|
Torell Land
Torell Land is a land area at the southeast part of Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is named after Otto Martin Torell. Two glaciers, Hornbreen and Hambergbreen, divide Torell Land from Sørkapp Land. Torell Land is included in the Sør-Spitsbergen National Park Sør-Spitsbergen National Park ( no, Sør-Spitsbergen nasjonalpark, eng, South Spitzbergen National Park) encompasses the southern end of Spitsbergen island in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. The park was opened in 1973 and includes Wedel Jarl .... References Geography of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
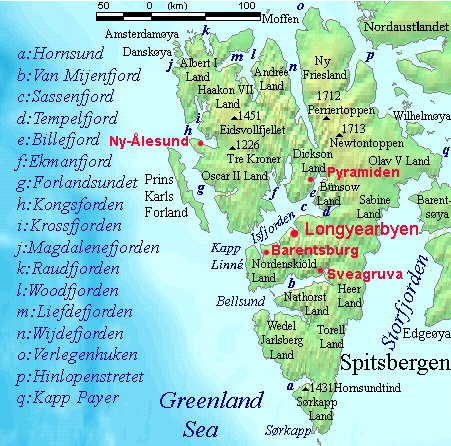
Spitsbergen Labelled
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
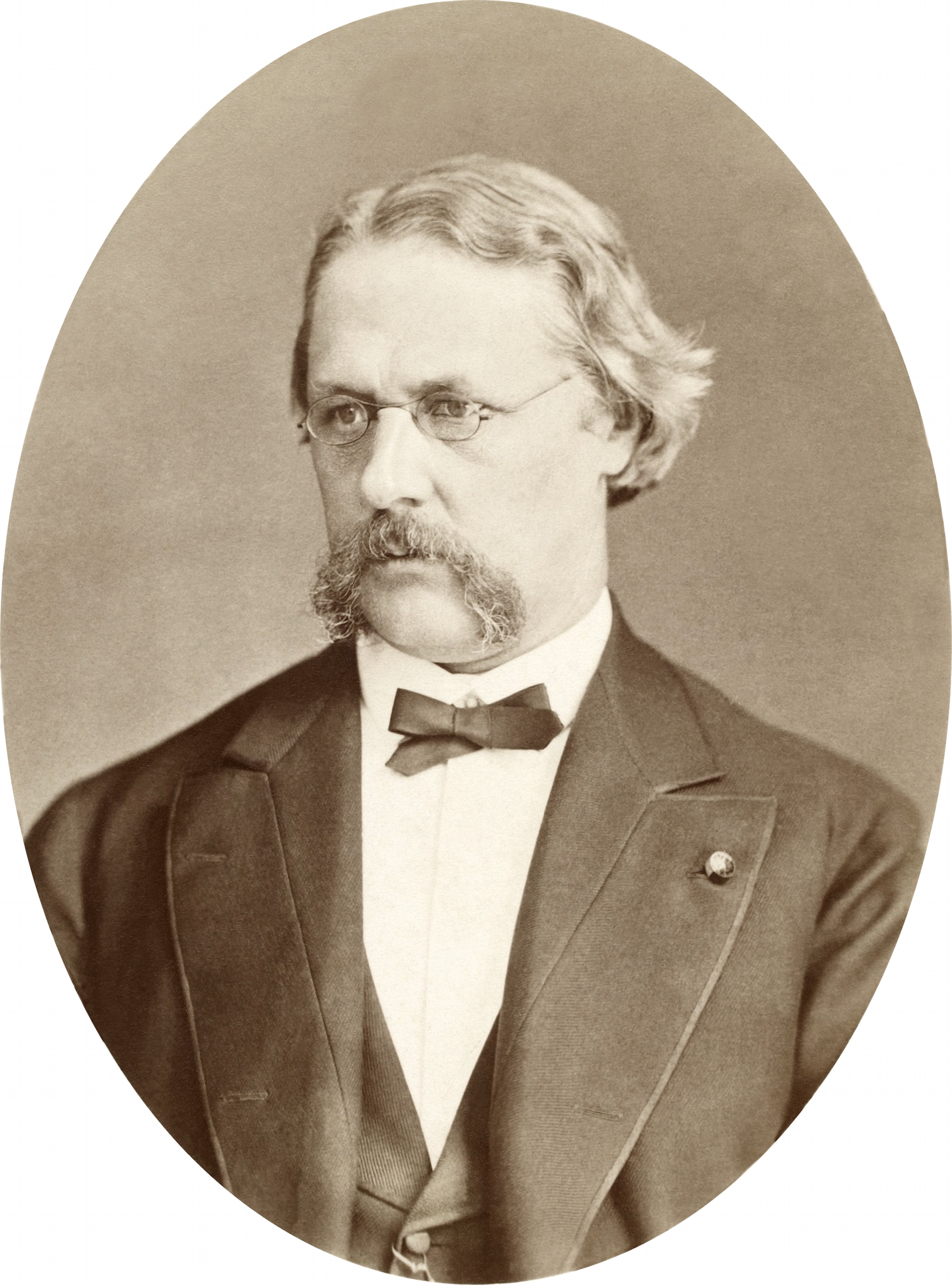
Otto Martin Torell
Prof Otto Martin Torell HFRSE (5 June 1828 – 11 September 1900) was a Swedish naturalist and geologist. Life He was born in Varberg, Sweden on 5 June 1828 the son of Johan Petter Torell and his wife, Susanna Charlotta Varenius. He was educated at Lund University for the medical profession, but became interested in zoological and geological studies, and being of independent means he devoted himself to science. He gave his attention first especially to the invertebrate fauna and the physical changes of pleistocene and recent times. In 1850 he applied Louis Agassiz's theory on ice ages to explain his observations of arctic molluscs on the coast of Sweden.History of geomorphology and Quaternary geology on |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornbreen
Hornbreen ("Horn glacier") lies between Torell Land and Sørkapp Land on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The glacier debouches into Hornsund Hornsund is a fjord on the western side of the southernmost tip of Spitsbergen island. The fjord's mouth faces west to the Greenland Sea, and is wide. The length is , the mean depth is , and the maximal depth is . Hornsund cuts different geol .... Former names of the glacier include ''Ramme Gletscher'' and ''Horn Glacier''. Hornbreen has a length of about 15 km, and width of 8 km. References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hambergbreen
Hambergbreen is a glacier on Spitsbergen, Svalbard, dividing Torell Land and Sørkapp Land, and debouching into the sea at the eastern coast of Spitsbergen. The glacier is named after Swedish geographer and explorer Axel Hamberg Axel Hamberg (17 January 1863 – 28 June 1933) was a Swedish mineralogist, geographer and explorer. Biography Hamberg was born in Stockholm, Sweden. He was the son of Nils Peter Hamberg (1815-1902) and Emma Augusta Christina Härnström (18 .... References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sørkapp Land
Sørkapp Land is the land area south of Hornsund, at the southern part of Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Two glaciers, Hornbreen and Hambergbreen, divide Sørkapp Land from Torell Land. Sørkapp Land is included in the Sør-Spitsbergen National Park Sør-Spitsbergen National Park ( no, Sør-Spitsbergen nasjonalpark, eng, South Spitzbergen National Park) encompasses the southern end of Spitsbergen island in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. The park was opened in 1973 and includes Wedel Jarl .... References Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sør-Spitsbergen National Park
Sør-Spitsbergen National Park ( no, Sør-Spitsbergen nasjonalpark, eng, South Spitzbergen National Park) encompasses the southern end of Spitsbergen island in the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. The park was opened in 1973 and includes Wedel Jarlsberg Land, Torell Land and Sørkapp Land. Over 65% of the region is ice cap, with much of the rest tundra. Important Bird Area The park contains bird sanctuaries which protect islands with grassy vegetation, freshwater ponds and areas of bare rock. One of these is the Isøyane Bird Sanctuary which has also recognised as a wetland of international importance by designation under the Ramsar Convention. The park has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports breeding populations of barnacle geese (850–950 pairs), common eiders (1000 pairs), black-legged kittiwakes (25,900 pairs) and thick-billed guillemot The thick-billed murre or Brünnich's guillemot (''Uria lomvia'') is a bird in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lovdata
Lovdata is a Norwegian foundation which publishes judicial information of Norway. It publishes the periodical '' Norsk lovtidend'', and ''Lov&Data'' and ''EuroRett'', and hosts a website with free, public access to all Norwegian laws and other judicial documents, including court rulings. Lovdata was established on 1 July 1981 by the Norwegian Ministry of Justice and the Police and the foundation Det juridiske fakultets lovsamlingsfond ovsamlingsfondet(The Norwegian Statute Book Foundation at the Faculty of Law at the University of Oslo). It has had a database since 1983 and published laws on CDs since 1990. Managing director is Odd Storm-Paulsen, and the board consists of Knut Kaasen (chairman), Ida Børresen, Ketil Gjøen, Anne K. Herse and Randi Birgitte Bull. In 2018, Lovdata sued Håkon Wium Lie Håkon Wium Lie (born July 26, 1965) is a Norwegian web pioneer, a standards activist, and the Chief Technology Officer of Opera Software from 1998 until the browser was so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Svalbard
Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean roughly centered on 78° north latitude and 20° east longitude. The archipelago is the northernmost part of the Kingdom of Norway. The three main islands in the group consist of Spitsbergen (the largest island), Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. There are also a number of smaller islands, such as Barents Island (Barentsøya) (), Kvitøya (), Prins Karls Forland (English: Prince Charles Foreland) (), Kongsøya (), Bear Island (), Svenskøya (), Wilhelm Island () and other smaller islands or skerries (). Climate There is no arable land in the island group due to heavy glaciation and the northern latitude. There are no trees native to the archipelago, but there are shrubs such as crowberry and cloudberry. The west coast of Spitsbergen remains navigable most of the year, due to favorable winds which keep the area ice-free. Norway claims a fishery protection zone, but this is not recognized by neighboring Russia. The climate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |