|
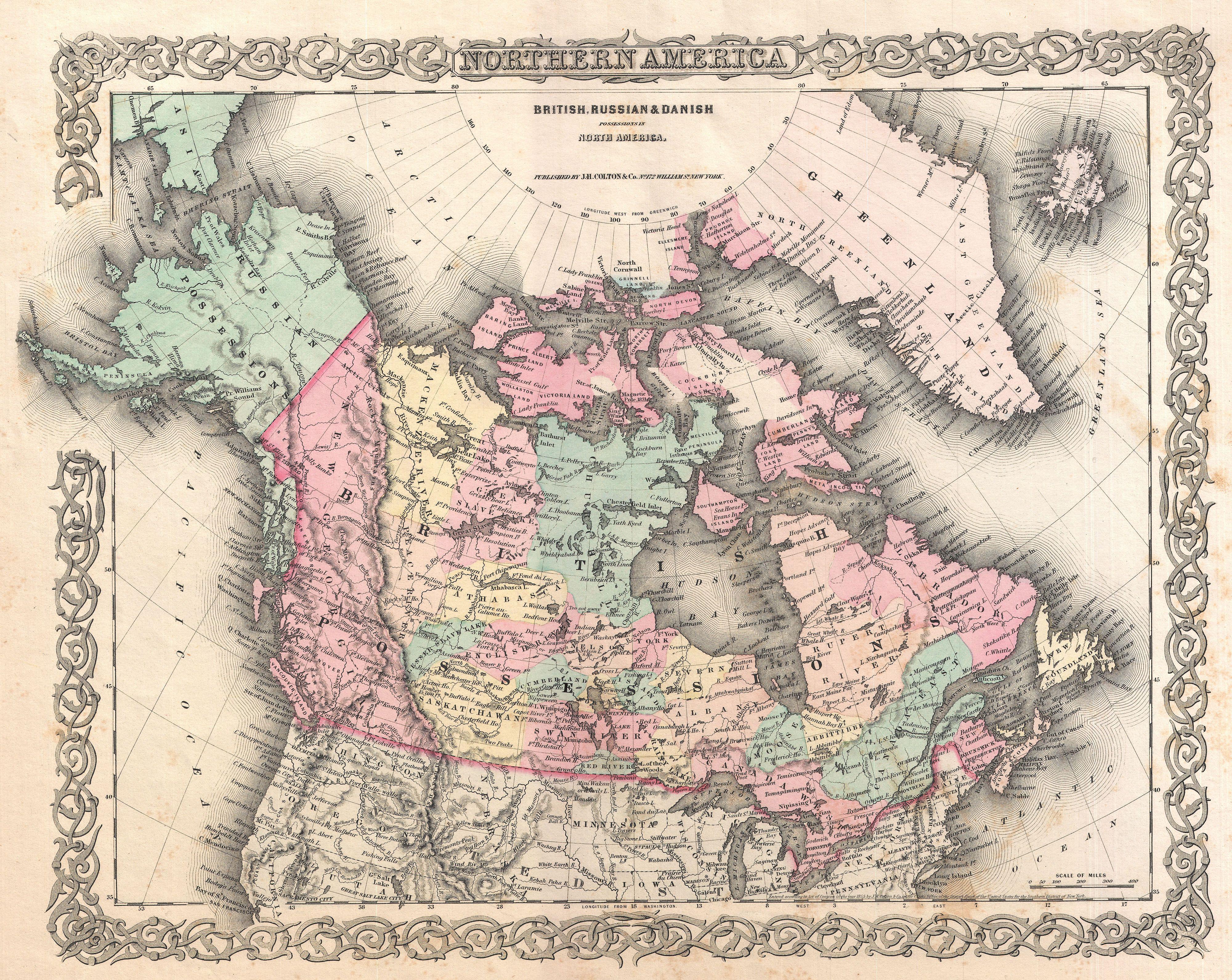
Toronto And Nipissing Railway
The Toronto and Nipissing Railway (T&N) was the first public narrow-gauge railway in North America. It chartered in 1868 to build from Toronto to Lake Nipissing in Ontario, Canada, via York, Ontario, and Victoria counties. At Nipissing it would meet the transcontinental lines of the Canadian Pacific, providing a valuable link to Toronto. It opened in 1871, with service between Scarborough and Uxbridge. By December 1872 it was extended to Coboconk, but financial difficulties led to plans of the line being built further abandoned at this point. The railway merged with the Midland Railway of Canada in 1882. A series of mergers, bankruptcies and ownership changes eventually turned this right of way into the CN Uxbridge Subdivision, at least the portions north of the CN Kingston Subdivision at Scarborough Junction. Passenger service was offered to Markham and then Stouffville, before the service passed to Via Rail, and then to GO Transit in 1982. The lines are currently used both by CN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CN Kingston Subdivision
Canadian National Railway's Kingston Subdivision, or Kingston Sub for short, is a major railway line connecting Toronto with Montreal that carries the majority of CN traffic between these points. The line was originally the main trunk for the Grand Trunk Railway between these cities, although there has been some realignment of the route between these cities. The majority of the Kingston Sub runs close to the northern bank of Lake Ontario and the Saint Lawrence River. The infrastructure consists of twin tracks, on which over 50 pieces of interlocking crossover tracks are grafted all along the subdivision. The extra length of these crossover tracks allows for high speed track interchange. Low gravity intermodal container trains are allowed to change tracks at 45 miles per hour, and VIA Rail's passenger trains, at 60, and in some areas, 90. The governing traffic control system is CTC. Since 1995, no OCS operation clearance forms need to be filled by train conductors on the Kingston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Morton Peto
Sir Samuel Morton Peto, 1st Baronet (4 August 1809 – 13 November 1889) was an English entrepreneur, civil engineer and railway developer, and, for more than 20 years, a Member of Parliament (MP). A partner in the firm of Grissell and Peto, he managed construction firms that built many major buildings and monuments in London, including the Reform Club, The Lyceum, Nelson's Column and the new Houses of Parliament; which made him a millionaire. As a partner in Peto and Betts, he then became one of the major contractors in the building of the rapidly expanding railways of the time. Along with a small group of other Master Builders in London he is credited as a founding member of the Chartered Institute of Building in 1834. Early life Samuel Morton Peto, normally called Morton Peto, was born on 4 August 1809, in Woking, Surrey. As a youth, he was apprenticed as a bricklayer to his uncle Henry Peto, who ran a building firm in London. Career When his uncle died in 1830, Peto and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarnia
Sarnia is a city in Lambton County, Ontario, Canada. It had a 2021 population of 72,047, and is the largest city on Lake Huron. Sarnia is located on the eastern bank of the junction between the Upper and Lower Great Lakes where Lake Huron flows into the St. Clair River in the Southwestern Ontario region, which forms the Canada–United States border, directly across from Port Huron, Michigan. The site's natural harbour first attracted the French explorer La Salle. He named the site "The Rapids" on 23 August 1679, when he had horses and men pull his 45-ton barque ''Le Griffon'' north against the nearly four-knot current of the St. Clair River. This was the first time that a vessel other than a canoe or other oar-powered vessel had sailed into Lake Huron, and La Salle's voyage was germinal in the development of commercial shipping on the Great Lakes. Located in the natural harbour, the Sarnia port remains an important centre for lake freighters and oceangoing ships carrying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portland, Maine
Portland is the largest city in the U.S. state of Maine and the seat of Cumberland County. Portland's population was 68,408 in April 2020. The Greater Portland metropolitan area is home to over half a million people, the 104th-largest metropolitan area in the United States. Portland's economy relies mostly on the service sector and tourism. The Old Port is known for its nightlife and 19th-century architecture. Marine industry plays an important role in the city's economy, with an active waterfront that supports fishing and commercial shipping. The Port of Portland is the second-largest tonnage seaport in New England. The city seal depicts a phoenix rising from ashes, a reference to recovery from four devastating fires. Portland was named after the English Isle of Portland, Dorset. In turn, the city of Portland, Oregon was named after Portland, Maine. The word ''Portland'' is derived from the Old English word ''Portlanda'', which means "land surrounding a harbor". The Greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada West
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838. The Act of Union 1840, passed on 23 July 1840 by the British Parliament and proclaimed by the Crown on 10 February 1841, merged the Colonies of Upper Canada and Lower Canada by abolishing their separate parliaments and replacing them with a single one with two houses, a Legislative Council as the upper chamber and the Legislative Assembly as the lower chamber. In the aftermath of the Rebellions of 1837–1838, unification of the two Canadas was driven by two factors. Firstly, Upper Canada was near bankruptcy because it lacked stable tax revenues, and needed the resources of the more populous Lower Canada to fund its internal transportation improvements. Secondly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada East
Canada East (french: links=no, Canada-Est) was the northeastern portion of the United Province of Canada. Lord Durham's Report investigating the causes of the Upper and Lower Canada Rebellions recommended merging those two colonies. The new colony, known as the Province of Canada, was created by the Act of Union 1840 passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom, having effect in 1841. For administrative purposes, the new Province was subdivided into Canada West and Canada East. The former name of "Lower Canada" came back into official use in 1849, and as of the Canadian Confederation of 1867 it formed the newly created province of Quebec. An estimated 890,000 people lived in Canada East in 1851. Geography It consisted of the southern portion of the modern-day Canadian province of Quebec. Formerly a British colony called the Province of Lower Canada, based on Lord Durham's report it was merged with the Province of Upper Canada (present-day southern portion of the Provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British North America, British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838. The Act of Union 1840, passed on 23 July 1840 by the British Parliament and proclaimed by the Monarchy of Great Britain, Crown on 10 February 1841, merged the Colonies of Upper Canada and Lower Canada by abolishing their separate parliaments and replacing them with a Parliament of the Province of Canada, single one with two houses, a Legislative Council of the Province of Canada, Legislative Council as the upper chamber and the Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada, Legislative Assembly as the lower chamber. In the aftermath of the Rebellions of 1837–1838, unification of the two Canadas was driven by two factors. Firstly, Upper Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stouffville Line
The Stouffville line is one of the seven train lines of the GO Transit system in the Greater Toronto Area, Ontario, Canada. Its southern terminus is Union Station in Toronto, and its northern terminus is (formerly "Lincolnville") in Whitchurch-Stouffville. There are connections from almost every station to Toronto Transit Commission or York Region Transit bus services. During peak periods on weekdays, trains operate approximately twice per hour over the entire route, but in the peak direction only. Otherwise, trains operate hourly in both directions seven days a week between either Unionville or Mount Joy stations and Union, with a small number of trips covering the full line to Old Elm. GO bus routes 70 and 71 provide service in the directions, time periods, and segments not covered by train service. However, buses to and from Union Station bypass all other stations within the City of Toronto. Weekend service was operated entirely by bus until November 2, 2019, when weekend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GO Transit
GO Transit is a regional public transit system serving the Greater Golden Horseshoe region of Ontario, Canada. With its hub at Union Station in Toronto, GO Transit's green-and-white trains and buses serve a population of more than seven million across an area over stretching from London in the west to Peterborough in the east, and from Barrie in the north to Niagara Falls in the south. In , the system had a ridership of . GO Transit operates diesel-powered double-decker trains and coach buses, on routes that connect with all local and some long-distance inter-city transit services in its service area. GO Transit began regular passenger service on May 23, 1967, as a part of the Ontario Ministry of Transportation. Since then, it has grown from a single train line to seven lines, and expanded to include complementary bus service. GO Transit has been constituted in a variety of public-sector configurations. Today, it is an operating division of Metrolinx, a provincial Crown a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |