|
Tosa Mitsunori
Tosa Mitsunori (土佐光則, January 16, 1583 to March 1, 1638) was an illustrator from the Tosa school of painting during the Azuchi–Momoyama period and the early Edo period. He was a son of Tosa Mitsuyoshi and the father of Tosa Mitsuoki. Although having moved to Sakai in his youth, he sometimes presented painted fanss to the Sentō Imperial Palace, but he did not receive a position at the court. About the age of 52, in his later years, he returned to Kyoto with his eldest son, Mitsuoki. Many small works with gold backgrounds using variegated paints kept up the tradition of the Tosa school and showed much skill in their delicacy of depiction and the combinations of colours. Among the few surviving works of Mitsunori is a scroll known as the “Legend of the Taima mandala The Taima Mandala (當麻曼荼羅,綴織当麻曼荼羅図) is an 8th century mandala in Japanese Pure Land Buddhism. It depicts Sukhavati, the western Pure Land, with the Buddha Amitābha (Japanese: A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosa School
of Japanese painting was founded in the early Muromachi period (14th–15th centuries),,p.988 and was devoted to ''yamato-e'', paintings specializing in subject matter and techniques derived from ancient Japanese art, as opposed to schools influenced by Chinese art, notably the Kanō school (狩野派). Tosa school paintings are characterised by "areas of flat opaque colour enclosed by simple outlines, where drawing is precise and conventional", with many narrative subjects from Japanese literature and history. However, by the 17th century both Tosa and Kanō artists broadened their range, and the distinction between these and other schools became less clear. The origins of this school of painting can be traced to (fl. first half 15th century), ''Encyclopedia of World Art"", pp. 1032–3 who first used the professional name of Tosa, though unverified claims to earlier origins were made later by Mitsunobu (1434?–?1525) who formally founded the school. Mitsunobu served as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azuchi–Momoyama Period
The was the final phase of the in Japanese history from 1568 to 1600. After the outbreak of the Ōnin War in 1467, the power of the Ashikaga Shogunate effectively collapsed, marking the start of the chaotic Sengoku period. In 1568, Oda Nobunaga entered Kyoto to install Ashikaga Yoshiaki as the 15th and ultimately final Ashikaga ''shōgun''. This entrance marked the start of the Azuchi-Momoyama period. Nobunaga overthrew Yoshiaki and dissolved the Ashikaga Shogunate in 1573, launching a war of conquest to politically unify Japan by force from his base in Azuchi. Nobunaga was forced to commit suicide in the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582. His successor Toyotomi Hideyoshi completed Nobunaga's campaign of unification and enacted reforms to consolidate his rule, marking the end of the Sengoku period. Hideyoshi launched the Japanese invasions of Korea in 1592, but the invasion's failure damaged his prestige, and his young son and successor Toyotomi Hideyori was challenged by Tokugawa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional '' daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tennō's court, to the Tok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosa Mitsuoki
was a Japanese painter. Tosa Mitsuoki succeeded his father, Tosa Mitsunori (1583–1638), as head of the Tosa school and brought the Tosa school to Kyoto after around 50 years in Sakai. When the school was settled in Sakai, Mitsunori painted for townsmen. The school was not as prolific as it once was when Mitsunobu, who painted many fine scrolls (1434–1525) ran the school. Mitsuoki moved out of Sakai with his father, in 1634 and into the city of Kyoto. There, he hoped to revive the Tosa school to gain status back into the Kyoto court. Around the time of 1654 he gained a position as court painter (edokoro azukari) that had for many years traditionally been held by the Tosa family, but was in possession of the Kano school since the late Muromachi period (1338–1573). Restoring the Tosa School In 1634, Mitsuoki relocataed from Sakai, Osaka prefecture to the capitol at the behest of Emperor Go-Mizunoo. Mitsunori began painting ceremonial fans sensu for the court. In 1654, Mitsuo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakai
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It has been one of the largest and most important seaports of Japan since the medieval era. Sakai is known for its keyhole-shaped burial mounds, or kofun, which date from the fifth century and include Daisen Kofun, the largest grave in the world by area. Once known for swords, Sakai is now famous for the quality of its cutlery. , the city had an estimated population of 819,965, making it the fourteenth most populous city in Japan (excluding Tokyo). Geography Sakai is located in southern Osaka Prefecture, on the edge of Osaka Bay and directly south of the city of Osaka. Neighboring municipalities Osaka Prefecture *Osaka * Matsubara *Habikino *Ōsakasayama *Kawachinagano * Izumi * Takaishi Climate Sakai has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Sakai is . The average annual rainfall is with June as the wettest mont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
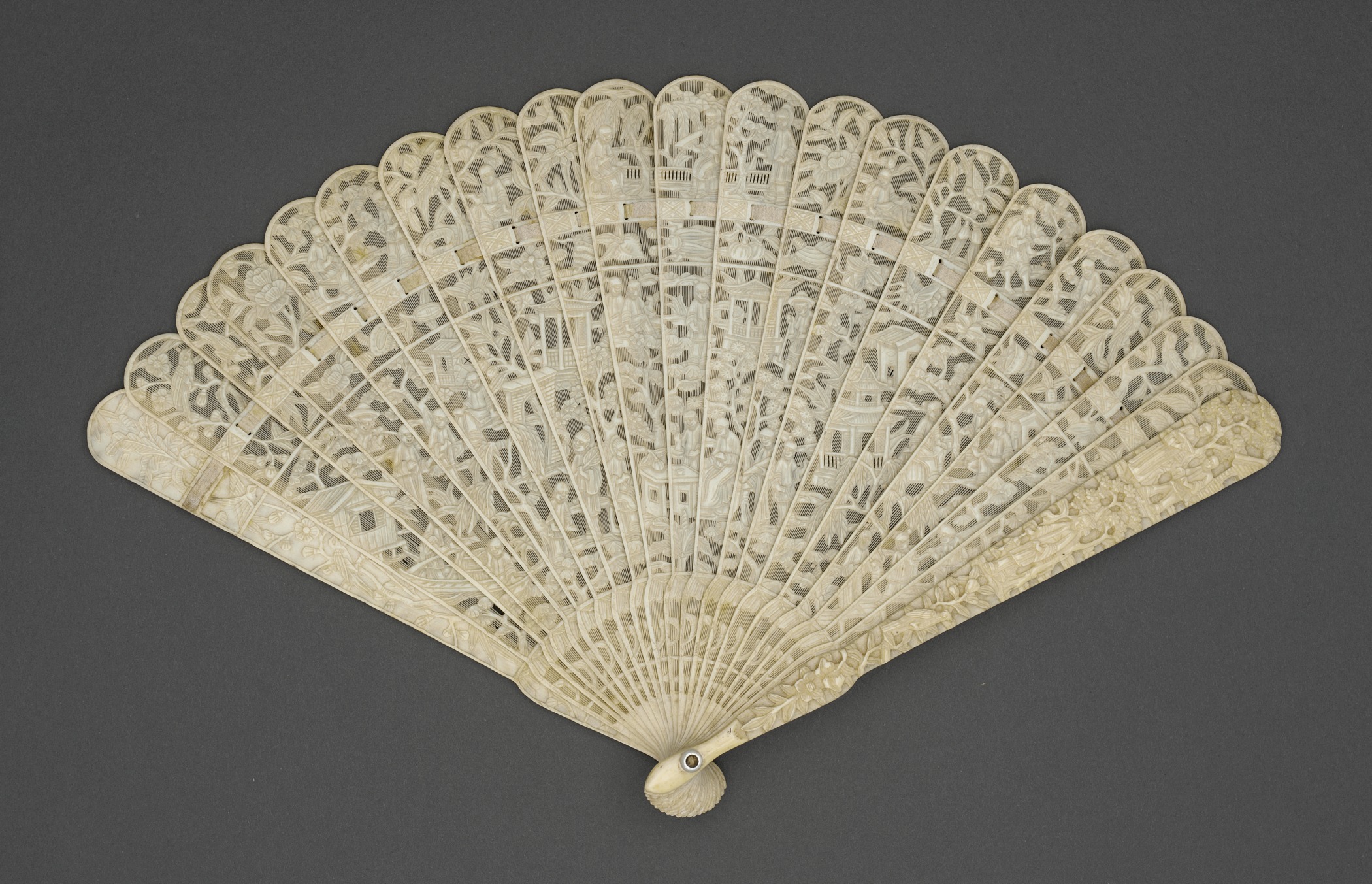
Hand Fan
A handheld fan, or simply hand fan, is any broad, flat surface that is waved back-and-forth to create an airflow. Generally, purpose-made handheld fans are folding fans, which are shaped like a sector of a circle and made of a thin material (such as paper or feathers) mounted on slats which revolve around a pivot so that it can be closed when not in use. Hand fans were used before mechanical fans were invented. On human skin, the airflow from handfans increases evaporation which has a cooling effect due to the latent heat of evaporation of water. It also increases heat convection by displacing the warmer air produced by body heat that surrounds the skin, which has an additional cooling effect, provided that the ambient air temperature is lower than the skin temperature – which is typically about . Fans are convenient to carry around, especially folding fans. Next to the folding fan, the rigid hand screen fan was also a highly decorative and desired object among the higher cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentō Imperial Palace
In Japan, the traditionally does not refer to a single location, but to any residence of retired emperors. Before Akihito abdicated in 2019, the last Emperor to retire did so in 1817, so the designation commonly refers to the historical . Kyoto Sentō Imperial Palace The ) is a large garden in Kyoto, Japan, formerly the grounds of a palace for retired emperors. It is administered by the Imperial Household Agency and is opened to visitors. History Sento Imperial Palace was completed in 1630 for Emperor Go-Mizunoo's retirement, along with the corresponding Ōmiya Palace for the Empress Dowager Nyoin. Both palaces were repeatedly destroyed by fire and reconstructed until a blaze in 1854, after which the Sento palace was never rebuilt. (Ōmiya Palace was, however, reconstructed in 1867 and is still used by the emperor whenever he visits Kyoto). Today only two Sento structures, the Seika-tei and Yushin-tei teahouses, remain. The excellent gardens, laid out in 1630 by renowned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the city had a population of 1.46 million. The city is the cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Kyoto, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 3.8 million people. Kyoto is one of the oldest municipalities in Japan, having been chosen in 794 as the new seat of Japan's imperial court by Emperor Kanmu. The original city, named Heian-kyō, was arranged in accordance with traditional Chinese feng shui following the model of the ancient Chinese capital of Chang'an/Luoyang. The emperors of Japan ruled from Kyoto in the following eleven centuries until 1869. It was the scene of several key events of the Muromachi period, Sengoku period, and the Boshin War, such as the Ōnin War, the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taima Mandala
The Taima Mandala (當麻曼荼羅,綴織当麻曼荼羅図) is an 8th century mandala in Japanese Pure Land Buddhism. It depicts Sukhavati, the western Pure Land, with the Buddha Amitābha (Japanese: Amida) in the center. The original copy was made around 763 AD, and is currently kept at Taima-dera temple in Nara. Many copies have been made since, and the original work has degraded considerably. According to popular legend, Chūjō-hime witnessed the creation of the mandala, crafted from fibers of lotus stems by two nuns who were thought to be Amida and Kannon in disguise. The imagery on the painting is largely based on the '' Sutra of the Contemplation of Amitayus'', and has been the subject of several doctrinal commentaries in Japanese Buddhism. The mandala was designated a national treasure of Japan on April 27, 1961. Description The central image is Sukhavati, the Pure Land of the west. The left, right, and lower borders are lined with images from the Contemplation Sutra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1583 Births
__NOTOC__ Events January–June * January 18 – François, Duke of Anjou, attacks Antwerp. * February 4 – Gebhard Truchsess von Waldburg, newly converted to Calvinism, formally marries Agnes von Mansfeld-Eisleben, a former canoness of Gerresheim, while retaining his position as Archbishop-Elector of Cologne. * March 10 – The ''Queen Elizabeth's Men'' troupe of actors is ordered to be founded in England. * May – Battle of Shizugatake in Japan: Shibata Katsuie is defeated by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who goes on to commence construction of Osaka Castle. * May 22 – Ernest of Bavaria is elected as Roman Catholic Archbishop of Cologne, in opposition to Gebhard Truchsess von Waldburg. The opposition rapidly turns into armed struggle, the Cologne War within the Electorate of Cologne, beginning with the Destruction of the Oberstift. July–December * July 25 – Cuncolim Revolt: The first documented battle of India's independence against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |