|
Trams In Neuchâtel
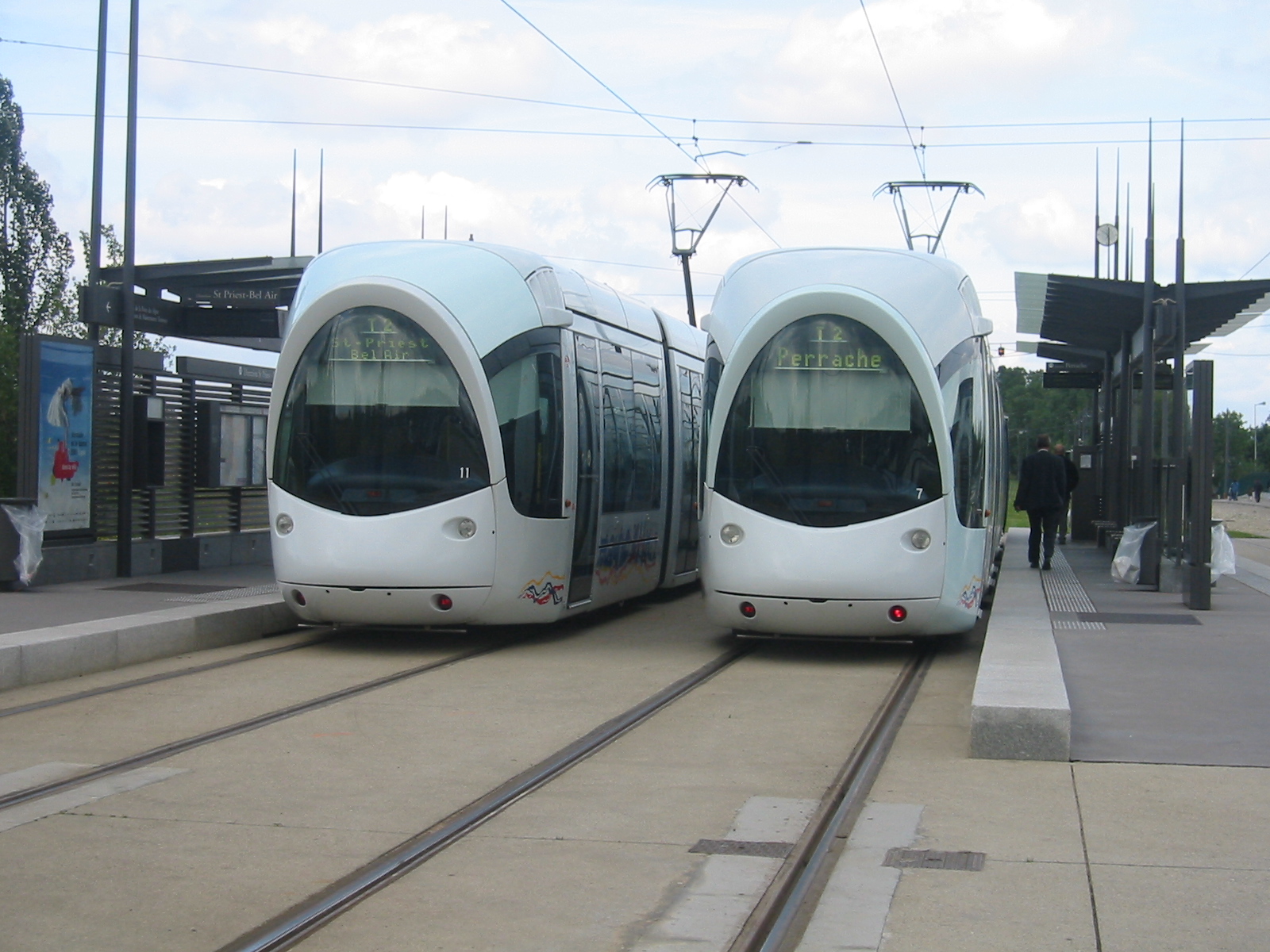
The Neuchâtel tramway (, or (locally) ''Tram'') is a tramway forming part of the public transport system in Neuchâtel, a city in Switzerland. Opened in 1892, the tramway has waxed and waned over the years. Currently, it comprises only one long interurban line, which runs via Auvernier and Colombier to Boudry, and is designated as line 5. All of the system's urban tram lines were converted to trolleybuses, the last such closure and conversion taking place in 1976, leaving just interurban line 5 (present line 215). The tramway is currently operated by ''Transports publics Neuchâtelois'' (transN) (formerly ''Compagnie des Tramways de Neuchâtel''), which also runs three funiculars, the Neuchâtel trolleybus system and various conventional bus lines. History Interurban line The line to Boudry, including an Areuse-to-Cortaillod branch line long,Vogt, H. (November/December 1984 issue). "Verkehrsveränderungen in Neuchâtel" (Operations changes in Neuchatel) (in German). ', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
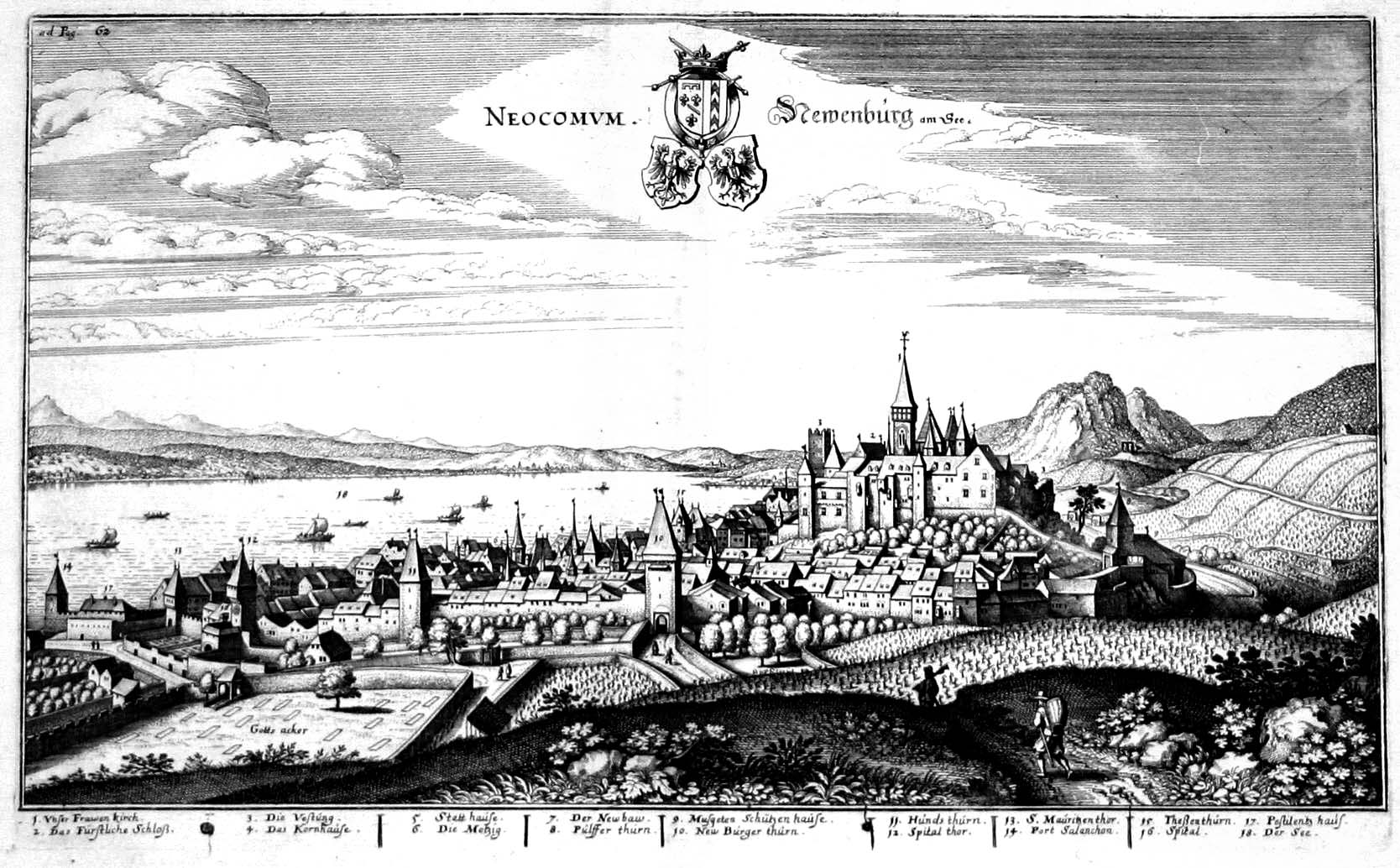
Neuchâtel
Neuchâtel (, ; ; ) is a list of towns in Switzerland, town, a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality, and the capital (political), capital of the cantons of Switzerland, Swiss canton of Neuchâtel (canton), Neuchâtel on Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, Neuchâtel, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 33,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". The castle after which the city is named was built by Rudolph III of Burgundy and completed in 1011. Originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the city was absorbed into the Holy Roman Empire in 1033. The domain of the counts of Neuchatel was first referred to as a city in 1214. The city came under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1806 to 1814. In 1848, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram Engine
A tram engine is a steam locomotive specially built, or modified, to run on a street, or roadside, tramway track. Legal requirements In the steam locomotive era, tram engines had to comply with certain legal requirements, although these varied from country to country: * The engine must be governed to a maximum speed of ( in the UK) * No steam or smoke may be emitted * It must be free from the noise produced by blast or clatter * The machinery must be concealed from view at all points above from rail level *Most of the locomotives must have a cab at each end To avoid smoke, the fuel used was coke, rather than coal. To prevent visible emission of steam, two opposite systems were used: * condensing the exhaust steam and returning the condensate to the water tank * Reheating the exhaust steam to make it invisible Builders United Kingdom ;Great Eastern Railway The Great Eastern Railway built ten Class G15 0-4-0T trams from 1883 to 1897 and twelve Class C53 0-6-0T trams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tramways & Urban Transit
''Tramways & Urban Transit'' ''(TAUT'' or ''T&UT)'', also known as ''Modern Tramway'', is a British monthly magazine about tramways and light rail transport, published continuously since 1938. Its content is orientated both to tramway enthusiasts and to persons working in the tram transport field or studying tramways. It has been issued monthly from the beginning.Claydon, Geoffrey (June 1997). "Sixty Years of the LRTA". ''Light Rail & Modern Tramway'', pp. 227–228. Although published in Britain, the magazine's coverage is international, and its regular "World News" column includes detailed news on electric trams (called streetcars or trolleys in American English) and light rail worldwide.Saitta, Joseph P. (Ed.) (1981). Review of ''Modern Tramway'' in ''Traction Yearbook '81'', p. 230. Merrick, NY (US): Traction Slides International. Quote: "Necessary reading for those wishing to keep abreast of light rail progress." From 1938 until 2007 the magazine was published by the Ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turning Loop
A balloon loop, turning loop, or reversing loop (Glossary of North American railway terms, North American Terminology) allows a rail vehicle or train to reverse direction without having to Shunting (rail), shunt or stop. Balloon loops can be useful for passenger trains and Unit train, unit freight trains. Balloon loops are common on tram, tram and streetcar systems. Many streetcar and tram systems use single-ended vehicles that have doors on only one side and controls at only one end. These systems may also haul trailers with no controls in the rear car, and, as such, must be turned at each end of the route. History Balloon loops were first introduced on tram and, later, Rapid transit, metro lines. They did not commonly appear on freight railways until the 1960s, when the modernising British Rail system introduced ''Merry-go-round train, merry-go-round'' (MGR) coal trains that operated from mines to power stations and back again without Shunting (rail), shunting. Tramways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bi-directional Vehicle , triangle junction, or turntable (railroad), turntable ...
A bi-directional vehicle is a vehicle that can be driven in either direction, forwards or backwards. Usually, the term refers to rail vehicles, such as trains or trams, and some airside transfer buses, that are equipped with driver's cabs at both ends. These vehicles generally have entry and exit doors on either side of the vehicle. One major benefit of bi-directional vehicles is the ability to reverse direction at a terminal station with a stub-end track. On a system using double track, a crossover switch is often used to move the vehicle to the other track. This situation contrasts with the use of uni-directional vehicles, which requires the use of a balloon loop A balloon loop, turning loop, or reversing loop ( North American Terminology) allows a rail vehicle or train to reverse direction without having to shunt or stop. Balloon loops can be useful for passenger trains and unit freight trains. Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlocking
In railway signalling, an interlocking is an arrangement of signal apparatus that prevents conflicting movements through an arrangement of tracks such as junctions or crossings. In North America, a set of signalling appliances and tracks interlocked together are sometimes collectively referred to as an ''interlocking plant'' or just as an ''interlocking''. An interlocking system is designed so that it is impossible to display a signal to proceed unless the route to be used is proven safe. Interlocking is a safety measure designed to prevent signals and points/switches from being changed in an improper sequence. For example, interlocking would prevent a signal from being changed to indicate a diverging route, unless the corresponding points/switches had been changed first. In North America, the official railroad definition of interlocking is: "''An arrangement of signals and signal appliances so interconnected that their movements must succeed each other in proper sequence''". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-of-way (transportation)
A right of way (also right-of-way) is a specific route that people, animals, vehicles, watercraft, or utility lines travel, or the legal status that gives them the right to do so. Rights-of-way in the physical sense include controlled-access highways, railroads, canals, hiking paths, bridle paths for horses, bicycle paths, the routes taken by high-voltage lines (also known as wayleave), utility tunnels, or simply the paved or unpaved local roads used by different types of traffic. The term ''highway'' is often used in legal contexts in the sense of "main way" to mean any public-use road or any public-use road or path. Some are restricted as to mode of use (for example, pedestrians only, pedestrians, horse and cycle riders, vehicles capable of a minimum speed). Rights-of-way in the legal sense (the right to pass through or to operate a transportation facility) can be created in a number of different ways. In some cases, a government, transportation company, or conservation n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Track (rail)
A single-track railway is a railway where trains traveling in both directions share the same track. Single track is usually found on lesser-used rail lines, often branch lines, where the level of traffic is not high enough to justify the cost of constructing and maintaining a second track. Advantages and disadvantages Single track is significantly cheaper to build and maintain, but has operational and safety disadvantages. For example, a single-track line that takes 15 minutes to travel through would have capacity for only two trains per hour in each direction safely. By contrast, a double track with signal boxes four minutes apart can allow up to 15 trains per hour in each direction safely, provided all the trains travel at the same speed. This hindrance on the capacity of a single track may be partly overcome by making the track one-way on alternate days. Long freight trains are a problem if the passing stretches are not long enough. Other disadvantages include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tram Stop
A tram stop, tram station, streetcar stop, or light rail station is a place designated for a tram, streetcar, or light rail vehicle to stop so passengers can board or alight it. Generally, tram stops share most characteristics of bus stops, but because trams operate on rails, they often include railway platforms, especially if stepless entries are provided for accessibility. However, trams may also be used with bus stop type flags and with mid-street pavements as platforms, in street running mode. Types of tram stops Tram stops without platforms Many tram or streetcar stops, especially on older tram lines street-running on narrower streets, have no dedicated platforms. Instead, stops are located in the middle of the roadway. Passengers need to cross lanes for motor vehicles to board or alight from trams. Examples of systems with this type of stops include: North America * Toronto, ON, Canada: Most stops on all Toronto streetcar system, TTC streetcar routes except 509, 51 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock-face Scheduling
A clock-face schedule, also cyclic schedule, is a timetable system under which public transport services run at consistent intervals, as opposed to a timetable that is purely driven by demand and has irregular headways. The name derives from the fact that departures take place at the same time or times during the day. For example, services with a half-hourly frequency might leave at 5:15, 5:45, 6:15, 6:45, 7:15, 7:45 etc. The goal is to enhance the attractiveness and versatility of public transport. Clock-face schedules are easy for passengers to memorise because departure and arrival times occur at consistent intervals, repeating during the day. A regular repeating schedule over the whole day can also improve services during off-peak hours. Clock-face timetables can be attractive for transport operators because the repeating pattern can allow the more efficient use of personnel, infrastructure and vehicles, and also make resource-planning easier. Repeating timetables were first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Block Signal
Automatic block signaling (ABS), spelled automatic block signalling or called track circuit block (TCB ) in the UK, is a railroad communications system that consists of a series of signals that divide a railway line into a series of sections, called ''blocks''. The system controls the movement of trains between the blocks using automatic signals. ABS operation is designed to allow trains operating in the same direction to follow each other in a safe manner without risk of rear-end collision. The introduction of ABS reduced railways' costs and increased their capacity. Older manual block systems required human operators. The automatic operation comes from the system's ability to detect whether blocks are occupied or otherwise obstructed, and to convey that information to approaching trains. The system operates without any outside intervention, unlike more modern traffic control systems that require external control to establish a flow of traffic. History The earliest way of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |