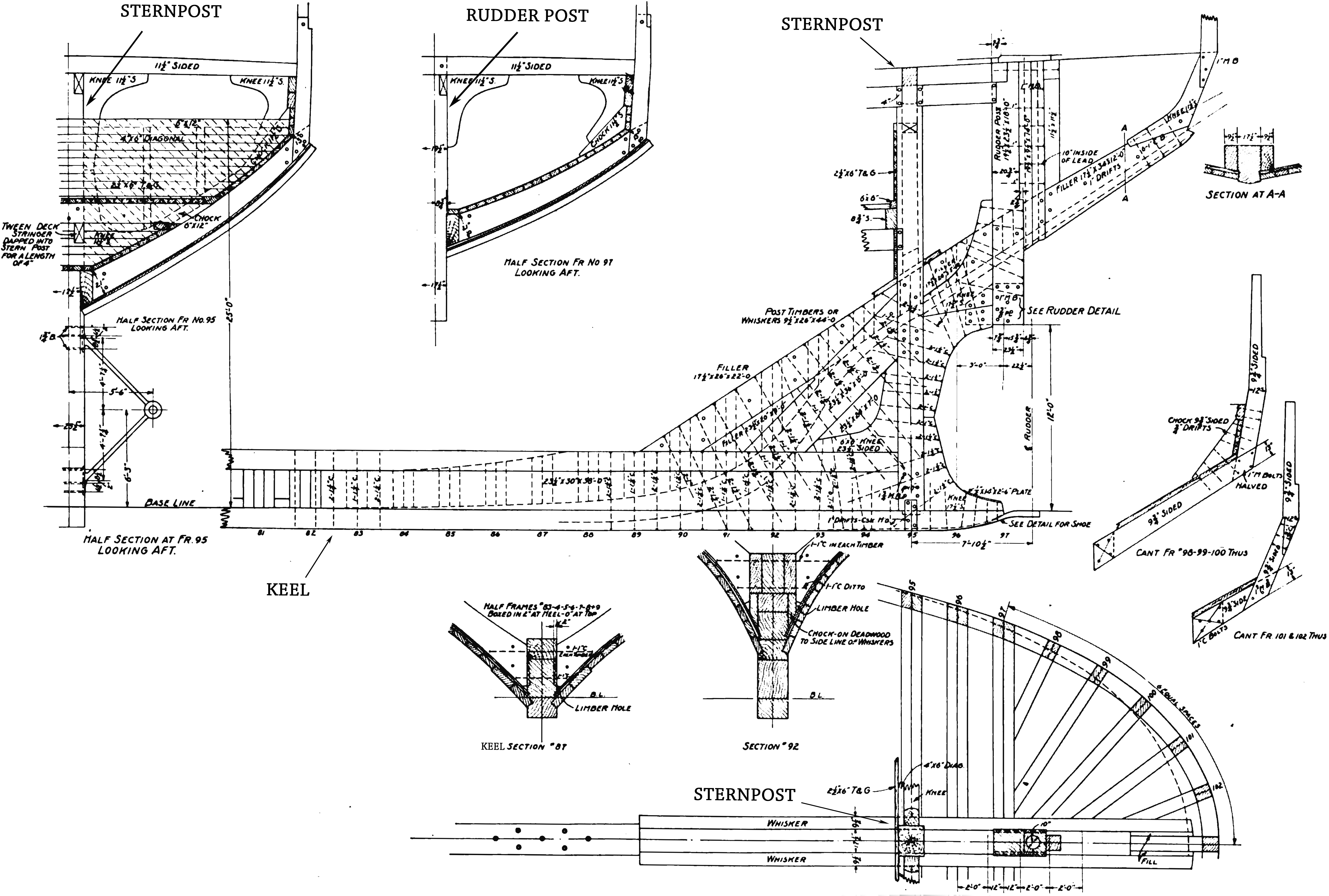
Stern Of Bro Elisabeth
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterline
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indicates the draft of the ship and the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures in order to safely maintain buoyancy, particularly with regard to the hazard of waves that may arise. Varying water temperatures will affect a ship's draft, because warm water is less dense than cold water, providing less buoyancy. In the same way, fresh water is less dense than salinated or seawater with a similar lessening effect upon buoyancy. For vessels with displacement hulls, the hull speed is defined by, among other things, the waterline length. In a sailing boat, the waterline length can change significantly as the boat heels, and can dynamically affect the speed of the boat. A waterline can also refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the '' Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligible yet diverse, spoken in the northern half of France. These dialects came to be collectively known as the , contrasting with the in the south of France. The mid-14th century witnessed the emergence of Middle French, the language of the French Renaissance in the Île de France region; this dialect was a predecessor to Modern French. Other dialects of Old French evolved themselves into modern forms ( Poitevin-Saintongeais, Gallo, Norman, Picard, Walloon, etc.), each with its own linguistic features and history. The region where Old French was spoken natively roughly extended to the northern half of the Kingdom of France and its vassals (including parts of the Angevin Empire, which during the 12th century remained under Anglo-N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
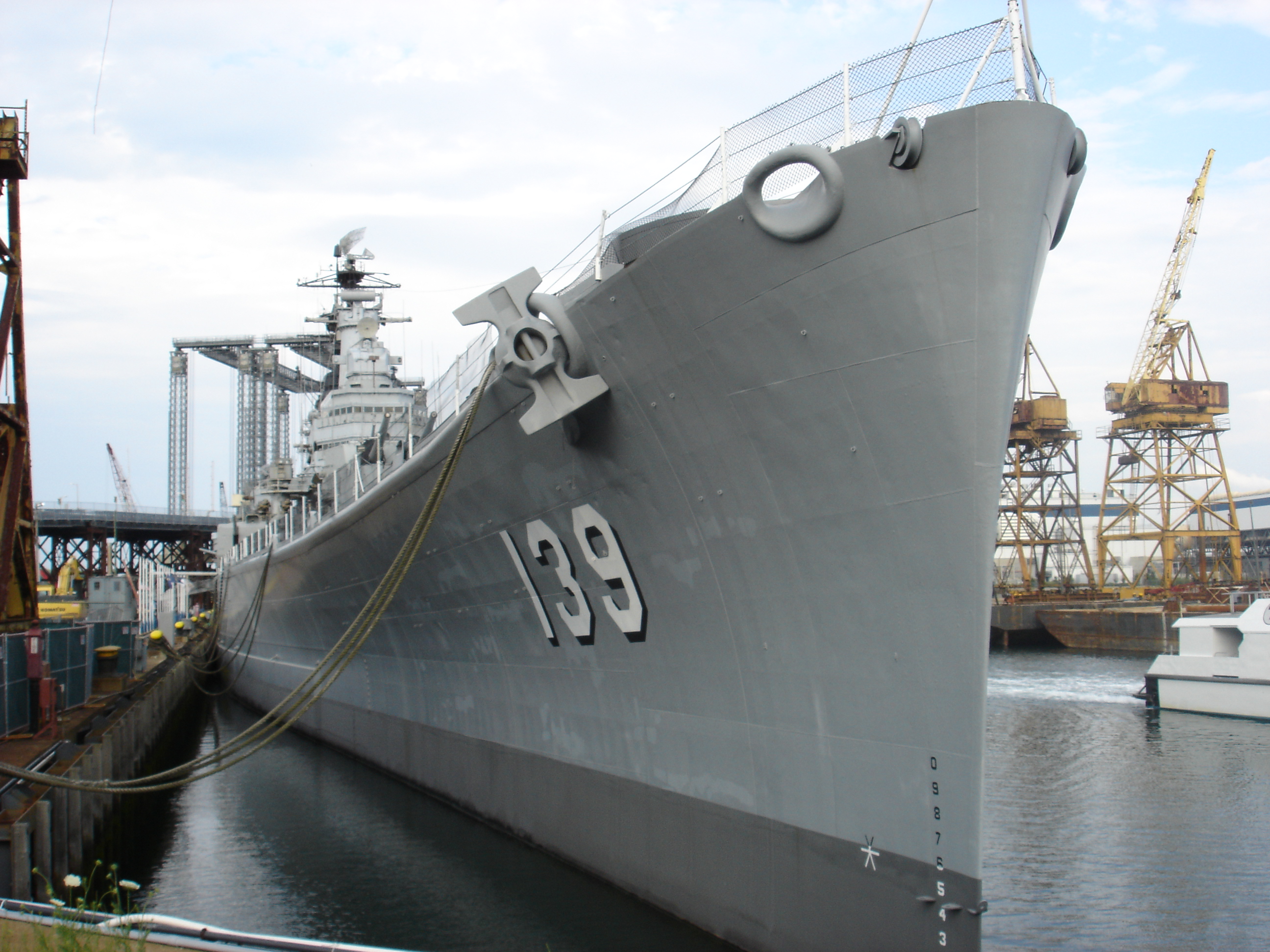
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or after end. Often rudders are shaped so as to minimize hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may be used to link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is operated by pedals via mechanical li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outboard Motor
An outboard motor is a propulsion system for boats, consisting of a self-contained unit that includes engine, gearbox and propeller or jet drive, designed to be affixed to the outside of the transom. They are the most common motorised method of propelling small watercraft. As well as providing propulsion, outboards provide steering control, as they are designed to pivot over their mountings and thus control the direction of thrust. The skeg also acts as a rudder when the engine is not running. Unlike inboard motors, outboard motors can be easily removed for storage or repairs. In order to eliminate the chances of hitting bottom with an outboard motor, the motor can be tilted up to an elevated position either electronically or manually. This helps when traveling through shallow waters where there may be debris that could potentially damage the motor as well as the propeller. If the electric motor required to move the pistons which raise or lower the engine is malfunctioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juniperus Bermudiana
''Juniperus bermudiana'' is a species of juniper endemic to Bermuda. This species is most commonly known as Bermuda cedar, but is also referred to as Bermuda juniper (Bermudians refer to it simply as ''cedar''). Historically, this tree formed woodland that covered much of Bermuda. Settlers cleared part of the forest and the tree was used for many purposes including building construction and was especially prized for shipbuilding. Scale insects introduced during the Second World War construction of United States airbases in Bermuda devastated the forests, killing over 99% of the species (an event known in Bermuda as 'the Blight' or 'the Cedar Blight'). Since then, the salt tolerant ''Casuarina equisetifolia'' has been planted as a replacement species, and a small number of Bermuda cedars have been found to be resistant to the scale insects. Populations of certain endemic birds which had co-evolved with the tree have plummeted as a result of its demise, while endemic cigalas (or ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirit Of Bermuda
The ''Spirit of Bermuda'' is a modern-built Bermuda sloop. She is a replica of a Royal Navy sloop-of-war, depicted in a well-known 1831 painting. History of the Bermuda sloop The Bermuda sloop was a type of small sailing ship built in Bermuda between the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries. Fitted with a gaff rig, a combination of gaff and square rig, or Bermuda rig, they were used by Bermudian merchants, privateers and other seafarers. Their versatility, and their manoeuvrability and speed, especially upwind, meant they were also jealously sought after by non-Bermudian operators for both merchant and naval roles. Bermudians built large numbers of them for their own merchant fleet and for export before being obliged to turn to other trades in the nineteenth century. At the end of the twentieth century, no Bermuda sloop remained anywhere in the world, and most Bermudians had no practical or romantic connection to the island's long history as a maritime economy. These were amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box in the case of scow barges to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bottom of a landing craft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |