|
Toxteth Riots
The Toxteth riots of July 1981 were a civil disturbance in Toxteth, inner-city Liverpool, which arose in part from long-standing tensions between the local police and the black community. They followed the Brixton riot earlier that year and were part of the 1981 England riots. Background The Merseyside police force had, at the time, a poor reputation within the black community for stopping and searching young black men in the area, under the "sus" laws, and the heavy-handed arrest of Leroy Alphonse Cooper on Friday 3 July near Granby Street, watched by an angry crowd, led to a disturbance in which three policemen were injured. The existing tensions between police and people had already been noticed by local magistrate, Councillor and Chair of the Merseyside Police Committee, Margaret Simey, who was frequently critical of the hardline tactics used by the then Chief Constable Kenneth Oxford. She said of the rioters "they would be apathetic fools ... if they didn't protest", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 England Riots
In April and July 1981, there were riots in several cities and towns in England. The riots mainly involved black English youth clashing with police. They were caused by tension between black people and the police, especially perceived racist discrimination against black people through increased use of stop-and-search,J. A. Cloake & M. R. Tudor. ''Multicultural Britain''. Oxford University Press, 2001. pp.60-64 and were also fuelled by inner city deprivation. The most serious riots were the April Brixton riots in London, followed in July by the Toxteth riots in Liverpool, the Handsworth riots in Birmingham, the Chapeltown riots in Leeds, and the Moss Side riots in Manchester. There were also a series of less serious riots in other towns and cities. As a result of the riots, the government commissioned the Scarman Report. Context Racial tensions In all the four main cases, these areas had large ethnic minority communities, who had largely immigrated from the Commonwealth in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
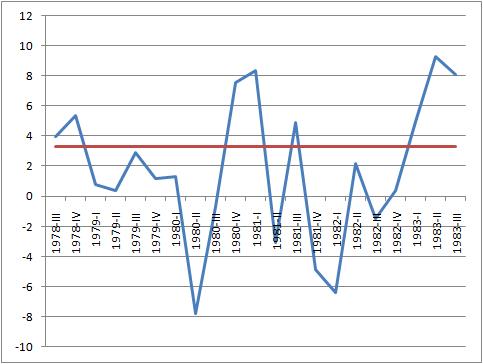
Early 1980s Recession
The early 1980s recession was a severe economic recession that affected much of the world between approximately the start of 1980 and 1983. It is widely considered to have been the most severe recession since World War II. A key event leading to the recession was the 1979 energy crisis, mostly caused by the Iranian Revolution which caused a disruption to the global oil supply, which saw oil prices rising sharply in 1979 and early 1980. The sharp rise in oil prices pushed the already high rates of inflation in several major advanced countries to new double-digit highs, with countries such as the United States, Canada, West Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom and Japan tightening their monetary policies by increasing interest rates in order to control the inflation. These G7 countries each, in fact, had " double-dip" recessions involving short declines in economic output in parts of 1980 followed by a short period of expansion, in turn, followed by a steeper, longer period of econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersey Basin Campaign
The Mersey Basin Campaign worked within the catchments of the River Mersey and the River Ribble, in the counties of Lancashire, Merseyside, Greater Manchester and Cheshire and in the High Peak (upland), High Peak area of Derbyshire in the United Kingdom, UK. Its primary goal was to repair the damage done by industrialisation and to foster a modern and prosperous future, with an improved environment. Mission The campaign's mission was to: *Improve water quality so that all rivers, streams and waters in the Mersey and Ribble catchments are clean enough to support fish by 2010. *Encourage waterside regeneration *Actively engage the public, private, community and voluntary sectors in the process. History The Mersey Basin Campaign was established in 1985 in the wake of the Toxteth riots in Liverpool. Michael Heseltine, then Environment Minister in Margaret Thatcher's Conservative government, was the driving force behind its creation. He spoke of the River Mersey at the time as "an af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Garden Festival
The International Garden Festival was a garden festival recognised by the International Association of Horticultural producers (AIPH) and the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE), which was held in Liverpool, England from 2 May to 14 October 1984. It was the first such event held in Britain, and became the model for several others held during the 1980s and early 1990s. The aim was to revitalise tourism and the city of Liverpool which had suffered cutbacks, and the idea came from Conservative Environment Minister Michael Heseltine. The festival was hugely popular, attracting 3,380,000 visitors. The festival The international horticultural exposition was held on a derelict industrial site south of Herculaneum Dock, near the Dingle and overlooking the River Mersey. On this site was built sixty individual gardens, including a Japanese garden and pagodas. A large exhibition space, the Festival Hall, formed the centrepiece of the site and housed numerous indoor exhibits. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Heseltine
Michael Ray Dibdin Heseltine, Baron Heseltine, (; born 21 March 1933) is a British politician and businessman. Having begun his career as a property developer, he became one of the founders of the publishing house Haymarket. Heseltine served as a Conservative Member of Parliament from 1966 to 2001, and was a prominent figure in the governments of Margaret Thatcher and John Major, and served as Deputy Prime Minister and First Secretary of State under Major. Heseltine entered the Cabinet in 1979 as Secretary of State for the Environment, where he promoted the "Right to Buy" campaign that allowed two million families to purchase their council houses. He was considered an adept media performer and a charismatic minister, although he was frequently at odds with Thatcher on economic issues. He was one of the most visible "wets", whose "One Nation" views were epitomised by his support for the regeneration of Liverpool in the early 1980s when it was facing economic collapse; this lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarman Report
The Scarman report was commissioned by the UK Government following the 1981 Brixton riots. Lord Scarman was appointed by then Home Secretary William Whitelaw on 14 April 1981 (two days after the rioting ended) to hold the enquiry into the riots. The Scarman report was published on 25 November 1981. The terms of reference for the enquiry were "to inquire urgently into the serious disorder in Brixton on 10–12 April 1981 and to report, with the power to make recommendations". 1981 Brixton riot The riot took place in Brixton, London on 11 April 1981. At the time when Brixton underwent deep social and economic problems — high unemployment, high crime, poor housing, no amenities — in a predominantly African-Caribbean community. The Metropolitan Police began ''Operation Swamp 81'' at the beginning of April, aimed at reducing street crime, mainly through the heavy use of the so-called sus law, which allowed police to stop and search (and ultimately jail) individuals on the basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 Moss Side Riot
In July 1981, the inner-city district of Moss Side in Manchester, England, was the scene of mass protesting. The protests at Moss Side started at the local police station and later moved into the surrounding streets over two days. Key factors seen as fuel for this protest were racial tension, due to frequent allegations of police officers racially abusing and using excessive force against black youths in the area,Manchester Evening News - Moss Side Riots 25 Years On and mass unemployment brought on by the . Unemployment was at a post-war high across the nation during 1981, but was mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Rover
Land Rover is a British brand of predominantly four-wheel drive, off-road capable vehicles, owned by multinational car manufacturer Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), since 2008 a subsidiary of India's Tata Motors. JLR currently builds Land Rovers in Brazil, China, India, Slovakia, and the United Kingdom. The Land Rover name was created in 1948 by the Rover Company for a utilitarian 4WD off-roader; yet today Land Rover vehicles comprise solely upmarket and luxury sport utility cars. Land Rover was granted a Royal Warrant by King George VI in 1951, and 50 years later, in 2001, it received a Queen's Award for Enterprise for outstanding contribution to international trade. Over time, Land Rover grew into its own brand (and for a while also a company), encompassing a consistently growing range of four-wheel drive, off-road capable models. Starting with the much more upmarket 1970 Range Rover, and subsequent introductions of the mid-range Discovery and entry-level Freelander line (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is a coastal county with cliffs and sandy beaches. Home to the largest open space in southern England, Dartmoor (), the county is predominately rural and has a relatively low population density for an English county. The county is bordered by Somerset to the north east, Dorset to the east, and Cornwall to the west. The county is split into the non-metropolitan districts of East Devon, Mid Devon, North Devon, South Hams, Teignbridge, Torridge, West Devon, Exeter, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth, and Torbay. Combined as a ceremonial county, Devon's area is and its population is about 1.2 million. Devon derives its name from Dumnonia (the shift from ''m'' to ''v'' is a typical Celtic consonant shift). During the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West Midlands metropolitan county, and approximately 4.3 million in the wider metropolitan area. It is the largest UK metropolitan area outside of London. Birmingham is known as the second city of the United Kingdom. Located in the West Midlands region of England, approximately from London, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands. Distinctively, Birmingham only has small rivers flowing through it, mainly the River Tame and its tributaries River Rea and River Cole – one of the closest main rivers is the Severn, approximately west of the city centre. Historically a market town in Warwickshire in the medieval period, Birmingham grew during the 18th century during the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's county town is Carlisle, in the north of the county. Other major settlements include Barrow-in-Furness, Kendal, Whitehaven and Workington. The administrative county of Cumbria consists of six districts ( Allerdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Carlisle, Copeland, Eden and South Lakeland) and, in 2019, had a population of 500,012. Cumbria is one of the most sparsely populated counties in England, with 73.4 people per km2 (190/sq mi). On 1 April 2023, the administrative county of Cumbria will be abolished and replaced with two new unitary authorities: Westmorland and Furness (Barrow-in-Furness, Eden, South Lakeland) and Cumberland ( Allerdale, Carlisle, Copeland). Cumbria is the third largest ceremonial county in England by area. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county in 1974 History Before the county During Roman times the area was part of the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
