|
Tracking (particle Physics)
In particle physics, tracking is the process of reconstructing the trajectory (or track) of electrically charged particles in a particle detector known as a tracker. The particles entering such a tracker leave a precise record of their passage through the device, by interaction with suitably constructed components and materials. The presence of a calibrated magnetic field, in all or part of the tracker, allows the local momentum of the charged particle to be directly determined from the reconstructed local curvature of the trajectory for known (or assumed) electric charge of the particle. Generally, track reconstruction is divided into two stages. First, track finding needs to be performed where a cluster of detector hits believed to originate from the same track are grouped together. Second, a track fitting is performed. Track fitting is the procedure of mathematically fitting a curve to the found hits and from this fit the momentum is obtained. Identification and reconstructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quark, Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BaBar Experiment
The BaBar experiment, or simply BaBar, is an international collaboration of more than 500 physicists and engineers studying the subatomic world at energies of approximately ten times the rest mass of a proton (~10 GeV). Its design was motivated by the investigation of charge-parity violation. BaBar is located at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, which is operated by Stanford University for the Department of Energy in California. Physics BaBar was set up to understand the disparity between the matter and antimatter content of the universe by measuring Charge Parity violation. CP symmetry is a combination of Charge-conjugation symmetry (C symmetry) and Parity symmetry (P symmetry), each of which are conserved separately except in weak interactions. BaBar focuses on the study of CP violation in the B meson system. The name of the experiment is derived from the nomenclature for the B meson (symbol ) and its antiparticle (symbol , pronounced B bar). The experiment' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nuclear Instruments And Methods In Physics Research A
''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research'' (Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res.) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, .... It was established in 1957 as ''Nuclear Instruments''. It focuses on detectors descriptions and data analysis methods. History *''Nuclear Instruments'' (1957–1958) *''Nuclear Instruments and Methods'' (1959–1981) *''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research'' (1981–present) :*''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment'' (1984–present) :*''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms'' (1984–present) External links'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Semiconductor Detector
In ionizing radiation detection physics, a semiconductor detector is a device that uses a semiconductor (usually silicon or germanium) to measure the effect of incident charged particles or photons. Semiconductor detectors find broad application for radiation protection, gamma spectroscopy, gamma and x-ray spectroscopy, X-ray spectrometry, and as particle detectors. Detection mechanism In semiconductor detectors, ionizing radiation is measured by the number of charge carriers set free in the detector material which is arranged between two electrodes, by the radiation. Ionizing radiation produces free electrons and electron holes. The number of electron-hole pairs is proportional to the energy of the radiation to the semiconductor. As a result, a number of electrons are transferred from the valence band to the conduction band, and an equal number of holes are created in the valence band. Under the influence of an electric field, electrons and holes travel to the electrodes, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Photolithography
Photolithography (also known as optical lithography) is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer. The process begins with a photosensitive material, called a photoresist, being applied to the substrate. A photomask that contains the desired pattern is then placed over the photoresist. Light is shone through the photomask, exposing the photoresist in certain areas. The exposed areas undergo a chemical change, making them either soluble or insoluble in a developer solution. After development, the pattern is transferred onto the substrate through etching, chemical vapor deposition, or ion implantation processes. Ultraviolet, Ultraviolet (UV) light is typically used. Photolithography processes can be classified according to the type of light used, including ultraviolet lithography, deep ultraviolet lithography, extreme ultraviolet lithography, extreme ultraviolet lithography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels are present in the same crystal, they form a semiconductor junction. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits. Semiconductor devices can display a range of different useful properties, such as passing current more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Time Projection Chamber
In physics, a time projection chamber (TPC) is a type of particle detector that uses a combination of electric fields and magnetic fields together with a sensitive volume of gas or liquid to perform a three-dimensional reconstruction of a particle trajectory or interaction. The original design The original TPC was invented by David R. Nygren, an American physicist, at Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory in the late 1970s. Its first major application was in the PEP-4 detector, which studied 29 GeV electron–positron collisions at the PEP storage ring at SLAC. A time projection chamber consists of a gas-filled detection volume in an electric field with a position-sensitive electron collection system. The original design (and the one most commonly used) is a cylindrical chamber with multi-wire proportional chambers (MWPC) as endplates. Along its length, the chamber is divided into halves by means of a central high-voltage electrode disc, which establishes an electric field between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wire Chamber
A wire chamber or multi-wire proportional chamber is a type of proportional counter that detects charged particles and photons and can give positional information on their trajectory, by tracking the trails of gaseous ionization. was located via Dr. C.N. BootPHY304 Particle Physics Sheffield University The technique was an improvement over the bubble chamber particle detection method, which used photographic techniques, as it allowed high speed electronics to track the particle path. Description The multi-wire chamber uses an array of wires at a positive dc voltage (anode)s, which run through a chamber with conductive walls held at a lower potential (cathode). The chamber is filled with gas, such as an argon/methane mix, so that any ionizing particle that passes through the tube will ionize surrounding gaseous atoms and produce ion pairs, consisting of positive ions and electrons. These are accelerated by the electric field across the chamber, preventing recombination; the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wire Chambers
Overhead power cabling. The conductor consists of seven strands of steel (centre, high tensile strength), surrounded by four outer layers of aluminium (high conductivity). Sample diameter 40 mm A wire is a flexible, round bar of metal. Wires are commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Wire gauges come in various standard sizes, as expressed in terms of a gauge number or cross-sectional area. Wires are used to bear mechanical loads, often in the form of wire rope. In electricity and telecommunications signals, ''wire'' can refer to electrical cable, which can contain a solid core of a single wire or separate strands in stranded or braided forms. Usually cylindrical in geometry, wire can also be made in square, hexagonal, flattened rectangular, or other cross-sections, either for decorative purposes, or for technical purposes such as high-efficiency voice coils in loudspeakers. Edge-wound coil springs, such as the Slinky toy, are made of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spark Chamber
A spark chamber is a particle detector: a device used in particle physics for detecting electrically charged Subatomic particle, particles. They were most widely used as research tools from the 1930s to the 1960s and have since been superseded by other technologies such as drift chambers and semiconductor detector, silicon detectors. Today, working spark chambers are mostly found in science museums and educational organisations, where they are used to demonstrate aspects of particle physics and astrophysics. Spark chambers consist of a stack of metal plates placed in a sealed box filled with a gas such as helium, neon or a mixture of the two. When a charged particle from a cosmic ray travels through the box, it ionises the gas between the plates. Ordinarily this ionisation would remain invisible. However, if a high enough voltage can be applied between each adjacent pair of plates before that ionisation disappears, then sparks can be made to form along the trajectory taken by the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bubble Chamber
A bubble chamber is a vessel filled with a superheated transparent liquid (most often liquid hydrogen) used to detect electrically charged particles moving through it. It was invented in 1952 by Donald A. Glaser, for which he was awarded the 1960 Nobel Prize in Physics. Supposedly, Glaser was inspired by the bubbles in a glass of beer; however, in a 2006 talk, he refuted this story, although saying that while beer was not the inspiration for the bubble chamber, he did experiments using beer to fill early prototypes. While bubble chambers were extensively used in the past, they have now mostly been supplanted by wire chambers, spark chambers, drift chambers, and silicon detectors. Notable bubble chambers include the Big European Bubble Chamber (BEBC) and Gargamelle. __TOC__ Function and use The bubble chamber is similar to a cloud chamber, both in application and in basic principle. It is normally made by filling a large cylinder with a liquid heated to just below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
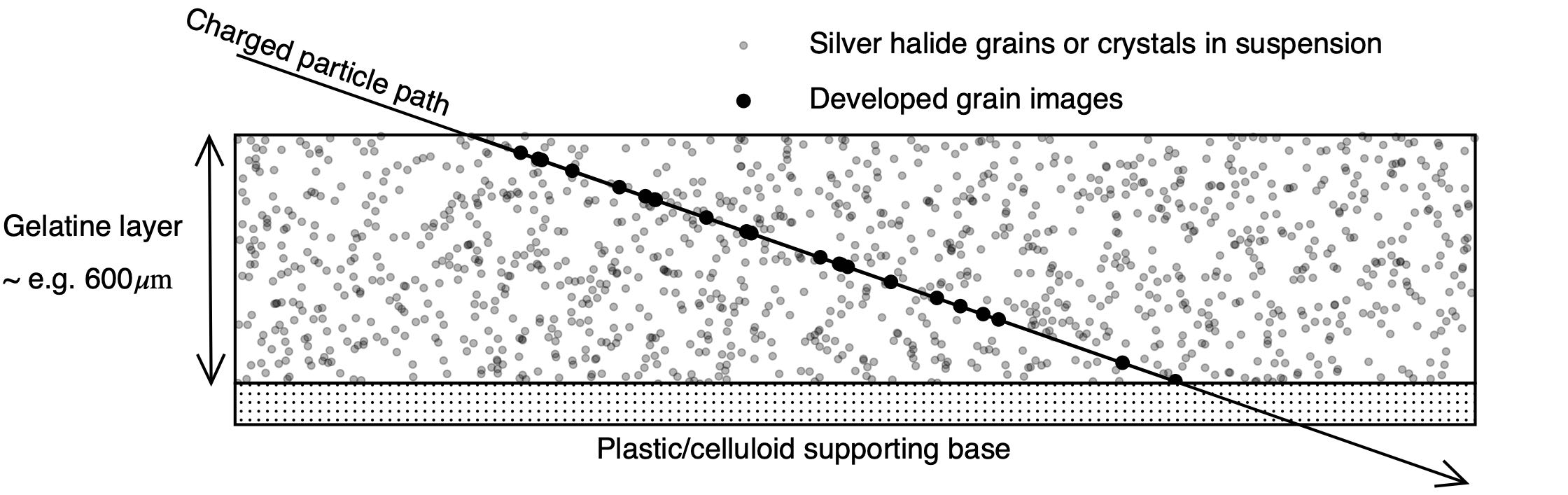
Nuclear Emulsion
A nuclear emulsion plate is a type of particle detector first used in nuclear and particle physics experiments in the early decades of the 20th century. https://cds.cern.ch/record/1728791/files/vol6-issue5-p083-e.pdf''The Study of Elementary Particles by the Photographic Method'', C.F.Powell, P.H.Fowler, D.H.Perkins: Pergamon Press, New York, 1959.Walter H. Barkas, ''Nuclear Research Emulsions I. Techniques and Theory'', in ''Pure and Applied Physics: A Series of Monographs and Textbooks, Vol. 15'', Academic Press, New York and London, 1963. http://becquerel.jinr.ru/text/books/Barkas_NUCL_RES_EMULSIONS.pdf It is a modified form of photographic plate that can be used to record and investigate fast charged particles like alpha-particles, nucleons, leptons or mesons. After exposing and developing the emulsion, single particle tracks can be observed and measured using a microscope. Description The nuclear emulsion plate is a modified form of photographic plate, coated with a thick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |