|
Trams In Graz
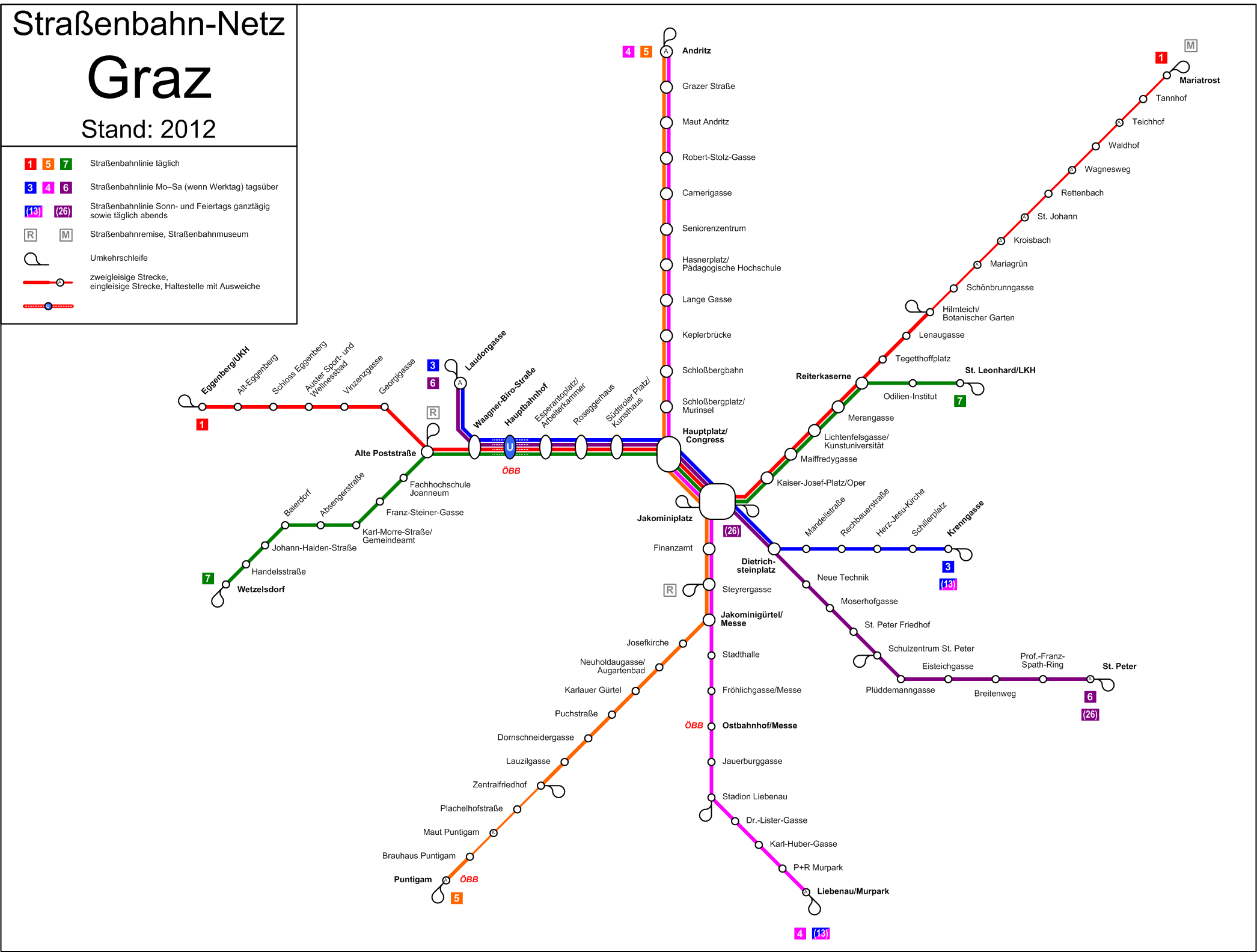
The Graz tramway network is a network of tramways forming an important part of the public transport system in Graz, which is both the capital city of the federal state of Styria, Austria, and the second largest city in Austria. In operation since 1878, the network presently has six daytime lines, and five evening and Sunday lines. , the Graz tram network ran on an almost of route, and served 53.56 million passengers. It is operated by the ''Graz Linien'' division of ''Holding Graz'', the city owned utility company who also operate the city's bus network and the ''Schlossbergbahn'' funicular railway. The trams form part of the styrian integrated fare system which covers all modes of public transport in Graz and Styria. The Tramway Museum Graz, at the terminus of line 1 in Mariatrost, holds many exhibits relating to the system. History The first trams to run in Graz were horse trams in private ownership, with service commencing in 1878. The lines were electrified from 1899. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graz
Graz (; sl, Gradec) is the capital city of the Austrian state of Styria and second-largest city in Austria after Vienna. As of 1 January 2021, it had a population of 331,562 (294,236 of whom had principal-residence status). In 2018, the population of the Graz larger urban zone (LUZ) stood at 652,654, based on principal-residence status. Graz is known as a college and university city, with four colleges and four universities. Combined, the city is home to more than 60,000 students. Its historic centre ('' Altstadt'') is one of the best-preserved city centres in Central Europe. In 1999, the city's historic centre was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites and in 2010 the designation was expanded to include Eggenberg Palace (german: Schloss Eggenberg) on the western edge of the city. Graz was designated the Cultural Capital of Europe in 2003 and became a City of Culinary Delights in 2008. Etymology The name of the city, Graz, formerly spelled Gratz, most likely stems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Gauge Conversion
Gauge conversion is the changing of one railway track gauge (the distance between the running rails) to another. Sleepers If tracks are converted to a narrower gauge, the existing sleepers (ties) may be used. However, replacement is required if the conversion is to a wider gauge. Some sleepers may be long enough to accommodate the fittings of both existing and alternative gauges. Wooden sleepers are suitable for conversion because they can be drilled for the repositioned rail spikes. Being difficult to drill, concrete sleepers are less suitable for conversion. Concrete sleepers may be cast with alternative gauge fittings in place, an example being those used during the conversion of the Melbourne–Adelaide railway from to . Steel sleepers may have alternative gauge fittings cast at production, may be drilled for new fittings or may be welded with new fittings. Structures Conversion from a narrow to a wider gauge may require enlargement of the structure gauge of the bridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eggenberg (Graz)
Eggenberg is the 14th city district of Graz in the Austrian province of Styria. It borders to the districts of Lend and Gries in the east and to the Plabutsch mountain in the west. The name originates from the Eggenberg palace and its founding family the House of Eggenberg. History The district is named after the Eggenbergers who built their medieval residence sometime after 1460 and which was expanded starting in 1625 to become Eggenberg palace. In 2010 the palace was added to the UNESCO World Cultural Heritage Site listing for Graz's "Old Town". Early discoveries indicate a settlement since the early stoneage. In Algersdorf two grave fields from the Roman age were found. The Alte Poststraße can be traced back to the Roman age as well. In the middle ages and up to the 19th century the landscape was dominated by agriculture and cultivating wineyards on the Plabutsch hillside. In locality Beierdorf near Graz - nowadays belonging to Eggenberg - the Baierdorf manor was situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Graz
The University of Graz (german: link=no, Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz, ), located in Graz, Austria, is the largest and oldest university in Styria, as well as the second-largest and second-oldest university in Austria. History The university was founded in 1585 by Archduke Charles II of Austria. The bull of 1 January 1586, published on 15 April 1586, was approved by Pope Sixtus V. For most of its existence it was controlled by the Catholic Church, and was closed in 1782 by Emperor Joseph II in an attempt to gain state control over educational institutions. Joseph II transformed it into a ''lyceum'', where civil servants and medical personnel were trained. In 1827 it was re-instituted as a university by Emperor Francis I, thus gaining the name ''Karl-Franzens-Universität'', meaning ''Charles Francis University''. Over 30,000 students are currently enrolled at the university. Academics The university is divided into six faculties, the two largest are the Faculty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graz Hauptbahnhof
Graz Hauptbahnhof, abbreviated Graz Hbf (German for ''Graz Main Station''; sometimes translated as Graz Central Station.), is the main railway station in Graz, the capital of the Austrian state of Styria. The station is located some west of the city centre, to which it is connected by the tram. The station serves as a major node on the Southern Railway, which links it to Vienna in the north, and Slovenia in the south. It is also the terminus of the Styrian Eastern Railway, which runs eastwards towards Hungary, and of the local Köflacherbahn to the west. In the future, the Koralm Railway will provide a direct link from Graz to Italy via Klagenfurt Klagenfurt am WörtherseeLandesgesetzblatt 2008 vom 16. Jänner 2008, Stück 1, Nr. 1: ''Gesetz vom 25. Oktober 2007, mit dem die Kärntner Landesverfassung und das Klagenfurter Stadtrecht 1998 geändert werden.'/ref> (; ; sl, Celovec), usually .... History The first Railway station was opened here in 1847 but due to a big in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variobahn
The Stadler Variobahn (formerly sold as the ABB Variotram, Adtranz Variotram and Bombardier Variotram) is a German-designed model of articulated low-floor tram and light rail vehicle. Since its introduction in 1993, the Variobahn has been manufactured variously by ABB, Adtranz, Bombardier Transportation, and since 2001 by Stadler Rail. As of 2009, 254 trams have been ordered, with an additional 110 on option. A unit costs about €2.5 million. Operators include the Graz Holding, the Bergen Light Rail, the Chemnitz Tramway, Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr, the Rhine Neckar Area Tramway and London Tramlink. History Prototypes and early deliveries The Variotram was first developed by ABB (ASEA Brown Boveri) at Henschel and a prototype was launched in 1993 for the Chemnitz tramway in Germany, operated by Chemnitzer Verkehrs-Aktiengesellschaft (CVAG). The serial delivery, with minor modifications, was made between 1998 and 2001—bringing the total number of units for Chemnitz to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadler Rail
Stadler Rail is a Swiss manufacturer of railway rolling stock, with an emphasis on regional train multiple units and trams. It is also focused on niche products, such as being one of the last European manufacturers of rack railway rolling stock. Stadler Rail is headquartered in Bussnang, Switzerland. The holding company consists of nine subsidiaries with locations in Algeria, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Switzerland, Spain, Czech Republic, Hungary, Belarus and the United States, and upcoming joint ventures with INKA in Indonesia and with Medha Servo Drives in India. Stadler Rail employed approximately 6,100 employees by 2012, including 2,750 in Switzerland, 1,200 in Germany, 1,000 in Belarus, 400 in Hungary and 400 in Poland. By 2017, this had increased to 7,000 employees. History Stadler Rail traces its origins back to an engineering office established by Ernst Stadler during 1942. Three years later, the company begun to manufacture its first locomotives, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cityrunner
The Bombardier Flexity Outlook is a series of low-floored, articulated light-rail trams manufactured by Bombardier Transportation. Part of the larger Bombardier Flexity product line (many of which are not low-floor), Flexity Outlook vehicles are modular in design and commonly used throughout Europe. Types Bombardier markets two types or families of designs as "Flexity Outlook". Eurotram The Eurotram was a design of electric tramcars designed by for use on the network of the ''Compagnie de Transports Strasbourgeois'' (CTS). It is initially contracted to Socimi and ABB. After Socimi went bankrupt, the order for Eurotrams was completed by ABB Group. Later models were manufactured under successor companies Adtranz and Bombardier Inc. Bombardier began to market this type as Flexity Outlook (E), when they made them until 2004. Cityrunner The more common Cityrunner, which has a more traditional tram design, is used by several cities in Austria (in Innsbruck, Linz and Graz), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombardier Transportation
Bombardier Transportation was a Canadian-German rolling stock and rail transport manufacturer, headquartered in Berlin, Germany. It was one of the world's largest companies in the rail vehicle and equipment manufacturing and servicing industry. Bombardier Transportation had many regional offices, production and development facilities worldwide. It produced a wide range of products including passenger rail vehicles, locomotives, bogies, propulsion and controls. In February 2020, the company had 36,000 employees, and 63 manufacturing and engineering locations around the world. Formerly a subsidiary and rail equipment division of Bombardier Inc., the company was acquired by French manufacturer Alstom on 29 January 2021. History 20th century 1970s: Formation and first orders Canadian company Bombardier Inc. entered the rail market in 1970 when it purchased Lohnerwerke GmbH of Austria. Bombardier Transportation's first order for mass transit rolling stock was in 1974 for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for charter purposes, or through private ownership. Although the average bus carries between 30 and 100 passengers, some buses have a capacity of up to 300 passengers. The most common type is the single-deck rigid bus, with double-decker and articulated buses carrying larger loads, and midibuses and minibuses carrying smaller loads. Coaches are used for longer-distance services. Many types of buses, such as city transit buses and inter-city coaches, charge a fare. Other types, such as elementary or secondary school buses or shuttle buses within a post-secondary education campus, are free. In many jurisdictions, bus drivers require a special large vehicle licence above and beyond a regular driving licence. Buses may be used for scheduled bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or trolleyDunbar, Charles S. (1967). ''Buses, Trolleys & Trams''. Paul Hamlyn Ltd. (UK). Republished 2004 with or 9780753709702.) is an electric bus that draws power from dual overhead wires (generally suspended from roadside posts) using spring-loaded trolley poles. Two wires, and two trolley poles, are required to complete the electrical circuit. This differs from a tram or streetcar, which normally uses the track as the return path, needing only one wire and one pole (or pantograph). They are also distinct from other kinds of electric buses, which usually rely on batteries. Power is most commonly supplied as 600-volt direct current, but there are exceptions. Currently, around 300 trolleybus systems are in operation, in cities and towns in 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)